Biology:LOC101928193
LOC101928193 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LOC101928193 gene. There are no known aliases for this gene or protein. Similar copies of this gene, called orthologs, are known to exist in several different species across mammals, amphibians, fish, mollusks, cnidarians, fungi, and bacteria.[1] The human LOC101928193 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 9 with a cytogenic location at 9q34.2.[2] The molecular location of the gene is from base pair 133,189,767 to base pair 133,192,979 on chromosome 9 for an mRNA length of 3213 nucleotides.[3] The gene and protein are not yet well understood by the scientific community, but there is data on its genetic makeup and expression. The LOC101928193 protein is targeted for the cytoplasm and has the highest level of expression in the thyroid, ovary, skin, and testes in humans.[4]
Gene
Locus

The cytogenic location of LOC101928193 in humans is located on the positive strand at 9q34.2. The molecular location of the protein-encoding region of LOC101928193 is from base pairs 133,189,767 to 133,192,979. Within this region, there is 1 intron and 2 exons.[3]
Gene neighborhood
LOC101928193 is flanked by GBGT1 and 0BP2B on chromosome 9.[4] GBGT1 encodes a member of the ABO gene family and also plays a role in synthesizing glycolipids that are involved in tropism and binding pathogens.[5] 0BP2B is a gene that associates with E-Selectin Level in the ABO gene region.[6]
mRNA
In humans, the LOC101928193 gene produces 3 transcript variants, which produce 3 isoforms of the protein.[3] The LOC101928193 isoform X1 is the longest one at 406 codons in length.[7] LOC101928193 isoform X2 is 388 codons long and LOC101928193 isoform X3 is 399 codons long.[8][9] All isoforms have 2 exons and their coding mRNA is 3213 nucleotides long.[3]
Protein
The molecular weight of LOC101928193 is 43.5 kilodaltons.[10] The isoelectric point is 9 pI.[10]
Composition

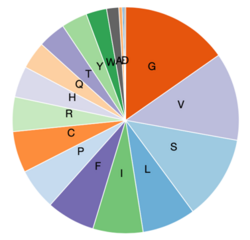
Compared to most human proteins, there are more valine, glycine, serine, histidine, and phenylalanine residues in LOC101928193.[11] LOC101928193 is an alanine, methionine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and lysine poor protein. The enrichment of all other amino acids is normal compared to other human proteins. LOC101928193 composition is highly conserved between mammals.[11]
| Amino acid | Enrichment level | Residues present | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valine (V) | Fully enriched | 51 (12.6%) | Hydrophobic |
| Glycine (G) | Semi-enriched | 62 (15.3%) | Polar |
| Serine (S) | Semi-enriched | 49 (12.1%) | Polar |
| Histidine (H) | Semi-enriched | 18 (4.4%) | Basic |
| Phenylalanine (F) | Semi-enriched | 28 (6.9%) | Hydrophobic |
| Alanine (A) | Fully depleted | 7 (1.7%) | Hydrophobic |
| Methionine (M) | Fully depleted | 1 (0.2%) | Hydrophobic |
| Asparagine (N) | Fully depleted | 0 (0%) | Polar |
| Aspartic acid (D) | Fully depleted | 1 (0.2%) | Polar |
| Glutamic acid (E) | Fully depleted | 2 (0.5%) | Polar |
| Lysine (K) | Fully depleted | 0 (0%) | Polar |
LOC101928193 has an amino acid charge distribution of 0.7% negative, 4.9% positive, and 94.4% neutral. There are no charge runs, hydrophobic segments, or transmembrane domains.
Domains and motifs
There are two different motifs present in LOC101928193. Myristoylation sites are found in the protein sequence 17 times, and a zinc finger domain motif occurs once.[14] The presence of myristoylation sites indicates that LOC101928193 may function in membrane targeting, protein-protein interactions, and signal transduction pathways. Zinc finger domain motifs aid in gene transcription, cell adhesion, protein folding, and chromatin remodeling.[14]
Primary sequence
The LOC101928193 primary coding sequence mRNA is 3213 nucleotides long.[7] There are no upstream open-reading frames, Kozak consensus sequences, or transmembrane regions.
