Chemistry:Aluminon
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
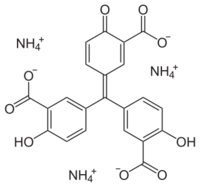
ammonium aurin-tricarboxylate; 5-[(3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)(3-carboxy-4-oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-ylidene)methyl]-2-hydroxybenzoic acid triammonium salt
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H23N3O9 | |
| Molar mass | 473.43 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow-brown crystals, red in aqueous solution |
| Solubility in other solvents | freely soluble in H2O |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aluminon, the triammonium salt of aurintricarboxylic acid, is a dye often used to detect the presence of the aluminium ion in an aqueous solution. Aluminon forms a red complex salt in combination with Al3+.[1]

In addition to its use in qualitative inorganic analysis, aluminon has applications in pigment production. It forms brilliantly colored lake pigments with many metals. The pigments are red in combination with Be2+ and Ga3+. The pigment is deep purple or reddish-brown in combination with Fe3+. Color of a particular pigment in acidic solutions may change: aluminon and Sc3+ form red pigments if the solution is acidic, but otherwise the solutions are colorless.[1]
Aluminon is prepared by reacting sodium nitrite with salicylic acid, adding formaldehyde, then treating with ammonia.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Clark, RA; Krueger, GL (1985). "Aluminon: its limited application as a reagent for the detection of aluminum species.". Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 33 (7): 729–732. doi:10.1177/33.7.3891845. ISSN 0022-1554. PMID 3891845.
- ↑ Merck Index, 13th Ed.
 |
