Chemistry:Pindone
From HandWiki
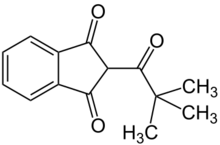
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl)-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione | |
| Other names
2-Pivaloyl-1,3-indandione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 230.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Bright-yellow powder[1] |
| Odor | almost none |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL |
| Melting point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| 0.002% (25°C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
280 mg/kg (rat, oral) 75 mg/kg (dog, oral) 150 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
100 mg/m3[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Pindone is an anticoagulant drug[3] for agricultural use. It is commonly used as a rodenticide in the management of rat and rabbit populations.
It is pharmacologically analogous to warfarin and inhibits the synthesis of Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0516". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0516.html.
- ↑ "Pindone". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/83261.html.
- ↑ "Effect of the anticoagulant, pindone, on the breeding performance and survival of merino sheep, Ovis aries". Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 140 (3): 465–73. March 2005. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.11.011. PMID 15694595.
 |
