Fourier optics
Fourier optics is the study of classical optics using Fourier transforms (FTs), in which the waveform being considered is regarded as made up of a combination, or superposition, of plane waves. It has some parallels to the Huygens–Fresnel principle, in which the wavefront is regarded as being made up of a combination of spherical wavefronts (also called phasefronts) whose sum is the wavefront being studied. A key difference is that Fourier optics considers the plane waves to be natural modes of the propagation medium, as opposed to Huygens–Fresnel, where the spherical waves originate in the physical medium.
A curved phasefront may be synthesized from an infinite number of these "natural modes" i.e., from plane wave phasefronts oriented in different directions in space. Far from its sources, an expanding spherical wave is locally tangent to a planar phase front (a single plane wave out of the infinite spectrum), which is transverse to the radial direction of propagation. In this case, a Fraunhofer diffraction pattern is created, which emanates from a single spherical wave phase center. In the near field, no single well-defined spherical wave phase center exists, so the wavefront isn't locally tangent to a spherical ball. In this case, a Fresnel diffraction pattern would be created, which emanates from an extended source, consisting of a distribution of (physically identifiable) spherical wave sources in space. In the near field, a full spectrum of plane waves is necessary to represent the Fresnel near-field wave, even locally. A "wide" wave moving forward (like an expanding ocean wave coming toward the shore) can be regarded as an infinite number of "plane wave modes", all of which could (when they collide with something such as a rock in the way) scatter independently of one other. These mathematical simplifications and calculations are the realm of Fourier analysis and synthesis – together, they can describe what happens when light passes through various slits, lenses or mirrors that are curved one way or the other, or is fully or partially reflected.
Fourier optics forms much of the theory behind image processing techniques, as well as applications where information needs to be extracted from optical sources such as in quantum optics. To put it in a slightly complex way, similar to the concept of frequency and time used in traditional Fourier transform theory, Fourier optics makes use of the spatial frequency domain (kx, ky) as the conjugate of the spatial (x, y) domain. Terms and concepts such as transform theory, spectrum, bandwidth, window functions and sampling from one-dimensional signal processing are commonly used.
Fourier optics plays an important role for high-precision optical applications such as photolithography in which a pattern on a reticle to be imaged on wafers for semiconductor chip production is so dense such that light (e.g., DUV or EUV) emanated from the reticle is diffracted and each diffracted light may correspond to a different spatial frequency (kx, ky). Due to generally non-uniform patterns on reticles, a simple diffraction grating analysis may not provide the details of how light is diffracted from each reticle.
Propagation of light in homogeneous, source-free media
Light can be described as a waveform propagating through a free space (vacuum) or a material medium (such as air or glass). Mathematically, a real-valued component of a vector field describing a wave is represented by a scalar wave function u that depends on both space and time: where represents a position in a three dimensional space (in the Cartesian coordinate system here), and t represents time.
The wave equation
Fourier optics begins with the homogeneous, scalar wave equation (valid in source-free regions): where is the speed of light and u(r,t) is a real-valued Cartesian component of an electromagnetic wave propagating through a free space (e.g., u(r, t) = Ei(r, t) for i = x, y, or z where Ei is the i-axis component of an electric field E in the Cartesian coordinate system).
Sinusoidal steady state
If light of a fixed frequency in time/wavelength/color (as from a single-mode laser) is assumed, then, based on the engineering time convention, which assumes an time dependence in wave solutions at the angular frequency with where is a time period of the waves, the time-harmonic form of the optical field is given as where is the imaginary unit, is the operator taking the real part of , is the angular frequency (in radians per unit time) of light waves, and is, in general, a complex quantity, with separate amplitude in non-negative real number and phase .
The Helmholtz equation
Substituting this expression into the scalar wave equation above yields the time-independent form of the wave equation, where with the wavelength in vacuum, is the wave number (also called propagation constant), is the spatial part of a complex-valued Cartesian component of an electromagnetic wave. Note that the propagation constant and the angular frequency are linearly related to one another, a typical characteristic of transverse electromagnetic (TEM) waves in homogeneous media.
Since the originally desired real-valued solution of the scalar wave equation can be simply obtained by taking the real part of , solving the following equation, known as the Helmholtz equation, is mostly concerned as treating a complex-valued function is often much easier than treating the corresponding real-valued function.
Solving the Helmholtz equation
Solutions to the Helmholtz equation in the Cartesian coordinate system may readily be found via the principle of separation of variables for partial differential equations. This principle says that in separable orthogonal coordinates, an elementary product solution to this wave equation may be constructed of the following form: i.e., as the product of a function of x, times a function of y, times a function of z. If this elementary product solution is substituted into the wave equation, using the scalar Laplacian in the Cartesian coordinates system then the following equation for the 3 individual functions is obtained which is readily rearranged into the form:
It may now be argued that each quotient in the equation above must, of necessity, be constant. To justify this, let's say that the first quotient is not a constant, and is a function of x. Since none of the other terms in the equation has any dependence on the variable x, so the first term also must not have any x-dependence; it must be a constant. (If the first term is a function of x, then there is no way to make the left hand side of this equation be zero.) This constant is denoted as -kx2. Reasoning in a similar way for the y and z quotients, three ordinary differential equations are obtained for the fx, fy and fz, along with one separation condition:
Each of these 3 differential equations has the same solution form: sines, cosines or complex exponentials. We'll go with the complex exponential as to be a complex function. As a result, the elementary product solution is with a generally complex number . This solution is the spatial part of a complex-valued Cartesian component (e.g., , , or as the electric field component along each axis in the Cartesian coordinate system) of a propagating plane wave. (, , or ) is a real number here since waves in a source-free medium has been assumed so each plane wave is not decayed or amplified as it propagates in the medium. The negative sign of (, , or ) in a wave vector (where ) means that the wave propagation direction vector has a positive (, , or )-component, while the positive sign of means a negative (, , or )-component of that vector.
