Biology:Mammoth
| Mammoth | |
|---|---|

| |
| Columbian mammoth in the Page Museum in Los Angeles . | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae |
| Subfamily: | Elephantinae |
| Tribe: | Elephantini |
| Genus: | †Mammuthus Brookes, 1828 |
| Type species | |
| †Elephas primigenius[1][2] Blumenbach, 1799
| |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus Mammuthus. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks. They lived from the Pliocene epoch (from around 5 million years ago) into the Holocene about 4,000 years ago, and various species existed in Africa, Europe, Asia, and North America. Mammoths are more closely related to living Asian elephants than African elephants.
The oldest mammoth representative, Mammuthus subplanifrons, appeared around five million years ago during the early Pliocene in what is now southern and Eastern Africa. Later in the Pliocene, by about three million years ago, mammoths dispersed into Eurasia, eventually covering most of Eurasia before migrating into North America around 1.5–1.3 million years ago, becoming ancestral to the Columbian mammoth (M. columbi). The last species to emerge, the woolly mammoth (M. primigenius), developed about 400,000 years ago in East Asia, with some surviving on Russia's Wrangel Island in the Arctic Ocean until as recently as roughly 3,700 to 4,000 years ago, still extant during the existence of the earliest civilisations in Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia.
Evolution
The earliest known proboscideans, the clade that contains the elephants, existed about 55 million years ago around the Tethys Sea area. The closest relatives of the Proboscidea are the sirenians and the hyraxes. The family Elephantidae is known to have existed six million years ago in Africa, and includes the living elephants and the mammoths. Among many now extinct clades, the mastodon is only a distant relative of the mammoths, and part of the separate Mammutidae family, which diverged 25 million years before the mammoths evolved.[3]
The following cladogram shows the placement of the genus Mammuthus among other proboscideans, based on hyoid characteristics and genetics:[4][5]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Since many remains of each species of mammoth are known from several localities, it is possible to reconstruct the evolutionary history of the genus through morphological studies. Mammoth species can be identified from the number of enamel ridges on their molars; the primitive species had few ridges, and the amount increased gradually as new species evolved and replaced the former ones. At the same time, the crowns of the teeth became longer, and the skulls became higher from top to bottom and shorter from the back to the front over time to accommodate this.[6]

The first known members of the genus Mammuthus were the African species Mammuthus subplanifrons from the Pliocene and Mammuthus africanavus from the Pleistocene. The former is thought to be the ancestor of later forms. Mammoths entered Europe around 3 million years ago; the earliest known type has been named M. rumanus, which spread across Europe and China. Only its molars are known, which show it had 8–10 enamel ridges. A population evolved 12–14 ridges and split off from and replaced the earlier type, becoming M. meridionalis. In turn, this species was replaced by the steppe mammoth, M. trogontherii, with 18–20 ridges, which evolved in East Asia ca. 1.8 million years ago. Steppe mammoth populations replaced M. meridionalis in Europe between 1 and 0.7 million years ago. The Columbian mammoth, M. columbi, evolved from a population of M. trogontherii that had entered North America around 1.5 million years ago.[7] Mammoths derived from M. trogontherii evolved molars with 26 ridges between 800,000 and 400,000 years ago in Siberia, becoming the woolly mammoth, M. primigenius. The woolly mammoth would replace the steppe mammoth in Europe during the late Middle Pleistocene around 200,000 years ago.[6] A 2011 genetic study showed that two examined specimens of the Columbian mammoth were grouped within a subclade of woolly mammoths. This suggests that the two populations interbred and produced fertile offspring. It also suggested that a North American form known as "M. jeffersonii" may be a hybrid between the two species.[8]
By the late Pleistocene, mammoths in continental Eurasia had undergone a major transformation, including a shortening and heightening of the cranium and mandible, increase in molar hypsodonty index, increase in plate number, and thinning of dental enamel. Due to this change in physical appearance, it became customary to group European mammoths separately into distinguishable clusters:
- Early Pleistocene – Mammuthus meridionalis
- Middle Pleistocene – Mammuthus trogontherii
- Late Pleistocene – Mammuthus primigenius
There is speculation as to what caused this variation within the three chronospecies. Variations in environment, climate change, and migration surely played roles in the evolutionary process of the mammoths. Take M. primigenius for example: Woolly mammoths lived in open grassland biomes. The cool steppe tundra of the Northern Hemisphere was the ideal place for mammoths to thrive because of the resources it supplied. With occasional warmings during the Ice Age, climate would change the landscape, and resources available to the mammoths would be altered accordingly.[6][9][10]
In February 2021, scientists reported that DNA from million-year-old mammoth remains had become the oldest ever sequenced.[11][12]
Etymology and early observations

The word mammoth was first used in Europe during the early 17th century, when referring to maimanto tusks discovered in Siberia.[13] John Bell,[14] who was on the Ob River in 1722, said that mammoth tusks were well known in the area. They were called "mammon's horn" and were often found in washed-out river banks. Some local people claimed to have seen a living mammoth, but they came out only at night and always disappeared under water when detected. He bought one and presented it to Hans Sloan who pronounced it an elephant's tooth.
