Astronomy:V957 Scorpii
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Right ascension | 17h 52m 13.662s[1] |
| Declination | −34° 47′ 57.11″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.87[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B5 IIIp[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.64[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.10[4] |
| Variable type | SX Ari[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −9.70[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 3.148[1] mas/yr Dec.: −5.604[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.6766 ± 0.1521[1] mas |
| Distance | 890 ± 40 ly (270 ± 10 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.441[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 5.13[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.00[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,148[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.94[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 16,600[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.01[8] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 30[9] km/s |
| Age | 50[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
V957 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation of Scorpius. It is a blue straggler in the open cluster Messier 7, a star that is unexpectedly hot compared to other members of the cluster. A 6th magnitude star, it is faintly visible to the naked eye under very good observing conditions.
Spectrum

V957 Scorpii shows a peculiar B5 or B6 spectrum. Its luminosity class has been given as main sequence (V), subgiant (IV), giant (III), and supergiant (Ib).[10] From its position in the H-R diagram, it is actually thought to be a main sequence star.[11] With a helium abundance 25 times lower than that of the sun,[12] it is classified as helium-weak. It also has a low carbon abundance and a strong magnetic field.[7]
Messier 7
Messier 7 is a naked eye open cluster. Except for one obvious orange giant star, most of its brightest members are mostly early A and late B main sequence stars and giants. Several of them are also chemically peculiar stars. However, two stars are hotter than the others and lie to the left of the isochrone for the cluster. These are the blue stragglers HD 162586 and V957 Scorpii. V957 Scorpii is considered 92% likely to be a member of M7. M7 has an age around 220 million years, but the apparent age of V957 Scorpii is less than 100 million years.[12]
Variability
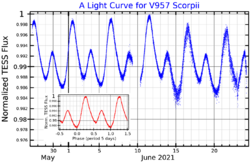
Pierre Louis North announced that the star is a variable star, in 1984.[14] It was given its variable star designation in 1987.[15] V957 Scorpii varies in brightness by about 0.05 magnitudes. This is thought to be due to its rotation and variations in its surface brightness. It is classified as an SX Arietis variable, also known as helium variables. Their spectral lines also vary as the stars rotate.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/GCVS. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Abt, H. A. (1985). "The spectra and ages of blue stragglers". The Astrophysical Journal 294: L103. doi:10.1086/184518. Bibcode: 1985ApJ...294L.103A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W. H. (1995). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Hoffleit+, 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: V/50. Originally Published in: 1964BS....C......0H 5050. Bibcode: 1995yCat.5050....0H.
- ↑ Conti, P. S.; Hensberge, G.; Van Den Heuvel, E. P. J.; Stickland, D. J. (1974). "A study of the blue stragglers in Praesepe, M7 and the Hyades cluster". Astronomy and Astrophysics 34: 393. Bibcode: 1974A&A....34..393C.
- ↑ Silaj, J.; Landstreet, J. D. (2014). "Accurate age determinations of several nearby open clusters containing magnetic Ap stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 566: A132. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201321468. Bibcode: 2014A&A...566A.132S.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 Glagolevskij, Yu. V. (2019). "On Properties of Main Sequence Magnetic Stars". Astrophysical Bulletin 74 (1): 66. doi:10.1134/S1990341319010073. Bibcode: 2019AstBu..74...66G.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2012). "Dependence of kinematics on the age of stars in the solar neighborhood". Astronomy Letters 38 (12): 771–782. doi:10.1134/S1063773712120031. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..771G.
- ↑ Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ Skiff, B. A. (2014). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Spectral Classifications (Skiff, 2009- )". VizieR On-line Data Catalog. Bibcode: 2014yCat....1.2023S.
- ↑ Mermilliod, J. -C (1982). "Stellar content of young open clusters. I. Blue stragglers". Astronomy and Astrophysics 109: 37. Bibcode: 1982A&A...109...37M.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Andrievsky, S. M.; Schönberner, D.; Drilling, J. S. (2000). "Blue stragglers in open clusters. Part II". Astronomy and Astrophysics 356: 517. Bibcode: 2000A&A...356..517A.
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ North, P. (February 1984). "Photometric variability of AP and He-weak stars in clusters and associations. I.". Astronomy and Astrophysics, Suppl. Ser. 55: 259–358. Bibcode: 1984A&AS...55..259N. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1984A%26AS...55..259N. Retrieved 16 September 2025.
- ↑ Kholopov, P. N.; Samus, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Kireeva, N. N. (August 1987). "The 68th Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3058. Bibcode: 1987IBVS.3058....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/3001/3058.pdf. Retrieved 16 September 2025.
 |