Chemistry:Hafnium nitrate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Hafnium tetranitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
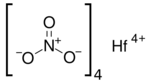
| Hf(NO3)4 | |
| Molar mass | 426.53 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| moderately soluble[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H272, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P220, P221, P305, P338, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Thorium nitrate, Zirconium nitrate, titanium nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Hafnium(IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of hafnium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Hf(NO3)4.[2][3][4]
Synthesis
Hafnium nitrate can be prepared by the reaction of hafnium tetrachloride and dinitrogen pentoxide.[5]
Properties
Hafnium nitrate is slightly volatile, and can be sublimed at 110 °C and 0.1 mmHg.[6] Hafnium nitrate decomposes on heating (≥ 160°C) to HfO(NO3)2 and then to HfO2.[6]
Applications
Hafnium nitrate can be used for the preparation of materials containing hafnium dioxide.[6]
References
- ↑ "Hafnium Nitrate (CAS: 15509-05-4) | Stanford Advanced Materials" (in en). samaterials.com. https://www.samaterials.com/hafnium-nitrate.html.
- ↑ "Hafnium(IV) nitrate". Sigma Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/en/product/aldrich/530778.
- ↑ "Hafnium Nitrate". American Elements. https://www.americanelements.com/hafnium-nitrate-15509-05-4.
- ↑ (in en) The Metallurgy of Hafnium. Naval Reactors, Division of Reactor Development, U.S. Atomic Energy Commission. 1960. p. 31. https://books.google.com/books?id=dqKgCIbq7hEC&dq=hafnium+nitrate&pg=PA31. Retrieved 29 October 2021.
- ↑ Zhuang, Weiwei; Conley, John F.; Ono, Yoshi; Evans, David R.; Solanki, R. (January 2002). "Hafnium Nitrate Precursor Synthesis and HfO2 Thin Film Deposition". Integrated Ferroelectrics 48 (1): 3–12. doi:10.1080/10584580215449. Bibcode: 2002InFer..48....3Z.
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 6.2 Conley, J. F.; Ono, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Tweet, D. J.; Gao, W.; Mohammed, S. K.; Solanki, R. (2002). "Atomic Layer Deposition of Hafnium Oxide Using Anhydrous Hafnium Nitrate" (in en). Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters 5 (5): C57. doi:10.1149/1.1462875. ISSN 1099-0062. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/1.1462875. Retrieved 29 October 2021.
Collapse
Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO3)−4 | C | NO−3, NH4NO3 |
O | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)3, Fe(NO3)2 |
Co(NO3)2, Co(NO3)3 |
Ni(NO3)2 | Cu(NO3)2 | Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y(NO3)3 | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd(NO3)2 | AgNO3 | Cd(NO3)2 | In | Sn | Sb(NO3)3 | Te | I | Xe(NO3)2 |
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg2(NO3)2, Hg(NO3)2 |
Tl(NO3)3, TlNO3 |
Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) |
Po | At | Rn | |
| FrNO3 | Ra(NO3)2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(NO3)3 | Ce(NO3)3, Ce(NO3)4 |
Pr | Nd(NO3)3 | Pm | Sm | Eu(NO3)3 | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb(NO3)3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac(NO3)3 | Th(NO3)4 | Pa | UO2(NO3)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