Product solutions to the Helmholtz equation are also readily obtained in cylindrical and spherical coordinates, yielding cylindrical and spherical harmonics (with the remaining separable coordinate systems being used much less frequently).
The complete solution: the superposition integral
A general solution to the homogeneous electromagnetic wave equation at a fixed time frequency in the Cartesian coordinate system may be formed as a weighted superposition of all possible elementary plane wave solutions as
|
|
() |
with the constraints of , each as a real number, and where . In this superposition, is the weight factor or the amplitude of the plane wave component with the wave vector where is determined in terms of and by the mentioned constraint.
Next, let Then:
The plane wave spectrum representation of a general electromagnetic field (e.g., a spherical wave) in the equation (2.1) is the basic foundation of Fourier optics (this point cannot be emphasized strongly enough), because at z = 0, the equation simply becomes a Fourier transform (FT) relationship between the field and its plane wave contents (hence the name, Fourier optics).
Thus: and
All spatial dependence of each plane wave component is described explicitly by an exponential function. The coefficient of the exponential is a function of only two components of the wave vector for each plane wave (since other remained component can be determined via the above mentioned constraints), for example and , just as in ordinary Fourier analysis and Fourier transforms.
Connection between Fourier optics and imaging resolution
Let's consider an imaging system where the z-axis is the optical axis of the system and the object plane (to be imaged on the image plane of the system) is the plane at . On the object plane, the spatial part of a complex-valued Cartesian component of a wave is, as shown above, with the constraints of , each as a real number, and where . The imaging is the reconstruction of a wave on the object plane (having information about a pattern on the object plane to be imaged) on the image plane via the proper wave propagation from the object to the image planes, (E.g., think about the imaging of an image in an aerial space.) and the wave on the object plane, that fully follows the pattern to be imaged, is in principle, described by the unconstrained inverse Fourier transform where takes an infinite range of real numbers. It means that, for a given light frequency, only a part of the full feature of the pattern can be imaged because of the above-mentioned constraints on ; (1) a fine feature which representation in the inverse Fourier transform requires spatial frequencies , where are transverse wave numbers satisfying , can not be fully imaged since waves with such do not exist for the given light of (This phenomenon is known as the diffraction limit.), and (2) spatial frequencies with but close to so higher wave outgoing angles with respect to the optical axis, requires a high NA (Numerical Aperture) imaging system that is expensive and difficult to build. For (1), even if complex-valued longitudinal wavenumbers are allowed (by an unknown interaction between light and the object plane pattern that is usually a solid material), give rise to light decay along the axis (Light amplification along the axis does not physically make sense if there is no amplification material between the object and image planes, and this is an usual case.) so waves with such may not reach the image plane that is usually sufficiently far way from the object plane.
In connection with photolithography of electronic components, these (1) and (2) are the reasons why light of a higher frequency (smaller wavelength, thus larger magnitude of ) or a higher NA imaging system is required to image finer features of integrated circuits on a photoresist on a wafer. As a result, machines realizing such an optical lithography have become more and more complex and expensive, significantly increasing the cost of the electronic component production.
The paraxial approximation
Paraxial wave propagation (optic axis assumed as z axis)
A solution to the Helmholtz equation as the spatial part of a complex-valued Cartesian component of a single frequency wave is assumed to take the form: where is the wave vector, and and is the wave number. Next, use the paraxial approximation, that is a small-angle approximation such that so, up to the second order approximation of trigonometric functions (that is, taking only up to the second term in the Taylor series expansion of each trigonometric function),
where is the angle (in radian) between the wave vector k and the z-axis as the optical axis of an optical system under discussion.
As a result, and
The paraxial wave equation
Substituting this expression into the Helmholtz equation, the paraxial wave equation is derived: where is the transverse Laplace operator in the Cartesian coordinates system. In the derivation of the paraxial wave equation, the following approximations are used.
- is small () so a term with is ignored.
- Terms with and are much smaller than a term with (or ) so these two terms are ignored.
- so a term with is ignored. It is the slowly varying envelope approximation, means that the amplitude or envelope of a wave is slowly varying compared with the major period of the wave .
The far field approximation
The equation (2.1) above may be evaluated asymptotically in the far field (using the stationary phase method) to show that the field at a distant point is indeed due solely to the plane wave component with the wave vector which propagates parallel to the vector , and whose plane is tangent to the phasefront at . The mathematical details of this process may be found in Scott [1998] or Scott [1990]. The result of performing a stationary phase integration on the expression above is the following expression,[1]
|
|
() |
which clearly indicates that the field at is directly proportional to the spectral component in the direction of , where,
and
Stated another way, the radiation pattern of any planar field distribution is the FT (Fourier Transform) of that source distribution (see Huygens–Fresnel principle, wherein the same equation is developed using a Green's function approach). Note that this is NOT a plane wave. The radial dependence is a spherical wave - both in magnitude and phase - whose local amplitude is the FT of the source plane distribution at that far field angle. A plane wave spectrum does not necessarily mean that the field as the superposition of the plane wave components in that spectrum behaves something like a plane wave at far distances.
Spatial versus angular bandwidth
The equation (2.2) above is critical to making the connection between spatial bandwidth (on the one hand) and angular bandwidth (on the other), in the far field. Note that the term "far field" usually means we're talking about a converging or diverging spherical wave with a pretty well defined phase center. The connection between spatial and angular bandwidth in the far field is essential in understanding the low pass filtering property of thin lenses. See the section 6.1.3 for the condition defining the far field region.
Once the concept of angular bandwidth is understood, the optical scientist can "jump back and forth" between the spatial and spectral domains to quickly gain insights which would ordinarily not be so readily available just through spatial domain or ray optics considerations alone. For example, any source bandwidth which lies past the edge angle to the first lens (This edge angle sets the bandwidth of the optical system.) will not be captured by the system to be processed.