The folklore of some native peoples of Siberia, who would routinely find mammoth bones, and sometimes frozen mammoth bodies, in eroding river banks, had various interesting explanations for these finds. Among the Khanty people of the Irtysh River basin, a belief existed that the mammoth was some kind of a water spirit. According to other Khanty, the mammoth was a creature that lived underground, burrowing its tunnels as it went, and would die if it accidentally came to the surface.[15] The concept of the mammoth as an underground creature was known to the Chinese, who received some mammoth ivory from the Siberian natives; accordingly, the creature was known in China as yǐn shǔ 隐鼠, "the hidden rodent".[16]
Thomas Jefferson, who famously had a keen interest in paleontology, is partially responsible for transforming the word mammoth from a noun describing the prehistoric elephant to an adjective describing anything of surprisingly large size. The first recorded use of the word as an adjective was in a description of a large wheel of cheese (the "Cheshire Mammoth Cheese") given to Jefferson in 1802.[17]
Description

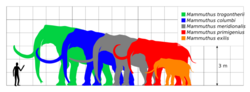
Like living elephants, mammoths typically had large body sizes. The largest known species like Mammuthus trogontherii (the steppe mammoth) were considerably larger than modern elephants, reaching heights in the region of 4 m (13.1 ft) at the shoulder and weights of 11 tonnes (12 short tons), while exceptionally large males may have reached 4.5 m (14.8 ft) at the shoulder and 14.3 tonnes (15.8 short tons) in weight.[18] However, woolly mammoths were considerably smaller, only about as large as modern Asian elephants and African bush elephants at about 2.3 m to 3.15 m high at the shoulder, and 2.8 to 6 tonnes in weight on average).[18][19] Both sexes bore tusks. A first, small set appeared at about the age of six months, and these were replaced at about 18 months by the permanent set. Growth of the permanent set was at a rate of about 2.5 to 15.2 cm (1 to 6 in) per year.[20] Mammoth tusks are among the largest known among proboscideans with some specimens over 4 m (13.1 ft) in length and likely 200 kg (440.9 lb) in weight with some historical reports suggesting tusks of Columbian mammoths could reach lengths of around 5 m (16.4 ft) substantially surpassing the largest known modern elephant tusks.[21]
The number of lamellae (ridge-like structures) on the molars, particularly on the third molars, substantially increased over the course of mammoth evolution, reaching an apex in Late Pleistocene woolly mammoths, which have 20-28 lamellae on the third molars. These changes also corresponded with reduced enamel thickness and increasing tooth height (hypsodonty).[22] These changes are thought to be adaptations to increased abrasion as a result of increasing adaptation of the mammoth lineage towards a grazing diet.[23]
Based on studies of their close relatives, the modern elephants, mammoths probably had a gestation period of 22 months, resulting in a single calf being born. Their social structure was probably the same as that of African and Asian elephants, with females living in herds headed by a matriarch, whilst bulls lived solitary lives or formed loose groups after sexual maturity.[24]
Scientists discovered and studied the remains of a mammoth calf, and found that fat greatly influenced its form, and enabled it to store large amounts of nutrients necessary for survival in temperatures as low as −50 °C (−58 °F).[25] The fat also allowed the mammoths to increase their muscle mass, allowing the mammoths to fight against enemies and live longer.[26] Woolly mammoths evolved a suite of adaptations for arctic life, including morphological traits such as small ears and tails to minimize heat loss, a thick layer of subcutaneous fat, long thick fur, and numerous sebaceous glands for insulation, as well as a large brown-fat hump like deposit behind the neck that may have functioned as a heat source and fat reservoir during winter.[27]
Diet
Depending on the species or race of mammoth, the diet differed somewhat depending on location, although all mammoths ate similar things. For the Columbian mammoth, M. columbi, the diet was mainly grazing. American Columbian mammoths fed primarily on cactus leaves, trees, and shrubs. These assumptions were based on mammoth feces and mammoth teeth. Mammoths, like modern day elephants, have hypsodont molars. These features also allowed mammoths to live an expansive life because of the availability of grasses and trees.[28]
For the Mongochen mammoth, its diet consisted of herbs, grasses, larch, and shrubs, and possibly alder. These inferences were made through the observation of mammoth feces, which scientists observed contained non-arboreal pollen and moss spores.[29]
