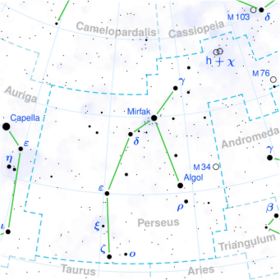
Astronomy:Rho Persei
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Perseus |
| Right ascension | 03h 05m 10.59385s[1] |
| Declination | +38° 50′ 24.9943″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.39[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[3] |
| Spectral type | M4 II[4] |
| U−B color index | +1.79[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.65[2] |
| Variable type | SRb[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +29.10±0.30[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +129.22[1] mas/yr Dec.: –105.70[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.60 ± 0.25[1] mas |
| Distance | 308 ± 7 ly (94 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.7[6] |
| Details[7] | |
| Mass | 1.9±0.7 M☉ |
| Radius | 143±12 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,692+192 −180 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.37±0.15 cgs |
| Temperature | 3,479±125 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.15 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 11.2[8] km/s |
| Age | 440[9] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Rho Persei, Latinized from ρ Persei, is a star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has the traditional name Gorgonea Tertia /ɡɔːrɡəˈniːə ˈtɜːrʃə/,[11] being the third member of the quartet called the Gorgonea in reference to the Gorgons from the legend of Perseus.[9] An apparent visual magnitude of +3.39[2] makes it visible to the naked eye, but a challenge to view from a well-lit urban environment. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of roughly 308 light-years (94 pc) from Earth.[1]

Johann Schmidt discovered that Rho Persei is a variable star, in 1854.[13][14] Rho Persei is a semiregular variable star, whose apparent magnitude varies between 3.3 and 4.0[15] with periods of 50, 120 and 250 days.[6] The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch of its evolution.[3] It is a bright giant star with a stellar classification of M4 II.[4] The outer envelope has an effective temperature of 3,479 K,[7] giving it the red-orange hue of an M-type star.[16]
This star has a mass 1.9 times the mass of the Sun, while its radius has expanded to 143 times solar. It is radiating some 2,700 times the Sun's luminosity.[7] Rho Persei is losing mass at the rate of 1.2×10−8 solar masses per year, or the equivalent of the Sun's mass every 83 million years.[17] It is about 440 million years in age.[9]
Naming
In Chinese, 大陵 (Dà Líng), meaning Mausoleum, refers to an asterism consisting of ρ Persei, 9 Persei, τ Persei, ι Persei, κ Persei, β Persei, 16 Persei and 12 Persei. Consequently, the Chinese name for ρ Persei itself is 大陵六 (Dà Líng liù, English: the Sixth Star of Mausoleum.).[18]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Nicolet, B. (1978), "Photoelectric photometric Catalogue of homogeneous measurements in the UBV System", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 34: 1–49, Bibcode: 1978A&AS...34....1N
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Eggen, Olin J. (July 1992), "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun", Astronomical Journal 104 (1): 275–313, doi:10.1086/116239, Bibcode: 1992AJ....104..275E
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ragland, S. et al. (November 2006), "First Surface-resolved Results with the Infrared Optical Telescope Array Imaging Interferometer: Detection of Asymmetries in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars", The Astrophysical Journal 652 (1): 650–660, doi:10.1086/507453, Bibcode: 2006ApJ...652..650R
- ↑ Famaey, B. et al. (May 2009), "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations", Astronomy and Astrophysics 498 (2): 627–640, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698, Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..627F
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yeşilyaprak, C.; Aslan, Z. (December 2004), "Period-luminosity relation for M-type semiregular variables from Hipparcos parallaxes", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 355 (2): 601–607, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08344.x, Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.355..601Y
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kallinger, T. et al. (April 2019), "Stellar masses from granulation and oscillations of 23 bright red giants observed by BRITE-Constellation", Astronomy & Astrophysics 624: 17, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834514, A35, Bibcode: 2019A&A...624A..35K.
- ↑ Massarotti, Alessandro et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal 135 (1): 209–231, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209, Bibcode: 2008AJ....135..209M
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Kaler, James B., "GORGONEA TERTIA (Rho Persei)", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/gorgtert.html, retrieved 2012-01-25
- ↑ "rho Per -- Semi-regular pulsating Star", SIMBAD (Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg), http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=Rho+Persei, retrieved 2012-01-24
- ↑ Allen, Richard Hinckley (1899), "Star-names and their meanings", New York (G. E. Stechert): 334, Bibcode: 1899sntm.book.....A, https://books.google.com/books?id=5xQuAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA334
- ↑ Enhanced LCG, AAVSO, https://www.aavso.org/LCGv2/, retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ↑ Cannon, Annie J. (1907). "Second catalogue of variable stars". Annals of Harvard College Observatory 55: 1–94. Bibcode: 1907AnHar..55....1C. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1907AnHar..55....1C. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ↑ "rho Per". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=26208.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V. et al. (1971), General Catalogue of Variable Stars (3rd ed.), Bibcode: 1971GCVS3.C......0K
- ↑ "The Colour of Stars", Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation), December 21, 2004, http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_colour.html, retrieved 2012-01-16
- ↑ Cox, Arthur N.; Becker, Stephen A.; Pesnell, W. Dean (2000), "Chapter 20. Theoretical Stellar Evolution", Allen's astrophysical quantities (4th ed.), New York: Springer, p. 516, ISBN 0-387-98746-0, http://extras.springer.com/2000/978-0-387-95189-8/BookChap/book20.pdf, retrieved 2012-01-25 See table 20.5
- ↑ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 11 日
External links
 |