Chemistry:Antimony(III) acetate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Antimony(III) acetate
| |
| Other names
Antimony triacetate
Acetic acid, antimony(3+) salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sb(CH3COO)3 | |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 1.22 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 128.5 °C (263.3 °F; 401.6 K) (decomposes to Sb2O3) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
4480 mg/kg (rat) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Antimony(III) acetate is the compound of antimony with the chemical formula of Sb(CH3CO2)3. It is a white powder, is moderately water-soluble, and is used as a catalyst in the production of polyesters.
Preparation
It can be prepared by the reaction of antimony(III) oxide with acetic anhydride:
- Sb2O3 + 3 C4H6O3 → 2 Sb(CH3CO2)3
Structure
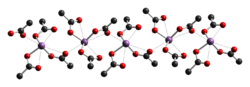
The crystal structure of antimony(III) acetate has been determined by X-ray crystallography. It consists of discrete Sb(OAc)3 monomers with monodentate acetate ligands. The monomers are linked together into chains by weaker C=O···Sb intermolecular interactions.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0036". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0036.html.
- ↑ Hall, M.; Sowerby, D. B. (1980). "Antimony(III) acetate and thioacetate: spectra and crystal structures". J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. (8): 1292–1296. doi:10.1039/DT9800001292.
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH |
B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc |
NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 |
Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 |
Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 |
Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 |
Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 |
Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 |
Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 |
Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 |
TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 |
Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 |
Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
 |