European mammoths had a major diet of C3 carbon fixation plants. This was determined by examining the isotopic data from the European mammoth teeth.[30]
The arctic tundra and steppe where the mammoths lived appears to have been dominated by forbs, not grass. These were richer in protein and easier to digest than grasses and wooden plants, which came to dominate the areas when the climate became wetter and warmer. This could have been a major contributor to why the arctic megafauna went extinct.[31][32][33]
The Yamal baby mammoth Lyuba, found in 2007 in the Yamal Peninsula in Western Siberia, suggests that baby mammoths, as do modern baby elephants, ate the dung of adult animals. The evidence to show this is that the dentition (teeth) of the baby mammoth had not yet fully developed to chew grass. Furthermore, there was an abundance of ascospores of coprophilous fungi from the pollen spectrum of the baby's mother. Coprophilous fungi are fungi that grow on animal dung and disperse spores in nearby vegetation, which the baby mammoth would then consume. Spores might have gotten into its stomach while grazing for the first few times. Coprophagy may be an adaptation, serving to populate the infant's gut with the needed microbiome for digestion.
Mammoths alive in the Arctic during the Last Glacial Maximum consumed mainly forbs, such as Artemisia; graminoids were only a minor part of their diet.[34]
Extinction

The woolly mammoth (M. primigenius) was the last species of the genus. Most populations of the woolly mammoth in North America and Eurasia, as well as all the Columbian mammoths (M. columbi) in North America, died out around the time of the last glacial retreat, as part of a mass extinction of megafauna in northern Eurasia and the Americas. Until recently, the last woolly mammoths were generally assumed to have vanished from Europe and southern Siberia about 12,000 years ago, but new findings show some were still present there about 10,000 years ago. Slightly later, the woolly mammoths also disappeared from continental northern Siberia.[35] A small population survived on St. Paul Island, Alaska, up until 3750 BC,[36][37][38] and the small[39] mammoths of Wrangel Island survived until about 2000 BC[40][41] Recent eDNA research of sediments indicates mammoths survived in north central Siberia at least as late as 2000 BC, in continental northeast Siberia until at least 5300 BC, and until at least 6600 BC in North America.[42]
The warming trend (Holocene) that occurred 12,000 years ago, accompanied by a glacial retreat and rising sea levels, has been suggested as a contributing factor. Forests replaced open woodlands and grasslands across the continent. The available habitat would have been reduced for some megafaunal species, such as the mammoth. However, such climate changes were nothing new; numerous very similar warming episodes had occurred previously within the ice age of the last several million years without producing comparable megafaunal extinctions, so climate alone is unlikely to have played a decisive role.[43][44] The spread of advanced human hunters through northern Eurasia and the Americas around the time of the extinctions, however, was a new development, and thus might have contributed significantly.[43][44]

Whether the general mammoth population died out for climatic reasons or due to overhunting by humans is controversial.[45] During the transition from the Late Pleistocene epoch to the Holocene epoch, there was shrinkage of the distribution of the mammoth because progressive warming at the end of the Pleistocene epoch changed the mammoth's environment. The mammoth steppe was a periglacial landscape with rich herb and grass vegetation that disappeared along with the mammoth because of environmental changes in the climate. Mammoths had moved to isolated spots in Eurasia, where they disappeared completely. Also, it is thought that Late Paleolithic and Mesolithic human hunters might have affected the size of the last mammoth populations in Europe.[46] There is evidence to suggest that humans did cause the mammoth extinction, although there is no definitive proof. It was found that humans living south of a mammoth steppe learned to adapt themselves to the harsher climates north of the steppe, where mammoths resided. It was concluded that if humans could survive the harsh north climate of that particular mammoth steppe then it was possible humans could hunt (and eventually extinguish) mammoths everywhere. Another hypothesis suggests mammoths fell victim to an infectious disease. A combination of climate change and hunting by humans may be a possible explanation for their extinction. Homo erectus is known to have consumed mammoth meat as early as 1.8 million years ago,[47] though this may mean only successful scavenging, rather than actual hunting. Later humans show greater evidence for hunting mammoths; mammoth bones at a 50,000-year-old site in South Britain suggest that Neanderthals butchered the animals,[48] while various sites in Eastern Europe dating from 15,000 to 44,000 years old suggest humans (probably Homo sapiens) built dwellings using mammoth bones (the age of some of the earlier structures suggests that Neanderthals began the practice).