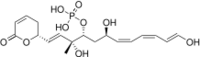
Chemistry:Fostriecin
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27O9P |
| Molar mass | 430.390 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fostriecin is a type I polyketide synthase (PKS) derived natural product, originally isolated from the soil bacterium Streptomyces pulveraceus.[1] It belongs to a class of natural products which characteristically contain a phosphate ester, an α,β-unsaturated lactam and a conjugated linear diene or triene chain produced by Streptomyces. This class includes structurally related compounds cytostatin and phoslactomycin.[2][3][4] Fostriecin is a known potent and selective inhibitor of protein serine/threonine phosphatases, as well as DNA topoisomerase II.[5][2][6][7] Due to its activity against protein phosphatases PP2A and PP4 (IC50 1.5nM and 3.0nM, respectively) which play a vital role in cell growth, cell division, and signal transduction, fostriecin was looked into for its antitumor activity in vivo and showed in vitro activity against leukemia, lung cancer, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer.[2][6][8][9] This activity is thought to be due to PP2A's assumed role in regulating apoptosis of cells by activating cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells involved in tumor surveillance, along with human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) transcription and replication.[10][11][12][13]
Biosynthesis
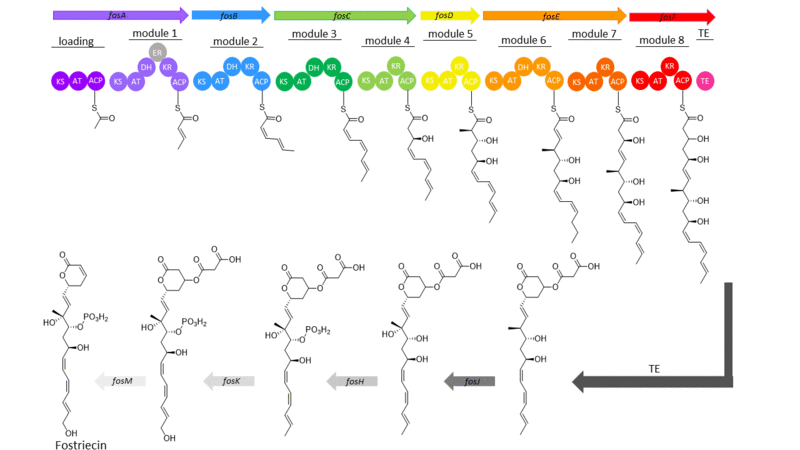
The gene cluster for fostriecin consists of 21 open reading frames (ORFs) that encode for six modular type I polyketide synthases and seven tailoring enzymes.[1] These enzymes within the fos gene have the nomenclature FosA-FosM, though not all are used in the biosynthesis of the target molecule. The six modular PKSs encoded in FosA-FosF give rise to a loading module, eight elongation modules, and a thioesterase domain.[1]
Conventional polyketide synthase pathway
The loading module starts out the biosynthetic pathway by tethering to an acyl group of the acyl carrier protein (ACP).This starter unit then gets carried to module 1 where a malonyl group gets added on by malonyl-CoA followed by the β-carbonyl getting reduced to a hydroxyl group by a ketoreductase (KR) enzyme that then undergoes dehydration to a trans double bond by a dehydratase enzyme (DH).[1] In this first module, there is an enoyl reductase enzyme (ER), but it is inactive.[1] This chain then goes through two more elongations in module 2 and module 3 which are similar to module 1, only they result in cis double bonds at their respective β-carbons.[1] The now 8-carbon chain then goes through another extension by malonyl-CoA in module 4, followed by a reduction by a KR domain.[1] In module 5, an elongation is performed by methylmalonyl-CoA in which the chain undergoes another reduction to a hydroxyl group. The polyketide intermediate is then passed on to module 6 where another malonyl-CoA is loaded, and here, a reduction, then dehydration of the β-carbon form the final double bond of the linear chain.[1] The growing chain is almost completely synthesized at this point and is taken through two elongations of 2 carbons in modules 7 and 8, each of which contain KRs to produce the final two hydroxyl groups in the alkyl chain.[1] The linear carbon chain is now fully synthesized and hydrolyzed off of ACP by a thioesterase domain (TE) to undergo post-synthetic tailoring steps.[1]
Post-synthetic tailoring
