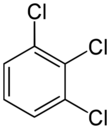
Chemistry:1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene | |||
| Other names
1,2,3-TCB
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 956882 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 847785 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H3Cl3 | |||
| Molar mass | 181.44 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white crystals | ||
| Density | 1.45 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 53.5 °C (128.3 °F; 326.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 218.5 °C (425.3 °F; 491.6 K) | ||
| Soluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H302, H410 | |||
| P273, P301, P312, P330 | |||
| Flash point | 112.7 °C (234.9 °F; 385.8 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound with the chemical formula C
6H
3Cl
3.[1][2] This is one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene; the two others are 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene and 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene.
Synthesis
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene can be prepared via dehydrohalogenation of hexachlorocyclohexane. Also, 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene is formed as a byproduct. Small amounts of 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene can also be produced while chlorinating benzene with iron(III) chloride as a catalyst.[3]
Physical properties
The compound forms white crystals with a faint aromatic odor. It is combustible[4] and poorly soluble in water.[5] The substance is irritating to eyes and the respiratory tract.
Uses
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene is used as a herbicide.[5][6] Also as a solvent for high-melting products, as a coolant in electrical installations and glass tempering.[7]
See also
- Chlorobenzenes—different numbers of chlorine substituents and isomeric forms.
References
- ↑ "1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene". Sigma Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/en/product/aldrich/t54402.
- ↑ "1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene". Thermo Fisher. https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/B22154.22.
- ↑ Beck, Uwe; Löser, Eckhard (15 October 2011). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" (in en). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. doi:10.1002/14356007.o06_o03. ISBN 978-3527306732. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14356007.o06_o03.
- ↑ "ICSC 1222 - 1,2,3-TRICHLOROBENZENE". International Labour Organization. https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_lang=en&p_card_id=1222&p_version=2.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank". gestis.dguv.de. https://gestis.dguv.de/data?name=015760.
- ↑ Montgomery, John H. (23 August 1991) (in en). Groundwater Chemicals Field Guide. CRC Press. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-87371-554-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=1vrekO_Rb74C&dq=1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene&pg=PA193. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ↑ (in en) National Study of Chemical Residues in Fish: Volume I.. DIANE Publishing. 1992. p. C-240. ISBN 978-1-4289-0620-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=pXFBw5UUTx0C&dq=1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene&pg=SL3-PA240. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
 |