[49] However, the American Institute of Biological Sciences notes that bones of dead elephants, left on the ground and subsequently trampled by other elephants, tend to bear marks resembling butchery marks, which have allegedly been misinterpreted as such by archaeologists.[50]
In 2021, a study using ancient environmental DNA concluded that the extinction of the mammoth was primarily caused by dramatic vegetation changes at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, due to a changed climate and precipitation regime. During the Last Glacial Maximum, the Arctic would have had a homogeneous flora consisting of mammoth steppe-associated plants, supporting a unique community of grazing mammals, including the mammoth. Increased precipitation following the end of the LGM caused a significant paludification of the steppe, which has been linked to a general decrease in species diversity of the region's former inhabitants, and not just mammoths. In addition, the study found mammoths to have persisted on the mainland for far longer than previously thought, with their shrinking distribution roughly tracking the shrinkage of the mammoth steppe; their final mainland refugium, the Taymyr Peninsula, was roughly concurrent with the Wrangel population. The close relationship between decreasing mammoth populations and steppe, as well as the lack of a sudden decline that would be associated with the human overkill hypothesis, indicates that humans and mammoths may have coexisted for millennia, and thus humans may have only played a minor role in the species' extinction.[42]
Many hypotheses also seek to explain the regional extinction of mammoths in specific areas. Scientists have speculated that the mammoths of Saint Paul Island (Alaska), an isolated enclave where mammoths survived until about 8,000 years ago, died out as the island shrank by 80–90% when sea levels rose, eventually making it too small to support a viable population.[51] Similarly, genome sequences of the Wrangel Island mammoths indicate a sharp decline in genetic diversity, though the extent to which this played a role in their extinction is still unclear.[52] Another hypothesis, said to be the cause of mammoth extinction in Siberia, comes from the idea that many may have drowned. While traveling to the Northern River, many of these mammoths broke through the ice and drowned. This also explains bones remains in the Arctic Coast and some of the New Siberian Islands.[citation needed]
Dwarfing occurred with the pygmy mammoth on the outer Channel Islands of California, but at an earlier period. Those animals were very likely killed by early Paleo-Native Americans, and habitat loss caused by a rising sea level that split Santa Rosae into the outer Channel Islands.[53]
Mammoth-elephant hybrid
One proposed scientific use of this preserved genetic material is to recreate living mammoths. This has long been discussed theoretically but has only recently become the subject of formal effort due to advances in molecular biology techniques and cloning of mammals.[54][55][56]
According to one research team, a mammoth cannot be recreated, but they will try to eventually grow in an "artificial womb" a hybrid elephant with some woolly mammoth traits.[57][58] Comparative genomics shows that the mammoth genome matches 99% of the elephant genome, so some researchers aim to engineer an elephant with some mammoth genes that code for the external appearance and traits of a mammoth.[59] The outcome would be an elephant-mammoth hybrid with no more than 1% mammoth genes.[59] Other projects are working on gradually adding mammoth genes to elephant cells in vitro.[54][55][60]
See also
- Genesis 2.0, a documentary
- Ivory trade
- La Brea tar pits
- List of mammoths
- The Mammoth Site in Hot Springs, South Dakota
- Niederweningen Mammoth Museum
- Pleistocene Park
- Waco Mammoth National Monument
References
- ↑ Garutt, W.E.; Gentry, Anthea; Lister, A.M. (1990). "Case 2726: Mammuthus Brookes 1828 (Mammalia Proboscidea) proposed conservation and Elephas primigenius Blumenbach, 1799 (currently Mammuthus primigenius) proposed designation as the type species of Mammuthus, and designation of a neotype". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature 47 (1): 38–44. doi:10.5962/bhl.part.2651. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/12230365.
- ↑ "Opinion 1661: Mammuthus Brookes, 1828 (Mammalia, Proboscidea): conserved, and Elephas primigenius Blumenbach, 1799 designated as the type species". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature 48 (3): 279–280. 1991. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/12230958.
- ↑ Lister, A.; Bahn, P. (2007). Mammoths – Giants of the Ice Age (3rd ed.). London: Frances Lincoln. ISBN 978-0520261600.
- ↑ Shoshani, J.; Ferretti, M. P.; Lister, A. M.; Agenbroad, L. D.; Saegusa, H.; Mol, D.; Takahashi, K. (2007). "Relationships within the Elephantinae using hyoid characters". Quaternary International 169-170: 174–185. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.02.003. Bibcode: 2007QuInt.169..174S.
- ↑ Palkopoulou, Eleftheria; Lipson, Mark; Mallick, Swapan; Nielsen, Svend; Rohland, Nadin; Baleka, Sina; Karpinski, Emil; Ivancevic, Atma M. et al. (2018-03-13). "A comprehensive genomic history of extinct and living elephants" (in en). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (11): E2566–E2574. doi:10.1073/pnas.1720554115. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 29483247. Bibcode: 2018PNAS..115E2566P.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Lister, A. M.; Sher, A. V.; Van Essen, H.; Wei, G. (2005). "The pattern and process of mammoth evolution in Eurasia". Quaternary International 126–128: 49–64. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.04.014. Bibcode: 2005QuInt.126...49L. http://doc.rero.ch/record/13496/files/PAL_E277.pdf.
- ↑ Lister, A. M.; Sher, A. V. (2015-11-13). "Evolution and dispersal of mammoths across the Northern Hemisphere" (in en). Science 350 (6262): 805–809. doi:10.1126/science.aac5660. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 26564853. Bibcode: 2015Sci...350..805L.
- ↑ Enk, J.; Devault, A.; Debruyne, R.; King, C. E.; Treangen, T.; O'Rourke, D.; Salzberg, S. L.; Fisher, D. et al. (2011). "Complete Columbian mammoth mitogenome suggests interbreeding with woolly mammoths". Genome Biology 12 (5): R51. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-r51. PMID 21627792.
- ↑ Nogués-Bravo, D.; Rodríguez, J. S.; Hortal, J. N.; Batra, P.; Araújo, M. B. (2008). Barnosky, Anthony. ed. "Climate Change, Humans, and the Extinction of the Woolly Mammoth". PLOS Biology 6 (4): e79. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060079. PMID 18384234.
- ↑ Stuart, A. J. (2005). "The extinction of woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius) and straight-tusked elephant (Palaeoloxodon antiquus) in Europe". Quaternary International 126–128: 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.04.021. Bibcode: 2005QuInt.126..171S. http://doc.rero.ch/record/13497/files/PAL_E278.pdf.
- ↑ Hunt, Katie (17 February 2021). "World's oldest DNA sequenced from a mammoth that lived more than a million years ago". CNN News. https://www.cnn.com/2021/02/17/world/mammoth-oldest-dna-million-years-ago-scn/index.html. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ↑ Callaway, Ewen (17 February 2021). "Million-year-old mammoth genomes shatter record for oldest ancient DNA - Permafrost-preserved teeth, up to 1.6 million years old, identify a new kind of mammoth in Siberia.". Nature 590 (7847): 537–538. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00436-x. PMID 33597786.
- ↑ Lister, A.; Bahn, P. (2007). Mammoths – Giants of the Ice Age (3rd ed.). London: Frances Lincoln. p. 49. ISBN 978-0520261600.
- ↑ John Bell, Travels from St Petersburg in Russia to diverse parts of Asia, Edinburgh, 1806, pages 383-386
- ↑ Patkanov, S. (1897), Die lrtysch-Ostjaken und ihre Volkspoesie, I, St. Petersburg: St. Petersburg, pp. 123–124, http://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=njp.32101073232413;view=1up;seq=137
- ↑ "Arabic and Chinese Trade in Walrus and Narwhal Ivory", T'oung Pao, Second Series 14 (3): 329, 1913, doi:10.1163/156853213X00213. Bertholds's source for the Irtysh Ostyaks' belief is Patkanov 1897, pp. 123–124
- ↑ Simpson, J. (2009). "Word Stories: Mammoth." Oxford English Dictionary Online, Oxford University Press. Accessed 05-JUN-2009.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Larramendi, A. (2016). "Shoulder height, body mass and shape of proboscideans". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 61. doi:10.4202/app.00136.2014. https://www.app.pan.pl/archive/published/app61/app001362014.pdf.
- ↑ Larramendi, Asier; Palombo, Maria Rita; Marano, Federica (2017). "Reconstructing the life appearance of a Pleistocene giant: size, shape, sexual dimorphism and ontogeny of Palaeoloxodon antiquus (Proboscidea: Elephantidae) from Neumark-Nord 1 (Germany)". Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana (3): 299–317. doi:10.4435/BSPI.2017.29. ISSN 0375-7633. https://www.paleoitalia.it/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/01_Larramendi_et_al_2017_BSPI_563.pdf.
- ↑ Agenbroad, Larry; Nelson, Lisa (2002). Mammoths. Minneapolis: Lerner. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-8225-2862-3. https://archive.org/details/mammothsiceagegi00larr/page/34.
- ↑ Larramendi, Asier (2023-12-10). "Estimating tusk masses in proboscideans: a comprehensive analysis and predictive model" (in en). Historical Biology: 1–14. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2286272. ISSN 0891-2963. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08912963.2023.2286272.
- ↑ Lister, Adrian M. (October 2022). "Mammoth evolution in the late Middle Pleistocene: The Mammuthus trogontherii-primigenius transition in Europe" (in en). Quaternary Science Reviews 294: 107693. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107693. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0277379122003249.
- ↑ Lister, Adrian M.; Sher, Andrei V. (2001-11-02). "The Origin and Evolution of the Woolly Mammoth" (in en). Science 294 (5544): 1094–1097. doi:10.1126/science.1056370. ISSN 0036-8075. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1056370.
- ↑ "Columbian Mammoth & Channel Island Mammoth". San Diego Zoo. http://library.sandiegozoo.org/factsheets/_extinct/mammoth/mammoth.htm.
- ↑ Peter D. Moore (2008). Tundra. Facts On File. p. 198. ISBN 978-0-8160-5933-1. https://archive.org/details/tundra0000moor.
- ↑ Maschenko, E. N.; Boeskorov, G. G.; Baranov, V. A. (2013). "Morphology of a mammoth calf (Mammuthus primigenius) from Ol'chan (Oimiakon, Yakutia)". Paleontological Journal 47 (4): 425–438. doi:10.1134/S0031030113040096.
- ↑ Lynch, Vincent (2 July 2015). "Elephantid Genomes Reveal the Molecular Bases of Woolly Mammoth Adaptations to the Arctic". Cell Reports 12 (2): P217-228. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.027. PMID 26146078.
- ↑ Pérez-Crespo, V. C. A. N.; Arroyo-Cabrales, J. N.; Benammi, M.; Johnson, E.; Polaco, O. J.; Santos-Moreno, A.; Morales-Puente, P.; Cienfuegos-Alvarado, E. (2012). "Geographic variation of diet and habitat of the Mexican populations of Columbian Mammoth (Mammuthus columbi)". Quaternary International 276–277: 8–16. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2012.03.014. Bibcode: 2012QuInt.276....8P.
- ↑ Kosintsev, P. A.; Lapteva, E. G.; Korona, O. M.; Zanina, O. G. (2012). "Living environments and diet of the Mongochen mammoth, Gydan Peninsula, Russia". Quaternary International 276-277: 253–268. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2011.11.004. Bibcode: 2012QuInt.276..253K.
- ↑ García-Alix, A.; Delgado Huertas, A.; Martín Suárez, E. (2012). "Unravelling the Late Pleistocene habitat of the southernmost woolly mammoths in Europe". Quaternary Science Reviews 32: 75–85. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.11.007. Bibcode: 2012QSRv...32...75G.
- ↑ Study shows flowers powered the woolly mammoth - Phys.org
- ↑ Woolly Mammoths Wiped Out by Grass Invasion? - Latest Stories
- ↑ When flowers died out in Arctic, so did mammoths: genetic analysis finds vegetation change around same time as megafauna extinction
- ↑ Willerslev, E.; Davison, J.; Moora, M.; Zobel, M.; Coissac, E.; Edwards, M. E.; Lorenzen, E. D.; Vestergård, M. et al. (2014). "Fifty thousand years of Arctic vegetation and megafaunal diet". Nature 506 (7486): 47–51. doi:10.1038/nature12921. PMID 24499916. Bibcode: 2014Natur.506...47W. https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/377215/1/131114_ms%252BSI.pdf.