As a side note, electromagnetics scientists have devised an alternative means to calculate an electric field in a far zone which does not involve stationary phase integration. They have devised a concept known as "fictitious magnetic currents" usually denoted by M, and defined as In this equation, it is assumed that the unit vector in the z-direction points into the half-space where the far field calculations will be made. These equivalent magnetic currents are obtained using equivalence principles which, in the case of an infinite planar interface, allow any electric currents J to be "imaged away" while the fictitious magnetic currents are obtained from twice the aperture electric field (see Scott [1998]). Then the radiated electric field is calculated from the magnetic currents using an equation similar to the equation for the magnetic field radiated by an electric current. In this way, a vector equation is obtained for the radiated electric field in terms of the aperture electric field, and the derivation requires no use of stationary phase ideas.
The plane wave spectrum: the foundation of Fourier optics
Fourier optics is somewhat different from ordinary ray optics typically used in the analysis and design of focused imaging systems such as cameras, telescopes and microscopes. Ray optics is the very first type of optics that most of us encounter in our lives; it's simple to conceptualize and understand, and works very well in gaining a baseline understanding of common optical devices. Unfortunately, ray optics does not explain the operation of Fourier optical systems, which are in general not focused systems. Ray optics is a subset of wave optics (In the jargon, it is "the asymptotic zero-wavelength limit" of wave optics.) and therefore has limited applicability. We have to know when it is valid and when it is not - and this is one of those times when it is not. For our current task, we must expand our understanding of optical phenomena to encompass wave optics, in which the optical field is seen as a solution to Maxwell's equations. This more general wave optics accurately explains the operation of Fourier optics devices.
In this section, we won't go all the way back to Maxwell's equations, but will start instead with the homogeneous Helmholtz equation (valid in source-free media), which is one level of refinement up from Maxwell's equations (Scott [1998]). From this equation, we'll show how infinite uniform plane waves comprise one field solution (out of many possible) in free space. These uniform plane waves form the basis for understanding Fourier optics.
The plane wave spectrum concept is the basic foundation of Fourier Optics. The plane wave spectrum is a continuous spectrum of uniform plane waves, and there is one plane wave component in the spectrum for every tangent point on the far-field phase front. The amplitude of that plane wave component would be the amplitude of the optical field at that tangent point. Again, this is true only in the far field, roughly defined as the range beyond where is the maximum linear extent of the optical sources and is the wavelength (Scott [1998]). The plane wave spectrum is often regarded as being discrete for certain types of periodic gratings, though in reality, the spectra from gratings are continuous as well, since no physical device can have the infinite extent required to produce a true line spectrum.
Likely to electrical signals, bandwidth in optics is a measure of how finely detailed an image is; the finer the detail, the greater the bandwidth required to represent it. A DC (Direct Current) electrical signal is constant and has no oscillations; a plane wave propagating parallel to the optic () axis has constant value in any x-y plane, and therefore is analogous to the (constant) DC component of an electrical signal. Bandwidth in electrical signals relates to the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies present in the spectrum of a signal, practically with a criterion to cut off high and low frequency edges of the spectrum to represent bandwidth in a number. For optical systems, bandwidth also relates to spatial frequency content (spatial bandwidth), but it also has a secondary meaning. It also measures how far from the optic axis the corresponding plane waves are tilted, and so this type of bandwidth is often referred to also as angular bandwidth. It takes more frequency bandwidth to produce a short pulse in an electrical circuit, and more angular (or, spatial frequency) bandwidth to produce a sharp spot in an optical system (see discussion related to Point spread function).
The plane wave spectrum arises naturally as the eigenfunction or "natural mode" solution to the homogeneous electromagnetic wave equation in rectangular coordinates (see also Electromagnetic radiation, which derives the wave equation from Maxwell's equations in source-free media, or Scott [1998]). In the frequency domain, with an assumed time convention of , the homogeneous electromagnetic wave equation becomes what is known as the Helmholtz equation and takes the form
|
|
() |
where and is the wavenumber of the medium.
Eigenfunction (natural mode) solutions: background and overview
In the case of differential equations, as in the case of matrix equations, whenever the right-hand side of an equation is zero (For example, a forcing function, forcing vector, or the source of a force is zero.), the equation may still admit a non-trivial solution, known in applied mathematics as an eigenfunction solution, in physics as a "natural mode" solution, and in electrical circuit theory as the "zero-input response." This is a concept that spans a wide range of physical disciplines. Common physical examples of resonant natural modes would include the resonant vibrational modes of stringed instruments (1D), percussion instruments (2D) or the former Tacoma Narrows Bridge (3D). Examples of propagating natural modes would include waveguide modes, optical fiber modes, solitons and Bloch waves. an Infinite homogeneous media admits the rectangular, circular and spherical harmonic solutions to the Helmholtz equation, depending on the coordinate system under consideration. The propagating plane waves that we'll study in this article are perhaps the simplest type of propagating waves found in any type of media.
There is a striking similarity between the Helmholtz equation (2.3) above, which may be written and the usual equation form for the eigenvalues / eigenvectors of a square matrix A,
particularly since both the scalar Laplacian and the matrix A are linear operators on their respective functions / vector spaces. (The minus sign in this matrix equation is, for all intents and purposes, immaterial. However, the plus sign in the Helmholtz equation is significant.) It is perhaps worthwhile to note that the eigenfunction solutions / eigenvector solutions to the Helmholtz equation / the matrix equation, often yield an orthogonal set of the eigenfunctions / the eigenvectors which span (i.e., form a basis set for) the function space / vector space under consideration. The interested reader may investigate other functional linear operators (so for different equations than the Helmholtz equation) which give rise to different kinds of orthogonal eigenfunctions such as Legendre polynomials, Chebyshev polynomials and Hermite polynomials.