Secondary structure
LOC101928193 has a predicted secondary structure of 56.40% random coils and 43.60% beta sheets.[12] No alpha helices are predicted to occur. Due to the lack of alpha helices in the protein, no coiled coils are predicted to occur in the LOC101928193 secondary structure.[15]
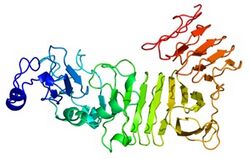
Tertiary structure
The tertiary structure of LOC101928193 is an all beta-sheet protein, as can be seen by its predicted tertiary structure. Both the N-terminus and the C-terminus lack beta-sheets.
Post-translational modifications
O-GlcNAc
There are 13 predicted O-GlcNAc sites within the LOC101928193 protein.[16] O-GlcNAc is a unique form of protein glycosylation that occurs exclusively in the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of the cell.[17] O-Glc-NAcylated proteins are abundant on proteins involved in signaling pathways, stress responses, cytoskeletal assembly, and energy metabolism.
N-linked glycosylation
There are no N-linked glycosylation sites due to the absence of asparagine residues.
Phosphorylation
LOC101928193 has many sites of phosphorylation at several serines, threonines, and tyrosines throughout its structure that results in a conformational change and aids in signaling pathways and regulation. There are 33 predicted phosphorylation sites.[18] The relative amount of phosphorylation sites is highly conserved throughout orthologs of LOC101928193.[18]
Subcellular localization
LOC101928193 is targeted to the cytoplasm for Homo sapiens, rodents, amphibians, fish, and mollusks.[19] It is predicted to localize in the nucleus for cnidarians, fungi, and bacteria.[19]
Expression
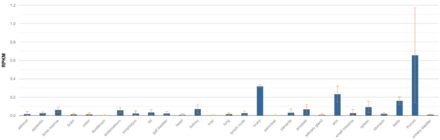
LOC101928193 is not expressed ubiquitously, but is instead tissue specific in low levels of mRNA abundance compared to other human proteins.[4] LOC101928193 has the highest level of expression in the thyroid and has high levels of expression in the ovaries, skin, and testes.[4] Additionally, the gene is expressed in 23 other tissues at levels lower than 0.1 RPKM (Reads Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads) in humans. Other studies have also found that tissue-specific circular RNA induction of LOC101928193 during human fetal development has the highest levels in the heart, kidney, and stomach at 10 weeks gestational time.[3]
Regulation of Expression
Epigenetic
Epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation and histone modification that control expression have not been found in LOC101928193.
Transcriptional
Promoter
There is one promoter for the LOC101928193 gene (GXP_6058323), and it is 1101 nucleotides long on the positive strand from base pairs 133,188,767 to 133,189,867 on chromosome 9.[20] The transcription start site can be found at the 1001 base pair position.[20]
Transcription factor binding sites
Several transcription factors are predicted to bind to the promoter sequence. Some examples include:[22]
- X-box binding factors
- Nuclear factor kappa B/c-rel
- MAF and AP1 related factors
- Interferon regulatory factors
- RBPJ-kappa
- MEF3 binding sites
- Cart-1 homeoprotein
- Fork head domain factors
Based on the functions of these transcription factors, it is possible that LOC101928193 may have been involved in gene repression, hematopoiesis regulation, fetal development, inhibition, DNA-binding, or limb development.
Translational and mRNA stability
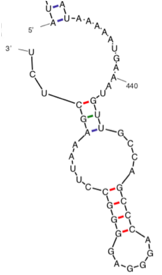
Under conditions consistent with the temperature in the human body, multiple stem loops are predicted to occur in the 5' UTR, the coding region of the protein, and in the 3' UTR. The stem loops direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for mRNA, provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions.[23] There is an interior loop and a stem loop in the mRNA near AUG on the 5' UTR.[21] These structures are often bound by proteins or cause the attenuation of a transcript in order to regulate translation. Furthermore, these stem-loops aid in mRNA stability and the predicted 5' UTR conformation has a free energy of -124.30 kcal/mol.[21] In the 3' UTR, there are 6 predicted stem loops to occur with a free energy of -310.70 kcal/mol, which is spontaneously formed.[21] There are no known microRNA targets in the 3' UTR.
