Astronomy:XY Ursae Majoris
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 09h 09m 55.935s[2] |
| Declination | +54° 29′ 17.72″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.50[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | G2V + K5V[4] |
| B−V color index | 0.765±0.039[3] |
| Variable type | Detached eclipsing binary, RS CVn[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −9.98±0.83[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −49.781[2] mas/yr Dec.: −182.641[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 14.7223 ± 0.0137[2] mas |
| Distance | 221.5 ± 0.2 ly (67.92 ± 0.06 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 5.41[3] |
| Orbit[7] | |
| Period (P) | 0.4789961 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 3.05±0.01 R☉[8] |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.0 |
| Inclination (i) | 79.81[8]° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,453,821.6344±0.0002 |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 124.74±0.28 km/s |
| Details | |
| Primary | |
| Mass | 1.01±0.01[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.22±0.01[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.10±0.02[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 5,780[4] K |
| Secondary | |
| Mass | 0.65±0.01[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.58±0.01[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.09±0.01[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,850[4] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
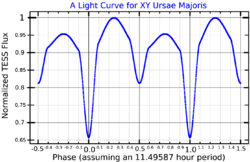
XY Ursae Majoris is a short period binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is an eclipsing binary with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 9.50.[3] The system is located at a distance of 221.5 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements,[2] but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10 km/s.[6] It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the angular rate of 0.191″·yr−1.[10]
The variability of this system was discovered by W. Strohmeier and its period was determined by R. Kippenhahn, with the findings announced in 1955.[11] It was found to be a detached eclipsing binary system, and by 1963 a variable primary component had been noted.[12] E. H. Geyer made intermittent light curve studies of the system starting with its discovery up until 1975,[11] ascribing variability in the light curve to star spot activity on the primary component. The orbital period of the pair was determined to be 0.479 d,[13] with the orbital plane inclined at an angle of 79.84° to the line of sight from the Earth.[8]
By 1990, enough data had been collected to identify a long term variation of the period, and it was hypothesized this was caused by a third body in the system orbiting the close binary.[14] The orbital period of this component was estimated to be ~30 years in 2001,[15] then refined to 26.7 years by 2010. If the orbital plane of this component is the same as the inner pair, its mass would be 18% of the mass of the Sun. An alternative solution to the period change suggests magnetic activity causes shifts in the angular momentum of the system, but this is considered less likely.[8]
This is a double-lined spectroscopic binary star system with an orbital period of 11.5 h.[7] The primary component is a G-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of G2V.[4] It is an RS Canum Venaticorum-type variable that is magnetically active[5] and a bright X-ray source.[16] Despite this, relatively few optical flares have been observed.[16] The cooler secondary is a K-type main-sequence star of class K5V that is smaller and less massive than the primary.[4]
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Lister, T. A. et al. (October 2001), "Starspot distributions on XY UMa during 1997-2000 from eclipse mapping", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 326 (4): 1489–1498, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2001.04712.x, Bibcode: 2001MNRAS.326.1489L.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Samus', N. N et al. (2017), "General catalogue of variable stars", Astronomy Reports, GCVS 5.1 61 (1): 80, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Karataș, Yüksel et al. (2004), "Kinematics of chromospherically active binaries and evidence of an orbital period decrease in binary evolution", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 349 (3): 1069–1092, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07588.x, Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.349.1069K.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Pribulla, Theodor et al. (May 2007), "Radial Velocity Studies of Close Binary Stars. XII", The Astronomical Journal 133 (5): 1977–1987, doi:10.1086/512772, Bibcode: 2007AJ....133.1977P.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 Yuan, Jinzhao (May 2010), "Period Variation and Asymmetry Light Curves of XY Ursae Majoris", The Astronomical Journal 139 (5): 1801–1807, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/5/1801, Bibcode: 2010AJ....139.1801Y.
- ↑ "XY UMa". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=XY+UMa.