In the matrix equation case in which A is a square matrix, eigenvalues may be found by setting the determinant of the matrix equal to zero, i.e. finding where the matrix has no inverse. (Such a square matrix is said to be singular.) Finite matrices have only a finite number of eigenvalues/eigenvectors, whereas linear operators can have a countably infinite number of eigenvalues/eigenfunctions (in confined regions) or uncountably infinite (continuous) spectra of solutions, as in unbounded regions.
In certain physics applications such as in the computation of bands in a periodic volume, it is often a case that the elements of a matrix will be very complicated functions of frequency and wavenumber, and the matrix will be non-singular (I.e., it has the inverse matrix.) for most combinations of frequency and wavenumber, but will also be singular (I.e., it does not have the inverse matrix.) for certain specific combinations. By finding which combinations of frequency and wavenumber drive the determinant of the matrix to zero, the propagation characteristics of the medium may be determined. Relations of this type, between frequency and wavenumber, are known as dispersion relations and some physical systems may admit many different kinds of dispersion relations. An example from electromagnetics is an ordinary waveguide, which may admit numerous dispersion relations, each associated with a unique propagation mode of the waveguide. Each propagation mode of the waveguide is known as an eigenfunction solution (or eigenmode solution) to Maxwell's equations in the waveguide. Free space also admits eigenmode (natural mode) solutions (known more commonly as plane waves), but with the distinction that for any given frequency, free space admits a continuous modal spectrum, whereas waveguides have a discrete mode spectrum. In this case, the dispersion relation is linear, as in section 1.3.
K-space
For a given such as for a homogeneous vacuum space, the separation condition, which is identical to the equation for the Euclidean metric in a three-dimensional configuration space, suggests the notion of a k-vector in a three-dimensional "k-space", defined (for propagating plane waves) in rectangular coordinates as: and in the spherical coordinate system as
Use will be made of these spherical coordinate system relations in the next section.
The notion of k-space is central to many disciplines in engineering and physics, especially in the study of periodic volumes, such as in crystallography and the band theory of semiconductor materials.
The two-dimensional Fourier transform
A spectrum analysis equation (calculating the spectrum of a function ):
A synthesis equation (reconstructing the function from its spectrum):
The normalizing factor of is present whenever angular frequency (radians) is used, but not when ordinary frequency (cycles) is used.
Optical systems: general overview and analogy with electrical signal processing systems
In a high level overview, an optical system consists of three parts; an input plane, and output plane, and a set of components between these planes that transform an image f formed in the input plane into a different image g formed in the output plane. The optical system output image g is related to the input image f by convolving the input image with the optical impulse response function of the optical system, h (known as the point-spread function, for focused optical systems). The impulse response function uniquely defines the input-output behavior of the optical system. By convention, the optical axis of the system is taken as the z-axis. As a result, the two images and the impulse response function are all functions of the transverse coordinates, x and y.
The impulse response of an optical imaging system is the output plane field which is produced when an ideal mathematical optical field point source of light, that is an impulse input to the system, is placed in the input plane (usually on-axis, i.e., on the optical axis). In practice, it is not necessary to have an ideal point source in order to determine an exact impulse response. This is because any source bandwidth which lies outside the bandwidth of the optical system under consideration won't matter anyway (since it cannot even be captured by the optical system), so therefore it's not necessary in determining the impulse response. The source only needs to have at least as much (angular) bandwidth as the optical system.
Optical systems typically fall into one of two different categories. The first is ordinary focused optical imaging systems (e.g., cameras), wherein the input plane is called the object plane and the output plane is called the image plane. An optical field in the image plane (the output plane of the imaging system) is desired to be a high-quality reproduction of an optical field in the object plane (the input plane of the imaging system). The impulse response function of an optical imaging system is desired to approximate a 2D delta function, at the location (or a linearly scaled location) in the output plane corresponding to the location of the impulse (an ideal point source) in the input plane. The actual impulse response function of an imaging system typically resembles an Airy function, whose radius is on the order of the wavelength of the light used. The impulse response function in this case is typically referred to as a point spread function, since the mathematical point of light in the object plane has been spread out into an Airy function in the image plane.
The second type is optical image processing systems, in which a significant feature in the input plane optical field is to be located and isolated. In this case, the impulse response of such a system is desired to be a close replica (picture) of that feature which is being searched for in the input plane field, so that a convolution of the impulse response (an image of the desired feature) against the input plane field will produce a bright spot at the feature location in the output plane. It is this latter type of optical image processing system that is the subject of this section. The section 6.2 presents one hardware implementation of the optical image processing operations described in this section.
Input plane
The input plane is defined as the locus of all points such that z = 0. The input image f is therefore
Output plane
The output plane is defined as the locus of all points such that z = d. The output image g is therefore
The 2D convolution of input function against the impulse response function
i.e.,
|
|
() |
The alert reader will note that the integral above tacitly assumes that the impulse response is NOT a function of the position (x',y') of the impulse of light in the input plane (if this were not the case, this type of convolution would not be possible). This property is known as shift invariance (Scott [1998]). No optical system is perfectly shift invariant: as the ideal, mathematical point of light is scanned away from the optic axis, aberrations will eventually degrade the impulse response (known as a coma in focused imaging systems). However, high quality optical systems are often "shift invariant enough" over certain regions of the input plane that we may regard the impulse response as being a function of only the difference between input and output plane coordinates, and thereby use the equation above with impunity.
Also, this equation assumes unit magnification. If magnification is present, then eqn. (4.1) becomes
|
|
() |
which basically translates the impulse response function, hM(), from x′ to x = Mx′. In eqn. (4.2), hM will be a magnified version of the impulse response function h of a similar, unmagnified system, so that hM(x,y) = h(x/M,y/M).