- ↑ Hsieh, T. H.; Chen, J. J. J.; Chen, L. H.; Chiang, P. T.; Lee, H. Y. (2011). "Time-course gait analysis of hemiparkinsonian rats following 6-hydroxydopamine lesion". Behavioural Brain Research 222 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.031. PMID 21435355.
- ↑ Dale Guthrie, R. (2004). "Radiocarbon evidence of mid-Holocene mammoths stranded on an Alaskan Bering Sea island". Nature 429 (6993): 746–749. doi:10.1038/nature02612. PMID 15201907. Bibcode: 2004Natur.429..746D.
- ↑ Veltre, D. W.; Yesner, D. R.; Crossen, K. J.; Graham, R. W.; Coltrain, J. B. (2008). "Patterns of faunal extinction and paleoclimatic change from mid-Holocene mammoth and polar bear remains, Pribilof Islands, Alaska". Quaternary Research 70 (1): 40–50. doi:10.1016/j.yqres.2008.03.006. Bibcode: 2008QuRes..70...40V.
- ↑ Enk, J. M.; Yesner, D. R.; Crossen, K. J.; Veltre, D. W.; O'Rourke, D. H. (2009). "Phylogeographic analysis of the mid-Holocene Mammoth from Qagnaxˆ Cave, St. Paul Island, Alaska". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 273 (3–4): 184–190. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.12.019. Bibcode: 2009PPP...273D...5.. http://doc.rero.ch/record/209769/files/PAL_E4204.pdf.
- ↑ Tikhonov, Alexei; Larry Agenbroad; Sergey Vartanyan (2003). "Comparative analysis of the mammoth populations on Wrangel Island and the Channel Islands". Deinsea 9: 415–420. ISSN 0923-9308. http://www.nmr.nl/nmr/pages/showPage.do?itemid=1896&instanceid=16.
- ↑ Arslanov, K., Cook, G.T., Gulliksen, S., Harkness, D.D., Kankainen, T., Scott, E.M., Vartanyan, S., and Zaitseva, G.I. (1998). "Consensus Dating of Remains from Wrangel Island". Radiocarbon 40 (1): 289–294. doi:10.1017/S0033822200018166. https://journals.uair.arizona.edu/index.php/radiocarbon/article/view/2015. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
- ↑ Vartanyan, S. L.; Arslanov, Kh. A.; Tertychnaya, T. V.; Chernov, S. B. (1995). "Radiocarbon Dating Evidence for Mammoths on Wrangel Island, Arctic Ocean, until 2000 BC". Radiocarbon 37 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1017/S0033822200014703. Bibcode: 1995Radcb..37....1V. https://journals.uair.arizona.edu/index.php/radiocarbon/article/view/1640/1644. Retrieved 2008-01-10.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Wang, Yuchang; Pedersen, M.W.; Alsos, I.G.; et a (October 20, 2021). "Late Quaternary dynamics of Arctic biota from ancient environmental genomics". Nature 600 (7887): 86–92. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04016-x. PMID 34671161. PMC 8636272. Bibcode: 2021Natur.600...86W. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04016-x. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Martin, P. S. (2005). Twilight of the Mammoths: Ice Age Extinctions and the Rewilding of America (Illustrated ed.). University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520231412. OCLC 58055404. https://archive.org/details/twilightofmammot00paul. Retrieved 2014-11-11.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Burney, D.; Flannery, T. (2005). "Fifty millennia of catastrophic extinctions after human contact". Trends in Ecology & Evolution 20 (7): 395–401. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2005.04.022. PMID 16701402. http://www.anthropology.hawaii.edu/Fieldschools/Kauai/Publications/Publication%204.pdf.
- ↑ Fountain, Henry (22 December 2009). "DNA Shifts Timeline For Mammoths' Exit". The New York Times: p. 3. https://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/22/science/22obtundra.html.
- ↑ Peterkin, G.L.; Bricker, H.M.; Mellars, P. (1993). Hunting and animal exploitation in the later Palaeolithic and Mesolithic of Eurasia. Archeological papers of the American Anthropological Association. American Anthropological Association. ISBN 978-0-913167-61-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=e1sSAQAAIAAJ. Retrieved 2019-10-24.
- ↑ Levy, S. (2006). "Clashing with Titans". BioScience 56 (4): 292. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2006)56[292:CWT2.0.CO;2].