Homology and Evolution
Paralogs
There are no known paralogs of LOC101928193.
Orthologs
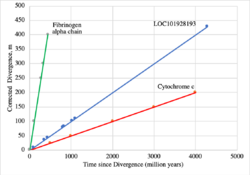
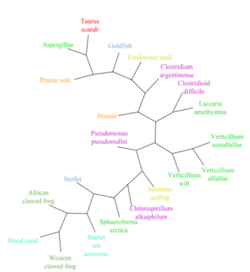
LOC101928193 has over 20 orthologs that are present in mammals, amphibians, fish, mollusks, cnidarians, fungi, and bacteria.[7] The most distant orthologs are found in bacteria that diverged from humans more than 4.29 billion years ago.[25] No orthologs for LOC101928193 have been discovered in close mammalian relatives of humans, including in primates. Below is a table of a range of organisms with orthologs related to the human LOC101928193 protein.
| Species | Common name | Date of divergence (MYA)[27] | NCBI accession # | Sequence length (amino acids) | Protein identity | Protein similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Humans | 0 | XP_011517577 | 406 | 100% | 100% |
| Microtus ochrogaster | Prairie vole | 90 | XP_026643651 | 173 | 33% | 45% |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Western clawed frog | 352 | OCA32729 | 259 | 25% | 33% |
| Xenopus laevis | African clawed frog | 352 | OCT75465 | 167 | 26% | 41% |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Sterlet | 435 | RXM92228 | 259 | 25% | 33% |
| Carassius auratus | Goldfish | 435 | XP_026133143 | 437 | 25% | 35% |
| Biomphalaria glabrata | Freshwater snail | 797 | XP_013067916 | 131 | 31% | 47% |
| Mizuhopecten yessoensis | Japanese scallop | 797 | OWF44451 | 284 | 15% | 32% |
| Onthophagus taurus | Taurus scarab | 797 | XP_022903359 | 294 | 24% | 33% |
| Stylophora pistillata | Hood coral | 824 | PFX21561 | 126 | 37% | 42% |
| Nematostella vectensis | Starlet sea anemone | 824 | XP_001641289 | 418 | 31% | 36% |
| Sphaeroforma arctica | Sphaeroforma arctica | 1023 | XP_014147604 | 123 | 34% | 47% |
| Verticillium alfalfe | Verticillium alfalfe | 1105 | XP_003000049 | 355 | 28% | 35% |
| Chitinispirillum alkaliphilum | Chitinispirillum alkaliphilum | 4290 | KMQ49642 | 105 | 42% | 55% |
| Burkholderia pseudomallei | Pseudomonas pseudomallei | 4290 | ALJ75351 | 238 | 33% | 42% |
Distant homologs
The most distant detectable homolog is in several viral and bacterial species that diverged from humans over 4.29 billion years ago.[25]
Homologous domains
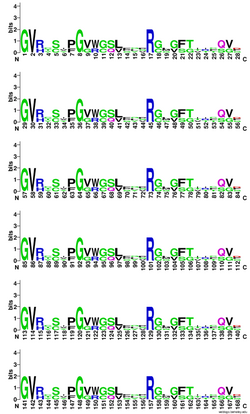
There is a conserved coding region of 28 amino acids that is repeated six times in the protein-encoding region within LOC101928193 and across its orthologs. This domain begins with a glycine at the amino acid position of 194, 222, 250, 278, 306, and 334 within LOC101928193. The domain is conserved across mammals, cnidarians, fish, bacteria, and amphibians, and even in some species within these taxonomic groups that are not orthologs but share the same domain. The sequence always begins with a polar glycine and a hydrophobic valine. There is also a conserved basic arginine within the middle of the sequence.
Phylogeny
No other species has LOC101928193 in the same form as in humans. Several species within mammals, amphibians, fish, mollusks, cnidarians, fungi, and bacteria have LOC101928193 in a slightly different form with a similarity usually between 30 and 50%. Several taxonomic groups do not express any proteins or genes similar to LOC101928193 including Archaeans, plants, and several animal species.