Derivation of the convolution equation
The extension to two dimensions is trivial, except for the difference that causality exists in the time domain, but not in the spatial domain. Causality means that the impulse response h(t − t′) of an electrical system, due to an impulse applied at time t', must of necessity be zero for all times t such that t − t′ < 0.
Obtaining the convolution representation of the system response requires representing the input signal as a weighted superposition over a train of impulse functions by using the sifting property of Dirac delta functions.
It is then presumed that the system under consideration is linear, that is to say that the output of the system due to two different inputs (possibly at two different times) is the sum of the individual outputs of the system to the two inputs, when introduced individually. Thus the optical system may contain no nonlinear materials nor active devices (except possibly, extremely linear active devices). The output of the system, for a single delta function input is defined as the impulse response of the system, h(t − t′). And, by our linearity assumption (i.e., that the output of system to a pulse train input is the sum of the outputs due to each individual pulse), we can now say that the general input function f(t) produces the output: where h(t − t′) is the (impulse) response of the linear system to the delta function input δ(t − t′), applied at time t'. This is where the convolution equation above comes from. The convolution equation is useful because it is often much easier to find the response of a system to a delta function input - and then perform the convolution above to find the response to an arbitrary input - than it is to try to find the response to the arbitrary input directly. Also, the impulse response (in either time or frequency domains) usually yields insight to relevant figures of merit of the system. In the case of most lenses, the point spread function (PSF) is a pretty common figure of merit for evaluation purposes.
The same logic is used in connection with the Huygens–Fresnel principle, or Stratton-Chu formulation, wherein the "impulse response" is referred to as the Green's function of the system. So the spatial domain operation of a linear optical system is analogous in this way to the Huygens–Fresnel principle.
System transfer function
If the last equation above is Fourier transformed, it becomes: where
- is the spectrum of the output signal
- is the system transfer function
- is the spectrum of the input signal
In like fashion, eqn. (4.1) may be Fourier transformed to yield:
The system transfer function, . In optical imaging this function is better known as the optical transfer function (Goodman).
Once again it may be noted from the discussion on the Abbe sine condition, that this equation assumes unit magnification.
This equation takes on its real meaning when the Fourier transform, is associated with the coefficient of the plane wave whose transverse wavenumbers are . Thus, the input-plane plane wave spectrum is transformed into the output-plane plane wave spectrum through the multiplicative action of the system transfer function. It is at this stage of understanding that the previous background on the plane wave spectrum becomes invaluable to the conceptualization of Fourier optical systems.
Applications of Fourier optics principles
Fourier optics is used in the field of optical information processing, the staple of which is the classical 4F processor.
The Fourier transform properties of a lens provide numerous applications in optical signal processing such as spatial filtering, optical correlation and computer generated holograms.
Fourier optical theory is used in interferometry, optical tweezers, atom traps, and quantum computing. Concepts of Fourier optics are used to reconstruct the phase of light intensity in the spatial frequency plane (see adaptive-additive algorithm).
Fourier transforming property of lenses
If a transmissive object is placed at one focal length in front of a lens, then its Fourier transform will be formed at one focal length behind the lens. Consider the figure to the right (click to enlarge)
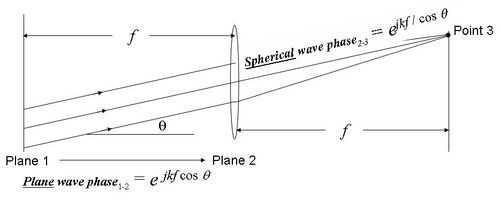
In this figure, a plane wave incident from the left is assumed. The transmittance function in the front focal plane (i.e., Plane 1) spatially modulates the incident plane wave in magnitude and phase, like on the left-hand side of eqn. (2.1) (specified to z = 0), and in so doing, produces a spectrum of plane waves corresponding to the FT of the transmittance function, like on the right-hand side of eqn. (2.1) (for z > 0). The various plane wave components propagate at different tilt angles with respect to the optic axis of the lens (i.e., the horizontal axis). The finer the features in the transparency, the broader the angular bandwidth of the plane wave spectrum. We'll consider one such plane wave component, propagating at angle θ with respect to the optic axis. It is assumed that θ is small (paraxial approximation), so that and and
In the figure, the plane wave phase, moving horizontally from the front focal plane to the lens plane, is and the spherical wave phase from the lens to the spot in the back focal plane is: and the sum of the two path lengths is f (1 + θ2/2 + 1 − θ2/2) = 2f; i.e., it is a constant value, independent of tilt angle, θ, for paraxial plane waves. Each paraxial plane wave component of the field in the front focal plane appears as a point spread function spot in the back focal plane, with an intensity and phase equal to the intensity and phase of the original plane wave component in the front focal plane. In other words, the field in the back focal plane is the Fourier transform of the field in the front focal plane.
All FT components are computed simultaneously - in parallel - at the speed of light. As an example, light travels at a speed of roughly 1 ft (0.30 m) per nanosecond, so if a lens has a 1 ft (0.30 m) focal length, an entire 2D FT can be computed in about 2 ns (2 × 10−9 seconds). If the focal length is 1 in, then the time is under 200 ps. No electronic computer can compete with these kinds of numbers or perhaps ever hope to, although supercomputers may actually prove faster than optics, as improbable as that may seem. However, their speed is obtained by combining numerous computers which, individually, are still slower than optics. The disadvantage of the optical FT is that, as the derivation shows, the FT relationship only holds for paraxial plane waves, so this FT "computer" is inherently bandlimited. On the other hand, since the wavelength of visible light is so minute in relation to even the smallest visible feature dimensions in the image i.e., (for all kx, ky within the spatial bandwidth of the image, so that kz is nearly equal to k), the paraxial approximation is not terribly limiting in practice. And, of course, this is an analog - not a digital - computer, so precision is limited. Also, phase can be challenging to extract; often it is inferred interferometrically.