The post-synthetic tailoring enzymes for the production of fostriecin add on the four functionalities not originally included in the PKS pathway of the linear molecule.[1] These enzymes include two cytochrome P450 enzymes (FosJ and FosK), one homoserine kinase (FosH), and one NAD-dependent epimerase/dehydratase family protein (FosM).[1][14] The first step after the thioesterase domain, which forms a six-membered lactone ring, is the oxidation at C8 by FosJ, followed by a phosphorylation at C9 by FosH.[1] This is then followed by an oxidation at the terminal carbon by FosK, and finally, a loss of malonic acid by FosM yields the desired natural product.[14]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 "Elucidation of the biosynthetic gene cluster and the post-PKS modification mechanism for fostriecin in Streptomyces pulveraceus". Chemistry & Biology 20 (1): 45–54. January 2013. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.10.018. PMID 23352138.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Fostriecin: chemistry and biology". Current Medicinal Chemistry 9 (22): 2005–2032. November 2002. doi:10.2174/0929867023368809. PMID 12369868.
- ↑ "Cytostatin, a novel inhibitor of cell adhesion to components of extracellular matrix produced by Streptomyces sp. MJ654-NF4. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities". The Journal of Antibiotics 47 (5): 536–540. May 1994. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.47.536. PMID 8040050.
- ↑ "Novel antitumor agents CI-920, PD 113 270, and PD 113 271. 3. Structure determination". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 50 (4): 462–466. February 1985. doi:10.1021/jo00204a007.
- ↑ "Cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of fostriecin on human promyelocytic HL-60 and lymphocytic MOLT-4 leukemic cells". Cancer Research 52 (6): 1530–1535. March 1992. PMID 1540962.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Fostriecin, an antitumor antibiotic with inhibitory activity against serine/threonine protein phosphatases types 1 (PP1) and 2A (PP2A), is highly selective for PP2A". FEBS Letters 416 (3): 230–234. October 1997. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01210-6. PMID 9373158.
- ↑ "Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitor fostriecin". British Journal of Cancer 79 (5–6): 882–887. February 1999. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690141. PMID 10070885.
- ↑ "Enhancement and selective production of phoslactomycin B, a protein phosphatase IIa inhibitor, through identification and engineering of the corresponding biosynthetic gene cluster". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (37): 35552–35557. September 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305082200. PMID 12819191.
- ↑ "Total synthesis of fostriecin (CI-920)". Journal of the American Chemical Society 123 (18): 4161–4167. May 2001. doi:10.1021/ja010195q. PMID 11457179.
- ↑ "Protein phosphatase inhibitors calyculin A and fostriecin protect rabbit cardiomyocytes in late ischemia". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 30 (1): 61–73. January 1998. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1997.0572. PMID 9500865.
- ↑ "Fostriecin, an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A, limits myocardial infarct size even when administered after onset of ischemia". Circulation 98 (9): 899–905. September 1998. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.98.9.899. PMID 9738645.
- ↑ "Comparison of in vitro preconditioning responses of isolated pig and rabbit cardiomyocytes: effects of a protein phosphatase inhibitor, fostriecin". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 29 (11): 3009–3024. November 1997. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1997.0507. PMID 9405176.
- ↑ "Protein phosphatase 2A enhances activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by phorbol myristate acetate". Journal of Virology 77 (3): 2276–2281. February 2003. doi:10.1128/jvi.77.3.2276-2281.2003. PMID 12525665.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Identification of the post-polyketide synthase modification enzymes for fostriecin biosynthesis in Streptomyces pulveraceus". Journal of Natural Products 76 (4): 524–529. April 2013. doi:10.1021/np300667r. PMID 23586868.
 |
