Biology:Erysipelotrichia
| Erysipelotrichia | |
|---|---|
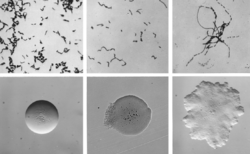
| |
| Cellular and colonial morphology of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Upper row: ×1200, crystal violet; lower row: ×32 | |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Bacillota |
| Class: | Erysipelotrichia Ludwig et al. 2010 |
| Order: | Erysipelotrichales Ludwig et al. 2010 |
| Families | |
| |
The Erysipelotrichia are a class of bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Species of this class are known to be common in the gut microbiome, as they have been isolated from swine manure[1] and increase in composition of the mouse gut microbiome for mice switched to diets high in fat.[2]
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[3] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[4]
| 16S rRNA based LTP_08_2023[5][6][7] | 120 marker proteins based GTDB 08-RS214[8][9][10] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
♦ Paraphyletic Erysipelotrichia
See also
References
- ↑ Han, Il; Congeevaram, Shankar; Ki, Dong-Won; Oh, Byoung-Taek; Park, Joonhong (5 October 2010). "Bacterial community analysis of swine manure treated with autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 89 (3): 835–842. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2893-8. PMID 20922382.
- ↑ Greiner, Thomas; Bäckhed, Fredrik (2011). "Effects of the gut microbiota on obesity and glucose homeostasis". Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 22 (4): 117–123. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2011.01.002. PMID 21353592.
- ↑ J.P. Euzéby. "Erysipelotrichia". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). https://lpsn.dsmz.de/class/erysipelotrichia.
- ↑ Sayers. "Erysipelotrichia". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Undef&id=526524&lvl=9&lin.
- ↑ "The LTP". https://imedea.uib-csic.es/mmg/ltp/#LTP.
- ↑ "LTP_all tree in newick format". https://imedea.uib-csic.es/mmg/ltp/wp-content/uploads/ltp/LTP_all_08_2023.ntree.
- ↑ "LTP_08_2023 Release Notes". https://imedea.uib-csic.es/mmg/ltp/wp-content/uploads/ltp/LTP_08_2023_release_notes.pdf.
- ↑ "GTDB release 08-RS214". https://gtdb.ecogenomic.org/about#4%7C.
- ↑ "bac120_r214.sp_label". https://data.gtdb.ecogenomic.org/releases/release214/214.0/auxillary_files/bac120_r214.sp_labels.tree.
- ↑ "Taxon History". https://gtdb.ecogenomic.org/taxon_history/.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q5396370 entry
 |