Optical processing is especially useful in real time applications where rapid processing of massive amounts of 2D data is required, particularly in relation to pattern recognition.
Object truncation and Gibbs phenomenon
The spatially modulated electric field, shown on the left-hand side of eqn. (2.1), typically only occupies a finite (usually rectangular) aperture in the x,y plane. The rectangular aperture function acts like a 2D square-top filter, where the field is assumed to be zero outside this 2D rectangle. The spatial domain integrals for calculating the FT coefficients on the right-hand side of eqn. (2.1) are truncated at the boundary of this aperture. This step truncation can introduce inaccuracies in both theoretical calculations and measured values of the plane wave coefficients on the RHS of eqn. (2.1).
Whenever a function is discontinuously truncated in one FT domain, broadening and rippling are introduced in the other FT domain. A perfect example from optics is in connection with the point spread function, which for on-axis plane wave illumination of a quadratic lens (with circular aperture), is an Airy function, J1(x)/x. Literally, the point source has been "spread out" (with ripples added), to form the Airy point spread function (as the result of truncation of the plane wave spectrum by the finite aperture of the lens). This source of error is known as Gibbs phenomenon and it may be mitigated by simply ensuring that all significant content lies near the center of the transparency, or through the use of window functions which smoothly taper the field to zero at the frame boundaries. By the convolution theorem, the FT of an arbitrary transparency function - multiplied (or truncated) by an aperture function - is equal to the FT of the non-truncated transparency function convolved against the FT of the aperture function, which in this case becomes a type of "Greens function" or "impulse response function" in the spectral domain. Therefore, the image of a circular lens is equal to the object plane function convolved against the Airy function (the FT of a circular aperture function is J1(x)/x and the FT of a rectangular aperture function is a product of sinc functions, sinx/x).
Fourier analysis and functional decomposition
Even though the input transparency only occupies a finite portion of the x-y plane (Plane 1), the uniform plane waves comprising the plane wave spectrum occupy the entire x-y plane, which is why (for this purpose) only the longitudinal plane wave phase (in the z-direction, from Plane 1 to Plane 2) must be considered, and not the phase transverse to the z-direction. It is of course, very tempting to think that if a plane wave emanating from the finite aperture of the transparency is tilted too far from horizontal, it will somehow "miss" the lens altogether but again, since the uniform plane wave extends infinitely far in all directions in the transverse (x-y) plane, the planar wave components cannot miss the lens.
This issue brings up perhaps the predominant difficulty with Fourier analysis, namely that the input-plane function, defined over a finite support (i.e., over its own finite aperture), is being approximated with other functions (sinusoids) which have infinite support (i.e., they are defined over the entire infinite x-y plane). This is unbelievably inefficient computationally, and is the principal reason why wavelets were conceived, that is to represent a function (defined on a finite interval or area) in terms of oscillatory functions which are also defined over finite intervals or areas. Thus, instead of getting the frequency content of the entire image all at once (along with the frequency content of the entire rest of the x-y plane, over which the image has zero value), the result is instead the frequency content of different parts of the image, which is usually much simpler. Unfortunately, wavelets in the x-y plane don't correspond to any known type of propagating wave function, in the same way that Fourier's sinusoids (in the x-y plane) correspond to plane wave functions in three dimensions. However, the FTs of most wavelets are well known and could possibly be shown to be equivalent to some useful type of propagating field.
On the other hand, sinc functions and Airy functions - which are not only the point spread functions of rectangular and circular apertures, respectively, but are also cardinal functions commonly used for functional decomposition in interpolation/sampling theory [Scott 1990] - do correspond to converging or diverging spherical waves, and therefore could potentially be implemented as a whole new functional decomposition of the object plane function, thereby leading to another point of view similar in nature to Fourier optics. This would basically be the same as conventional ray optics, but with diffraction effects included. In this case, each point spread function would be a type of "smooth pixel," in much the same way that a soliton on a fiber is a "smooth pulse."
Perhaps a lens figure-of-merit in this "point spread function" viewpoint would be to ask how well a lens transforms an Airy function in the object plane into an Airy function in the image plane, as a function of radial distance from the optic axis, or as a function of the size of the object plane Airy function. This is somewhat like the point spread function, except now we're really looking at it as a kind of input-to-output plane transfer function (like MTF), and not so much in absolute terms, relative to a perfect point. Similarly, Gaussian wavelets, which would correspond to the waist of a propagating Gaussian beam, could also potentially be used in still another functional decomposition of the object plane field.
Far-field range and the 2D2 / λ criterion
In the figure above, illustrating the Fourier transforming property of lenses, the lens is in the near field of the object plane transparency, therefore the object plane field at the lens may be regarded as a superposition of plane waves, each one of which propagates at some angle with respect to the z-axis. In this regard, the far-field criterion is loosely defined as: Range = 2D2/λ where D is the maximum linear extent of the optical sources and λ is the wavelength (Scott [1998]). The D of the transparency is on the order of cm (10−2 m) and the wavelength of light is on the order of 10−6 m, therefore D/λ for the whole transparency is on the order of 104. This times D is on the order of 102 m, or hundreds of meters. On the other hand, the far field distance from a PSF spot is on the order of λ. This is because D for the spot is on the order of λ, so that D/λ is on the order of unity; this times D (i.e., λ) is on the order of λ (10−6 m).
Since the lens is in the far field of any PSF spot, the field incident on the lens from the spot may be regarded as being a spherical wave, as in eqn. (2.2), not as a plane wave spectrum, as in eqn. (2.1). On the other hand, the lens is in the near field of the entire input plane transparency, therefore eqn. (2.1) - the full plane wave spectrum - accurately represents the field incident on the lens from that larger, extended source.