- ↑ Sapsted, David (June 26, 2002). "Woolly mammoth butchery site unearthed". The Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/science-news/3296348/Woolly-mammoth-butchery-site-unearthed.html.
- ↑ Gray, Richard (December 18, 2011). "Neanderthals built homes with mammoth bones". Telegraph.co.uk. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/science/science-news/8963177/Neanderthals-built-homes-with-mammoth-bones.html.
- ↑ Surovell, Todd A.; Waguespack, Nicole M. (November 2008). "How many elephant kills are 14?". Quaternary International 191 (1): 82–97. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.12.001. Bibcode: 2008QuInt.191...82S.
- ↑ Schirber, Michael (October 19, 2004). "Surviving Extinction: Where Woolly Mammoths Endured". livescience. http://www.livescience.com/14-surviving-extinction-woolly-mammoths-endured.html.
- ↑ Palkopoulou, Eleftheria; Mallick, Swapan; Skoglund, Pontus; Enk, Jacob; Rohland, Nadin; Li, Heng; Omrak, Ayça; Vartanyan, Sergey et al. (2015). "Complete Genomes Reveal Signatures of Demographic and Genetic Declines in the Woolly Mammoth". Current Biology 25 (10): 1395–1400. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.04.007. PMID 25913407.
- ↑ Rocha, Veronica (16 September 2016). "Well-preserved mammoth skull unearthed on Channel Islands puzzles scientists". Los Angeles Times. http://www.latimes.com/local/lanow/la-me-ln-mammoth-fossil-channel-islands-20160915-snap-story.html.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Mammoth genome sequence completed. BBC News, 23 April 2015.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 The Long Now Fouldation - Revive and Restore.
- ↑ Timmons, Jeanne (January 7, 2013). "Could Ancient Giants Be Cloned? Is It Possible, And Is It Wise?". Valley News. http://www.vnews.com/home/3694233-95/cloning-mammoth-mammoths-extinct.
- ↑ Reviving woolly mammoth will take more than 2 years. BBC News. Helen Pilcher, 22 February 2017.
- ↑ De-extinction and Conservation. Gregory E. Kaebnick, and Bruce Jennings. The Hastings Center Report. 26 July 2017
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 The Mammoth Genome Project. Pennsylvania State University. Accessed: October 2018.
- ↑ "Mammoth: Back from the Dead" . National Geographic Channel.
Further reading
| Wikisource has the text of the 1879 American Cyclopædia article Mammoth. |
- Bahn, Paul G.; Lister, Adrian (1994). Mammoths. New York: Macmillan USA. ISBN 978-0-02-572985-8. https://archive.org/details/mammoths00list.
- Capelli, C.; MacPhee, R. D. E.; Roca, A. L.; Brisighelli, F.; Georgiadis, N.; O'Brien, S. J.; Greenwood, A. D. (2006). "A nuclear DNA phylogeny of the woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 40 (2): 620–627. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.03.015. PMID 16631387.
- Conniff, R. (2010). "Mammoths and Mastodons: All American Monsters". Smithsonian Magazine. http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/Mammoths-and-Mastodons-All-American-Monsters.html. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
- "Mammoth genome cracked: key to cloning". COSMOS magazine. 2008. http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/news/2346/mammoth-genome-cracked-key-cloning.
- "National Park Service Findings 'Good News' For Waco Mammoth Site". Baylor University. 2007-03-27. http://www.baylor.edu/pr/news.php?action=story&story=44819.
- Hayes, J. (2006). "Back from the dead". COSMOS magazine. http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/node/903.
- Keddie, G.. "The Mammoth Story" (PDF). Royal BC Museum. http://www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca/Content_Files/Files/mammoth-1.pdf+.
- Levy, S. (2006). "Clashing with Titans". BioScience 56 (4): 292. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2006)56[292:CWT2.0.CO;2].
- Martin, Paul (2005). Twilight of the mammoths: ice age extinctions and the rewilding of America. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23141-2. https://archive.org/details/twilightofmammot00paul.
- Mercer, Henry Chapman (2010). The Lenape Stone: Or The Indian And The Mammoth (1885). Kessinger Publishing, LLC. ISBN 978-1161697537.
- Rodgers, J. (2006). "Mammoth skeleton found in Siberia". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/5008664.stm.
- Stone, Richard G. (2003). Mammoth: The Resurrection of an Ice Age Giant. Fourth Estate Ltd. ISBN 978-1-84115-518-0.
Wikidata ☰ Q36715 entry
 |

