Medicine:Diencephalic syndrome
| Diencephalic syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Diencephalic syndrome of emaciation |
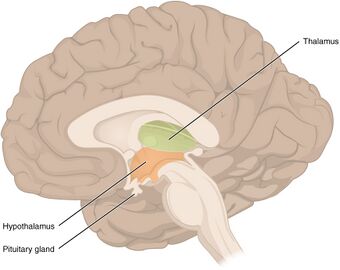 | |
| The diencephalon, which is affected by diencaphalic syndrome, consists of the thalamus, the subthalamus, the hypothalamus, and the epithalamus. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
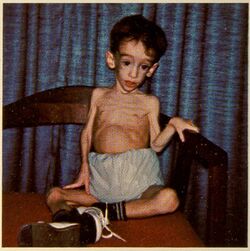
Diencephalic syndrome, or Russell's syndrome, is a rare neurological disorder seen in infants and children and characterised by failure to thrive and severe emaciation despite normal or slightly decreased caloric intake. Classically there is also locomotor hyperactivity and euphoria. Less commonly diencephalic syndrome may involve skin pallor without anaemia, hypoglycaemia, and hypotension.[1] The syndrome is a rare but potentially fatal cause of failure to thrive in children. Failure to thrive presents on average at seven months of age.[1] Of note the syndrome is not associated with developmental delay.[2] There may be associated hydrocephalus.[citation needed]
Diencephalic syndrome was first described by Dr. A. Russell in 1951.[3] It is usually caused by a brain tumor such as a low-grade glioma or astrocytoma located in the hypothalamic-optic chiasmatic region.[1] It is not yet understood how diencephalic syndrome causes the effects on appetite and metabolism which are seen, though inappropriately high growth hormone release has been proposed,[4] as has excessive β-lipotropin secretion[1] and overall increased metabolic demand.[5] It is treated with nutritional optimisation while the underlying lesion is treated with chemotherapy, surgery or radiotherapy.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Diencephalic syndrome: a frequently neglected cause of failure to thrive in infants". Korean J Pediatr 58 (1): 28–32. Jan 2015. doi:10.3345/kjp.2015.58.1.28. PMID 25729396.
- ↑ "Diencephalic syndrome: a cause of failure to thrive and a model of partial growth hormone resistance". Pediatrics 115 (6): 724–6. June 2005. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-2237. PMID 15930202.
- ↑ "A diencephalic syndrome of emaciation in infancy and childhood". Arch Dis Child 26: 274. 1951. doi:10.1136/adc.26.127.270.
- ↑ "Inappropriate growth hormone release in the diencephalic syndrome of childhood: case report and 4 year endocrinological follow-up". Clin Endocrinol 13 (2): 181–7. August 1980. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1980.tb01040.x. PMID 7438472.
- ↑ "Increased energy expenditure in a patient with diencephalic syndrome". J Pediatr 122 (6): 922–4. June 1993. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(09)90021-x. PMID 8501572.
 |