Lens as a low-pass filter
A lens is basically a low-pass plane wave filter (see Low-pass filter). Consider a "small" light source located on-axis in the object plane of the lens. It is assumed that the source is small enough that, by the far-field criterion, the lens is in the far field of the "small" source. Then, the field radiated by the small source is a spherical wave which is modulated by the FT of the source distribution, as in eqn. (2.2), Then, the lens passes - from the object plane over onto the image plane - only that portion of the radiated spherical wave which lies inside the edge angle of the lens. In this far-field case, truncation of the radiated spherical wave is equivalent to truncation of the plane wave spectrum of the small source. So, the plane wave components in this far-field spherical wave, which lie beyond the edge angle of the lens, are not captured by the lens and are not transferred over to the image plane. Note: this logic is valid only for small sources, such that the lens is in the far field region of the source, according to the 2D2/λ criterion mentioned previously. If an object plane transparency is imagined as a summation over small sources (as in the Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula, Scott [1990]), each of which has its spectrum truncated in this fashion, then every point of the entire object plane transparency suffers the same effects of this low pass filtering.
Loss of the high (spatial) frequency content causes blurring and loss of sharpness (see discussion related to point spread function). Bandwidth truncation causes a (fictitious, mathematical, ideal) point source in the object plane to be blurred (or, spread out) in the image plane, giving rise to the term, "point spread function." Whenever bandwidth is expanded or contracted, image size is typically contracted or expanded accordingly, in such a way that the space-bandwidth product remains constant, by Heisenberg's principle (Scott [1998] and Abbe sine condition).
Coherence and Fourier transforming
While working in the frequency domain, with an assumed ejωt (engineering) time dependence, coherent (laser) light is implicitly assumed, which has a delta function dependence in the frequency domain. Light at different (delta function) frequencies will "spray" the plane wave spectrum out at different angles, and as a result these plane wave components will be focused at different places in the output plane. The Fourier transforming property of lenses works best with coherent light, unless there is some special reason to combine light of different frequencies, to achieve some special purpose.
Hardware implementation of the system transfer function: The 4F correlator
The theory on optical transfer functions presented in the section 5 is somewhat abstract. However, there is one very well known device which implements the system transfer function H in hardware using only 2 identical lenses and a transparency plate - the 4F correlator. Although one important application of this device would certainly be to implement the mathematical operations of cross-correlation and convolution, this device - 4 focal lengths long - actually serves a wide variety of image processing operations that go well beyond what its name implies. A diagram of a typical 4F correlator is shown in the figure below (click to enlarge). This device may be readily understood by combining the plane wave spectrum representation of the electric field (section 1.5) with the Fourier transforming property of quadratic lenses (section 6.1) to yield the optical image processing operations described in the section 5.

The 4F correlator is based on the convolution theorem from Fourier transform theory, which states that convolution in the spatial (x,y) domain is equivalent to direct multiplication in the spatial frequency (kx, ky) domain (aka: spectral domain). Once again, a plane wave is assumed incident from the left and a transparency containing one 2D function, f(x,y), is placed in the input plane of the correlator, located one focal length in front of the first lens. The transparency spatially modulates the incident plane wave in magnitude and phase, like on the left-hand side of eqn. (2.1), and in so doing, produces a spectrum of plane waves corresponding to the FT of the transmittance function, like on the right-hand side of eqn. (2.1). That spectrum is then formed as an "image" one focal length behind the first lens, as shown. A transmission mask containing the FT of the second function, g(x,y), is placed in this same plane, one focal length behind the first lens, causing the transmission through the mask to be equal to the product, F(kx,ky) × G(kx,ky). This product now lies in the "input plane" of the second lens (one focal length in front), so that the FT of this product (i.e., the convolution of f(x,y) and g(x,y)), is formed in the back focal plane of the second lens.
If an ideal, mathematical point source of light is placed on-axis in the input plane of the first lens, then there will be a uniform, collimated field produced in the output plane of the first lens. When this uniform, collimated field is multiplied by the FT plane mask, and then Fourier transformed by the second lens, the output plane field (which in this case is the impulse response of the correlator) is just our correlating function, g(x,y). In practical applications, g(x,y) will be some type of feature which must be identified and located within the input plane field (see Scott [1998]). In military applications, this feature may be a tank, ship or airplane which must be quickly identified within some more complex scene.
The 4F correlator is an excellent device for illustrating the "systems" aspects of optical instruments, alluded to in the section 5 above. The FT plane mask function, G(kx,ky) is the system transfer function of the correlator, which we'd in general denote as H(kx,ky), and it is the FT of the impulse response function of the correlator, h(x,y) which is just our correlating function g(x,y). And, as mentioned above, the impulse response of the correlator is just a picture of the feature we're trying to find in the input image. In the 4F correlator, the system transfer function H(kx,ky) is directly multiplied against the spectrum F(kx,ky) of the input function, to produce the spectrum of the output function. This is how electrical signal processing systems operate on 1D temporal signals.
Image Restoration
Image blurring by a point spread function is studied extensively in optical information processing, one way to alleviate the blurring is to adopt Wiener Filter. For example, assume that is the intensity distribution from an incoherent object, is the intensity distribution of its image which is blurred by a space-invariant point-spread function and a noise introduced in the detection process:
The goal of image restoration is to find a linear restoration filter that minimize the mean-squared error between the true distribution and the estimation . That is, to minimize
The solution of this optimization problem is Wiener filter: where , , are the power spectral densities of the point-spread function, the object and the noise.