Inheritance
LOC101928193 may not follow a normal inheritance pattern or occur regularly in the genome as it has a scattered occurrence throughout evolutionarily related species.[1] Furthermore, the similarity between orthologs of LOC101928193 is constant over time and is not higher in closely related taxonomic groups or lower in distantly related taxonomic groups. It is possible that LOC101928193 incorporates into the genome of different species through viral pathways as LOC101928193 has been found to have ligand binding sites for cyanobacteria proteins, like chlorophyll a.[28] Orthologs of LOC101928193 have been found to contain UL36, which is a large tegument protein that functions in the viral cycle and is commonly found in human herpesvirus simplex virus 1.[29][30]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Uncharacterized protein LOC101928193 isoform X1". NCBI BLAST. https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 "LOC101928193 Gene". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uids=101928193.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "uncharacterized LOC101928193 [Homo sapiens (human)"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=DetailsSearch&Term=101928193.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 13 (2): 397–406. February 2014. doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.035600. PMID 24309898.
- ↑ "GBGT1 Gene (Protein Coding)". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=GBGT1.
- ↑ "Genome-wide association identifies the ABO blood group as a major locus associated with serum levels of soluble E-selectin". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 29 (11): 1958–67. November 2009. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.192971. PMID 19729612.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Uncharacterized protein LOC101928193 isoform X1". https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ "uncharacterized protein LOC101928193 isoform X2 [Homo sapiens"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/XP_011517578.1.
- ↑ "uncharacterized protein LOC101928193 isoform X3 [Homo sapiens"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/XP_011547076.1.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.0 10.1 "ExPASy". SIB. https://www.expasy.org.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 "SAPS". 2019. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/services/web/toolresult.ebi?jobId=saps-I20190416-012932-0056-60065109-p1m.
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 "GOR IV Secondary Structure Prediction Method". 2016. https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_gor4.html.
- ↑ "The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis". Nature Protocols 10 (6): 845–58. June 2015. doi:10.1038/nprot.2015.053. PMID 25950237. PMC 5298202. http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/phyre2_output/4a7825ff73c16783/summary.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 "MyHits Motif Scan". https://myhits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/motif_scan.
- ↑ "Prediction of Coiled Coil Regions in Proteins". ExPASy COILS. https://embnet.vital-it.ch/software/COILS_form.html.
- ↑ "YinOYang 1.2 Server". Technical University of Denmark. http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/cgi-bin/webface2.fcgi?jobid=5CBCB01C000070BF3C51FCED&wait=20.
- ↑ Hart, Gerald (2009). The O-GlcNAc Modification. New York, NY: Cold Spring Harbor.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 "NetPhos DTU Bioinformatics". http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 "PSORT II". Expasy. http://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Gene2Promoter". Genomatix. https://www.genomatix.de.
- ↑ Jump up to: 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 "MFold". The RNA Institute. http://unafold.rna.albany.edu/?q=mfold/RNA-Folding-Form.
- ↑ "Gene2Promoter". 2019. https://www.genomatix.de/.
- ↑ "Hairpin RNA: a secondary structure of primary importance". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 63 (7–8): 901–8. April 2006. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5558-5. PMID 16568238. http://doc.rero.ch/record/313306/files/18_2005_Article_5558.pdf.
- ↑ "Multiple Sequence Alignment". ClustalW. https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw.
- ↑ Jump up to: 25.0 25.1 25.2 "TimeTree of Life". http://timetree.org.
- ↑ "WebLogo Database". University of California – Berkeley. http://weblogo.berkeley.edu.
- ↑ "Synthesis of phylogeny and taxonomy into a comprehensive tree of life". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (TimeTree) 112 (41): 12764–9. October 2015. doi:10.1073/pnas.1423041112. PMID 26385966. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..11212764H.
- ↑ "I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions". Nucleic Acids Research 43 (W1): W174-81. July 2015. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv342. PMID 25883148.
- ↑ "Keratin-associated protein 10-4 [Verticillium alfalfae VaMs.102"]. NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/XP_003000049.1?report=graph.
- ↑ "UniProtKB – P10220 (LTP_HHV11)". UniProt. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P10220.
Suggested Reading
- "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell 127 (3): 635–48. November 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Research 14 (10B): 2121–7. October 2004. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (26): 16899–903. December 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M.
 |