- ↑ Lépine, Sébastien; Shara, Michael M. (March 2005), "A Catalog of Northern Stars with Annual Proper Motions Larger than 0.15" (LSPM-NORTH Catalog)", The Astronomical Journal 129 (3): 1483–1522, doi:10.1086/427854, Bibcode: 2005AJ....129.1483L.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Geyer, E. H. (1976), Eggleton, P.; Mitton, S.; Whelan, J., eds., "Starspot Activities as an Interpretation for the Light Curve Changes of the Close Binary Star XY UMA", Structure and Evolution of Close Binary Systems; Proceedings of the Symposium, Cambridge, England, July 28-August 1, 1975 (Dordrecht: D. Reidel Publishing Co.) 73 (73): p. 313, Bibcode: 1976IAUS...73..313G. Symposium sponsored by the International Astronomical Union.
- ↑ Lorenzi, L.; Scaltriti, F. (1977), "The variable light-curve of the eclipsing binary XY UMa", Acta Astronomica 27: 273–279, Bibcode: 1977AcA....27..273L.
- ↑ Geyer, E. H. (May 1977), "Remarks on Erratic Period Fluctuations of Detached Close Binaries and the Constancy of the Orbital Period of XY UMa", Astrophysics and Space Science 48 (1): 137–144, doi:10.1007/BF00643045, Bibcode: 1977Ap&SS..48..137G.
- ↑ Pojmanski, G.; Geyer, E. H. (1990), "The period behaviour of the spotted binary XY UMa", Acta Astronomica 40: 245, Bibcode: 1990AcA....40..245P.
- ↑ Pribulla, T. et al. (June 2001), "An active binary XY UMa revisited", Astronomy and Astrophysics 371 (3): 997–1011, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010459, Bibcode: 2001A&A...371..997P.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Gong, Hang et al. (August 2016), "Three X-ray flares near primary eclipse of the RS CVn binary XY UMa", Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics 16 (8): 014, doi:10.1088/1674-4527/16/8/131, 131, Bibcode: 2016RAA....16..131G.
Further reading
- Sowell, James R. et al. (October 2001), "Period Changes in Four Short-Period Spotted Binaries: UV Piscium, YY Geminorum, CG Cygni, and XY Ursae Majoris", The Astronomical Journal 122 (4): 1965–1973, doi:10.1086/323091, Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.1965S.
- Yeates, C. M. et al. (August 2000), "Times of Minimum Light for XY Ursae Majoris", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4943 (1): 1, Bibcode: 2000IBVS.4943....1Y.
- Kjurkchieva, D. et al. (February 2000), "Multicolour high-speed photometry and Hα spectroscopy of XY UMa", Astronomy and Astrophysics 354: 909–914, Bibcode: 2000A&A...354..909K.
- Arévalo, M. J.; Lázaro, C. (August 1999), "Time-resolved Spectroscopy of RS Canum Venaticorum Short-Period Systems. II. RT Andromedae, WY Cancri, and XY Ursae Majoris", The Astronomical Journal 118 (2): 1015–1033, doi:10.1086/300952, Bibcode: 1999AJ....118.1015A.
- Chochol, D. et al. (December 1998), "The RS CVn binary XY UMa as a member of a triple system", Astronomy and Astrophysics 340: 415–418, Bibcode: 1998A&A...340..415C.
- Pojmanski, G. (December 1998), "Orbital Solutions for Three RS CVn Systems: WY Cnc, SV Cam and XY UMa", Acta Astronomica 48: 711–727, Bibcode: 1998AcA....48..711P.
- Jeffries, R. D. (April 1998), "A ROSAT observation of the eclipsing binary system XY UMa", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 295 (4): 825–833, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01272.x, Bibcode: 1998MNRAS.295..825J.
- Erdem, A.; Gudur, N. (January 1998), "The orbital period study and photometric analysis of XY Ursae Majoris", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 127 (2): 257–267, doi:10.1051/aas:1998348, Bibcode: 1998A&AS..127..257E.
- Pojmanski, G.; Udalski, A. (October 1997), "An Orbital Solution for RS CVn Binary Star XY UMa", Acta Astronomica 47: 451–466, Bibcode: 1997AcA....47..451P.
- Collier Cameron, A.; Hilditch, R. W. (May 1997), "Eclipse mapping of starspots on XY UMa in 1992 and 1995", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 287 (3): 567–574, doi:10.1093/mnras/287.3.567, Bibcode: 1997MNRAS.287..567C.
- Jeffries, R. D. et al. (December 1995), "V-Band Photometry of XY UMa in 1993 and 1995", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4277 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1995IBVS.4277....1J.
- Hilditch, R. W.; Bell, S. A. (April 1994), "High Precision Photometry of the RS-Canum Binary System XY-Ursae and a Dark-Zone Photometric Model", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 267 (4): 1081, doi:10.1093/mnras/267.4.1081, Bibcode: 1994MNRAS.267.1081H.
- Rainger, P. P. et al. (January 1991), "Spectroscopic observations of the RS CVn-type binary systems SV Cam and XY UMa", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 248: 168, doi:10.1093/mnras/248.1.168, Bibcode: 1991MNRAS.248..168R.
- Geyer, E. H. (1991), "On the long term variability of the chromospheric active close binary XY Ursae Majoris", Astronomische Gesellschaft Abstract Series 6: 79, Bibcode: 1991AGAb....6...79G.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (October 1990), "1990 BVR Photometry of XY UMa", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3535 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1990IBVS.3535....1Z.
- Arévalo, M. J.; Lázaro, C. (July 1990), "Infrared Photometry of XY-Ursae", Astrophysics and Space Science 169 (1–2): 247–249, doi:10.1007/BF00640725, Bibcode: 1990Ap&SS.169..247A.
- Bedford, D. K. et al. (April 1990), "Coronal X-ray emission from the short-period eclipsing binary XY UMa", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 243: 557–564, Bibcode: 1990MNRAS.243..557B.
- Arevalo, M. J.; Lazaro, C. (March 1990), "Infrared Photometry of the RS CVn Short-Period Systems XY UMa and WY CNC", Astronomical Journal 99: 983, doi:10.1086/115389, Bibcode: 1990AJ.....99..983A.
- Banks, T.; Budding, E. (March 1989), "Light Curves for XY UMa", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3304 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1989IBVS.3304....1B.
- Heckert, P. et al. (October 1988), "1987 Photometry of XY Ursae Majoris", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3253 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1988IBVS.3253....1H.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (June 1988), "1988 BVRI Photometry of XY UMa", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3200 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1988IBVS.3200....1Z.
- Jassur, D. M. Z. (December 1986), "Photometric Observations and Interpretation of the Eclipsing Binary System Xy-Ursae", Astrophysics and Space Science 128 (2): 369–375, doi:10.1007/BF00644585, Bibcode: 1986Ap&SS.128..369J.
- Bedford, D. K. et al. (October 1986), "The X-Ray Light Curve of XY Ursae Maioris", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2946 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1986IBVS.2946....1B.
- Bedford, D. K.; Geyer, E. H. (1986), "Simultaneous Optical- and EXOSAT-Observations of the Spot Active Eclipsing Binary XY UMa", Mitteilungen der Astronomischen Gesellschaft 67: 305, Bibcode: 1986MitAG..67..305B.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (April 1983), "The short-period eclipsing system XY UMa : 1982 UBV light curves and a flare-like event", Astronomical Journal 88: 532–534, doi:10.1086/113339, Bibcode: 1983AJ.....88..532Z.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (September 1982), "An Intense Optical Flare from XY UMa", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2200 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1982IBVS.2200....1Z.
- Zeilik, M. et al. (June 1982), "1982 UBVR Photometric Observations of XY UMa", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2169: 1, Bibcode: 1982IBVS.2169....1Z.
- Geyer, E. H.; Metz, K. (December 1977), "A Polarimetric Investigation of the Eclipsing Binary XY Ursae Majoris", Astrophysics and Space Science 52 (2): 351–356, doi:10.1007/BF01093871, Bibcode: 1977Ap&SS..52..351G.
 |