Chemistry:Rubidium carbonate
From HandWiki
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rubidium carbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
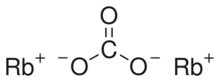
| Rb2CO3 | |
| Molar mass | 230.945 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder, very hygroscopic |
| Melting point | 837 °C (1,539 °F; 1,110 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 900 °C (1,650 °F; 1,170 K) (decomposes) |
| 4500 g/L @20°C[1] | |
| −75.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Lithium carbonate Sodium carbonate Potassium carbonate Caesium carbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rubidium carbonate, Rb2CO3, is a convenient[clarification needed] compound of rubidium; it is stable, not particularly reactive, and readily soluble in water, and is the form in which rubidium is usually sold.
Preparation
This salt can be prepared by adding ammonium carbonate to rubidium hydroxide.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; refs with no name must have content
Uses
It is used in some kinds of glass-making to enhance stability and durability and reduce conductivity. It is also used as a part of a catalyst to prepare short-chain alcohols from feed gas.[3]
References
- ↑ "Rubidium carbonate, 99%, Thermo Scientific Chemicals". 1970-01-01. https://www.fishersci.com/shop/products/rubidium-carbonate-99-thermo-scientific/AAA1224006.
- ↑ Patnaik, Pradyot (2002). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-049439-8.
- ↑ "Canada Patents". http://brevets-patents.ic.gc.ca/opic-cipo/cpd/eng/introduction.html.[not specific enough to verify]
| H2CO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li2CO3, LiHCO3 |
BeCO3 | B | C | (NH4)2CO3, NH4HCO3 |
O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na2CO3, NaHCO3, Na3H(CO3)2 |
MgCO3, Mg(HCO3)2 |
Al2(CO3)3 | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K2CO3, KHCO3 |
CaCO3, Ca(HCO3)2 |
Sc | Ti | V | Cr | MnCO3 | FeCO3 | CoCO3 | NiCO3 | CuCO3 | ZnCO3 | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb2CO3 | SrCO3 | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag2CO3 | CdCO3 | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs2CO3, CsHCO3 |
BaCO3 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl2CO3 | PbCO3 | (BiO)2CO3 | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La2(CO3)3 | Ce2(CO3)3 | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2CO3 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |
