Chemistry:Triphenylstibine
From HandWiki
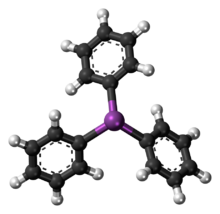
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Triphenylstibane | |
| Other names
Triphenylantimony
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H15Sb | |
| Molar mass | 353.07 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless solid |
| Density | 1.53 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 52 to 54 °C (126 to 129 °F; 325 to 327 K) |
| Boiling point | 377 °C (711 °F; 650 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| trigonal pyramidal | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Triphenylamine Triphenylphosphine Triphenylarsine Stibine |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | mildly toxic |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H302, H332, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+310, P301+312, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P330, P391, P405 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Triphenylstibine is the chemical compound with the formula Sb(C6H5)3. Abbreviated SbPh3, this colourless solid is often considered the prototypical organoantimony compound. It is used as a ligand in coordination chemistry[2] and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Like the related molecules triphenylamine, triphenylphosphine and triphenylarsine, SbPh3 is pyramidal with a propeller-like arrangement of the phenyl groups. The Sb-C distances average 2.14-2.17 Å and the C-Sb-C angle are 95°.[3]
SbPh3 was first reported in 1886, being prepared from antimony trichloride by the reaction:[4]
- 6 Na + 3 C6H5Cl + SbCl3 → (C6H5)3Sb + 6 NaCl
An alternative method treats phenylmagnesium bromide with SbCl3.[5]
References
- ↑ "Triphenylantimony" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/11777#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ C. A. McAuliffe, ed (1973). Transition Metal Complexes of Phosphorus, Arsenic, and Antimony Ligands. J. Wiley. ISBN 0-470-58117-4.
- ↑ Adams, E. A.; Kolis, J. W.; Pennington, W. T. "Structure of triphenylstibine" Acta Crystallographica 1990, volume C46, pp. 917-919. doi:10.1107/S0108270189012862
- ↑ Michaelis, A.; Reese, A. "Ueber die Verbindungen der Elemente der Stickstoffgruppe mit den Radicalen der aromatischen Reihe. Achte Abhandlung Ueber aromatische Antimonverbindungen" Liebigs Annallen der Chemie volume 233, pages 39-60 (1886). doi:10.1002/jlac.18862330104.
- ↑ Hiers, G. S. (1927). "Triphenylstibine". Organic Syntheses 7: 80. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0080.
 |


