Biology:6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase
| 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.5.1.46 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 75216-15-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
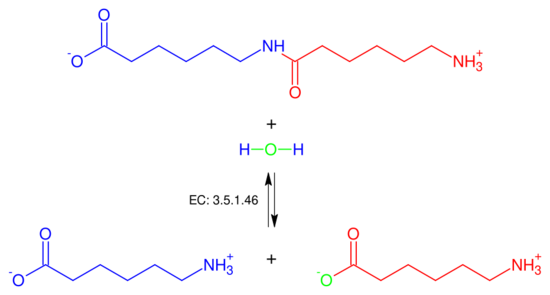
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.46) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O [math]\displaystyle{ \rightleftharpoons }[/math] 2 6-aminohexanoate. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate and H2O, whereas its product is two molecules of 6-aminohexanoate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate amidohydrolase. This enzyme is also called 6-aminohexanoic acid oligomer hydrolase.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 3 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1WYB, 1WYC, and 2DCF.
See also
References
- "Purification and characterization of 6-aminohexanoic-acid-oligomer hydrolase of Flavobacterium sp. Ki72". European Journal of Biochemistry 116 (3): 547–51. June 1981. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05371.x. PMID 7262074.
 |