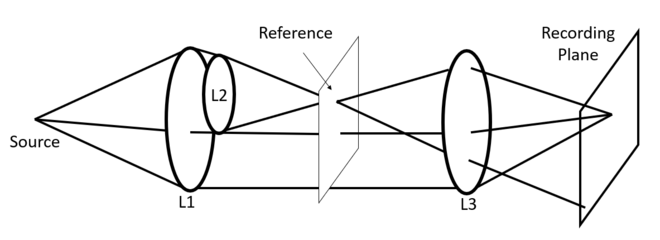
Ragnarsson proposed a method to realize Wiener restoration filters optically by holographic technique like setup shown in the figure.[2][3] The derivation of the function of the setup is described as follows.
Assume there is a transparency as the recording plane and an impulse emitted from a point source S. The wave of impulse is collimated by lens L1, forming a distribution equal to the impulse response . Then the distribution is then split into two parts:
- The upper portion is first focused (i.e., Fourier transformed) by a lens L2 to a spot in the front focal plan of lens L3, forming a virtual point source generating a spherical wave. The wave is then collimated by lens L3 and produces a tilted plane wave with the form at the recording plane.
- The lower portion is directly collimated by lens L3, yielding an amplitude distribution .
Therefore, the total intensity distribution is
Assume has an amplitude distribution and a phase distribution such that
then we can rewrite intensity as follows:
Note that for the point at the origin of the film plane (), the recorded wave from the lower portion should be much stronger than that from the upper portion because the wave passing through the lower path is focused, which leads to the relationship .
In Ragnarsson' s work, this method is based on the following postulates:
- Assume there is a transparency, with its amplitude transmittance proportional to , that has recorded the known impulse response of the blurred system.
- The maximum phase shift introduced by the filter is much smaller than radians so that .
- The phase shift of the transparency after bleaching is linearly proportional to the silver density present before bleaching.
- The density is linearly proportional to the logarithm of exposure
- The average exposure is much stronger than varying exposure
By these postulates, we have the following relationship:
Finally, we get a amplitude transmittance with the form of a Wiener filter:
Afterword: Plane wave spectrum within the broader context of functional decomposition
Electrical fields can be represented mathematically in many different ways. In the Huygens–Fresnel or Stratton-Chu viewpoints, the electric field is represented as a superposition of point sources, each one of which gives rise to a Green's function field. The total field is then the weighted sum of all of the individual Green's function fields. That seems to be the most natural way of viewing the electric field for most people - no doubt because most of us have, at one time or another, drawn out the circles with protractor and paper, much the same way Thomas Young did in his classic paper on the double-slit experiment. However, it is by no means the only way to represent the electric field, which may also be represented as a spectrum of sinusoidally varying plane waves. In addition, Frits Zernike proposed still another functional decomposition based on his Zernike polynomials, defined on the unit disc. The third-order (and lower) Zernike polynomials correspond to the normal lens aberrations. And still another functional decomposition could be made in terms of Sinc functions and Airy functions, as in the Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula and the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. All of these functional decompositions have utility in different circumstances. The optical scientist having access to these various representational forms has available a richer insight to the nature of these marvelous fields and their properties. These different ways of looking at the field are not conflicting or contradictory, rather, by exploring their connections, one can often gain deeper insight into the nature of wave fields.
Functional decomposition and eigenfunctions
The twin subjects of eigenfunction expansions and functional decomposition, both briefly alluded to here, are not completely independent. The eigenfunction expansions to certain linear operators defined over a given domain, will often yield a countably infinite set of orthogonal functions which will span that domain. Depending on the operator and the dimensionality (and shape, and boundary conditions) of its domain, many different types of functional decompositions are, in principle, possible.
See also
- Angular spectrum method
- Abbe sine condition
- Adaptive-additive algorithm
- Huygens–Fresnel principle
- Point spread function
- Phase contrast microscopy
- Fraunhofer diffraction
- Fresnel diffraction
- Geometrical optics
- Hilbert space
- Optical correlator
- Optical Hartley transform
- Wave field synthesis
References
- ↑ The equation 2.3 below suggests that u in this equation is such as u = x, y, or z. Need to confirm if this is the right understanding.
- ↑ Ragnarsson, SI. "Physica Scripta A new Holographic Method of Generating a High Efficiency, Extended Range Spatial Filter with Application to Restoration of Defocussed Images". Physica Scripta.
- ↑ Goodman, Joseph W. (2005) (in en). Introduction to Fourier Optics. Roberts and Company Publishers. ISBN 978-0-9747077-2-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=ow5xs_Rtt9AC&pg=PR7.
- The Fourier Transform and its Applications to Optics. New York, USA: John Wiley & Sons. 1983.
- Introduction to Fourier Optics (3 ed.). Roberts & Company Publishers. 2005. ISBN 0-9747077-2-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=ow5xs_Rtt9AC. Retrieved 2017-10-28.
- Optics (2 ed.). Addison Wesley. 1987. ISBN 0-201-11609-X.
- Fourier Series and Optical Transform Techniques in Contemporary Optics. John Wiley & Sons. 1995. ISBN 0-471-30357-7.
- Introduction to Optics and Optical Imaging. John Wiley & Sons. 1998. ISBN 0-7803-3440-X.
- Modern Methods of Reflector Antenna Analysis and Design. Artech House. 1990. ISBN 0-89006-419-9.
- The Spectral Domain Method in Electromagnetics. Artech House. 1989. ISBN 0-89006-349-4.
- Intro to Fourier Optics and the 4F correlator
External links
- Ambs, Pierre (2010). "Optical Computing: A 60-Year Adventure". Advances in Optical Technologies (Hindawi Limited) 2010: 1–15. doi:10.1155/2010/372652. ISSN 1687-6393.
- Stratton, J. A.; Chu, L. J. (1939-07-01). "Diffraction Theory of Electromagnetic Waves". Physical Review (American Physical Society (APS)) 56 (1): 99–107. doi:10.1103/physrev.56.99. ISSN 0031-899X. http://server.physics.miami.edu/~curtright/Diffraction/StrattonChu1939.pdf.
 |
