Chemistry:Rubidium permanganate
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| RbMnO4 | |
| Molar mass | 204.404 |
| Appearance | purple crystals[1] |
| Density | 3.325 g·cm−3[2] |
| Melting point | 295 °C (decomposes)[2] |
| 10.6 g·l−1 (19 °C)[3] | |
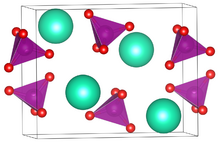
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Pnma (Nr. 62) | |
a = 954.11 pm, b = 573.926 pm, c = 763.63 pm
| |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
rubidium perchlorate rubidium periodate rubidium pertechnetate |
Other cations
|
lithium permanganate sodium permanganate potassium permanganate ammonium permanganate caesium permanganate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rubidium permanganate is the permanganate salt of rubidium, with the chemical formula RbMnO4.
Preparation
Rubidium permanganate can be formed by the reaction of potassium permanganate and rubidium chloride:[4][5]
- RbCl + KMnO
4 → KCl + RbMnO
4 ↓
Properties
Physical
Rubidium permanganate is soluble in water with a solubility of 6.03 g/L at 7 °C,[3] 10.6 g/L at 19 °C,[2] and 46.8 g/L at 60 °C.[6] Its crystal structure is orthorhombic,[1] the same as caesium permanganate, ammonium permanganate and potassium permanganate.
Chemical
Similar to potassium permanganate, the two-step decomposition of rubidium permanganate leads to the formation of rubidium manganate intermediates. It breaks down into manganese dioxide, rubidium oxide and oxygen.[4] The decomposition temperature is between 200 and 300 °C.[7] Drift-away oxygen caused an 8% mass loss in the product.[7]
- 10RbMnO
4 → 3Rb
2MnO
4 + 7MnO
2 + 2Rb
2O + 6O
2 ↑ - 2Rb
2MnO
4 → 2MnO
2 + 2Rb
2O + O
2 ↑
Total reaction:
- 4RbMnO
4 → 4MnO
2 + 2Rb
2O + 3O
2 ↑
Uses
In qualitative analysis, rubidium permanganate is used as a reagent to detect perchlorate ions. It is produced as an intermediate from rubidium nitrate and potassium permanganate and precipitates with existing perchlorate ions as RbClO4·RbMnO4 mixed crystal.[8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 R. Hoppe, D. Fischer, J. Schneider (1999), "Zur Kenntnis von Oxyden A[MO4]: Über LiMnO4, KMnO4, RbMnO4, CsMnO4 sowie RbIO4 und CsIO4. (– Was heißt eigentlich "Die Kristallstruktur von …"? –)", Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 625 (7): 1521–3749, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3749(199907)625:7<1135::AID-ZAAC1135>3.0.CO;2-L
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8, S. 336 ([1], p. 336, at Google Books).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Aterton Seidell (1940), [Volltext Solubilities of Organic Compounds], 1, pp. 1438, Volltext
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Michael W. Beck, Michael E. Brown (1983), "Thermal analysis of antimony/potassium permanganate pyrotechnic compositions", Thermochimica Acta 65 (2–3): 197–212, doi:10.1016/0040-6031(83)80022-7, http://eprints.ru.ac.za/252/3/PUBLICATIONS/TCA65.pdf
- ↑ P. J. Herley, E. G. Prout (1960), "The Thermal Decomposition of Rubidium Permanganate", The Journal of Physical Chemistry 64 (5): 675–677, doi:10.1021/j100834a503
- ↑ Austin M. Patterson (1906), "Solubilities of Permanganates of the Alkali Metals", Journal of the American Chemical Society 28 (12): 1734–1736, doi:10.1021/ja01978a009, https://zenodo.org/record/1428880
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Z. Gontarz, B. Pisarska (September 1990), "Thermal decomposition stages of potassium, rubidium and caesium permanganates", Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 36 (6): 2113–2117, doi:10.1007/BF01914135
- ↑ E. Gerdes (2001), [[2], p. 139, at Google Books Qualitative anorganische Analyse] (2 ed.), Springer, pp. 139, ISBN 978-3-540-67875-5, [3], p. 139, at Google Books
 |

