Medicine:Multiple system atrophy
| Multiple system atrophy | |
|---|---|
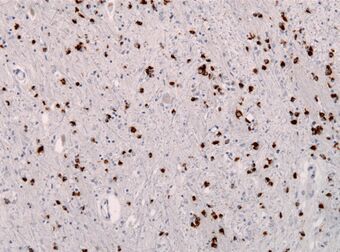 | |
| Alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry of the brain showing many glial inclusion bodies | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Parkinsonism, xerostomia, dysautonomia, ataxia |
| Complications | Cardiac arrest, infections, aspiration pneumonia |
| Usual onset | 50–60 years |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types |
|
| Causes | Unknown |
| Diagnostic method | MRI, CT scan, autopsy |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, hospice care |
| Medication | L-DOPA, fludrocortisone, midodrine |
| Prognosis | Life expectancy 6–12 years after onset of symptoms |
| Frequency | 5 per 100,000 people |
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder[1] characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome.[2]
Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder.
A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA.[3] About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 years.[4] MSA often presents with some of the same symptoms as Parkinson's disease. However, those with MSA generally show little response to the dopamine agonists used to treat Parkinson's disease and only about 9% of MSA patients with tremor exhibit a true parkinsonian pill-rolling tremor.[5]
MSA is distinct from multisystem proteinopathy, a more common muscle-wasting syndrome. MSA is also different from multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, sometimes referred to as multiple organ failure, and from multiple organ system failures, an often-fatal complication of septic shock and other severe illnesses or injuries.
Signs and symptoms
MSA is characterized by the following: Autonomic and at least one Motor (clinically established MSA criteria 2022)[6][7]
- autonomic dysfunction: Post-void urinary residual volume ≥100 mL (usually by ultrasound); Unexplained urinary urge incontinence; or Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (≥20/10 mmHg blood pressure drop) within 3 minutes (usually by head‐up tilt)
- parkinsonism (muscle rigidity +/ tremor and slow movement: MSA-P)
- cerebellar ataxia (Poor coordination/unsteady walking: MSA-C)
A variant with combined features of MSA and dementia with Lewy bodies may also exist.[unreliable medical source?][8] There have also been occasional instances of frontotemporal lobar degeneration associated with MSA.[9]
Initial presentation
The most common first sign of MSA is the appearance of an "akinetic-rigid syndrome" (i.e. slowness of initiation of movement resembling Parkinson's disease) found in 62% at first presentation. Other common signs at onset include problems with balance (cerebellar ataxia) found in 22% at first presentation, followed by genito-urinary symptoms (9%): both men and women often experience urgency, frequency, incomplete bladder emptying, or an inability to pass urine (retention). About 1 in 5 MSA patients experience a fall in their first year of disease.[10]
For men, the first sign can be erectile dysfunction. Women have also reported reduced genital sensitivity.[11]
Progression
As the disease progresses, one of three groups of symptoms predominates. These are:[12]
- Parkinsonism - slow, stiff movement, writing becomes small and spidery[13][14]
- Cerebellar dysfunction - difficulty coordinating movement and balance[15]
- Autonomic nervous system dysfunction - impaired automatic body functions, including one, some, or all of the following:[16]
- postural or orthostatic hypotension, resulting in dizziness or fainting upon standing up[17]
- urinary incontinence or urinary retention[18][19][20]
- impotence[21]
- constipation[22]
- vocal cord paralysis
- dry mouth and skin
- trouble regulating body temperature due to sweating deficiency in all parts of the body
- loud snoring, abnormal breathing or inspiratory stridor during sleep
- other sleep disorders including sleep apnea, REM behavior disorder[23]
- double vision[24]
- muscle twitches[24]
- Cognitive impairment[25]
Genetics
One study found a correlation between the deletion of genes in a specific genetic region and the development of MSA in a group of Japanese patients. The region in question includes the SHC2 gene which, in mice and rats, appears to have some function in the nervous system. The authors of this study hypothesized that there may be a link between the deletion of the SHC2 and the development of MSA.[26]
A follow-up study was unable to replicate this finding in American MSA patients.[27] The authors of the study concluded that "Our results indicate that SHC2 gene deletions underlie few, if any, cases of well-characterized MSA in the US population. This is in contrast to the Japanese experience reported by Sasaki et al., likely reflecting heterogeneity of the disease in different genetic backgrounds."[clarification needed]
Another study investigated the frequency of RFC1 intronic repeat expansions, a phenomenon implicated in CANVAS; a disease with a diagnostic overlap with MSA.[28][29] The study concluded that these repeats were absent in pathologically confirmed MSA, suggesting an alternative genetic cause.[28]
Pathophysiology
The defining pathologic feature of multiple system atrophy is the presence of inclusion bodies (known as glial cytoplasmic inclusions or Papp-Lantos bodies) consisting of alpha-synuclein in oligodendrocytes.[30][31] In addition, neurons are lost in several regions of the nervous system, particularly in the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nuclei, cerebellum, pons, and spinal cord.[32] Reactive astrocytes and microglia are prominent in damaged areas of the central nervous system, especially in regions with abundant oligodendroglial inclusions.[32] Neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions also are present in MSA, although these are much less numerous than are oligodendroglial inclusions.[32] Inclusions sometimes occur in the cell nucleus of neurons and oligodendrocytes.[33][31] Outside of the central nervous system, alpha‐synuclein inclusions may be found in Schwann cells of cranial, spinal and autonomic nerves and in the enteric nervous system.[31]
The major proteinaceous component of glial and neuronal inclusions in MSA is alpha-synuclein[34][33] that is phosphorylated at serine residue 129.[32] Mutations in the gene for alpha-synuclein may play a role in the disease,[35] and a variety of other potential genetic and environmental risk factors have been proposed.[33] The conformation of alpha-synuclein in MSA is different from that of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies, indicative of variant proteopathic strains.[3][36]
The origin of the alpha-synuclein that forms inclusions in oligodendrocytes is uncertain. Compared to neurons, oligodendrocytes produce little or no alpha-synuclein themselves, suggesting that these cells take up the protein that is generated by neurons.[37] For example, it has been proposed that the α-synuclein inclusions found in oligodendrocytes result from the pruning and engulfment of diseased axonal segments containing aggregated α-synuclein, i.e., of Lewy neurites.[38] Research has shown that the strain of the protein generated by oligodendrocytes causes a more aggressive type of disease than does the Lewy body strain.[37] The factors in oligodendrocytes that induce the formation of especially potent alpha-synuclein seeds are not known.[37]
In addition to the primary protein alpha-synuclein, glial cytoplasmic inclusions contain several other types of protein as well as lysosomes and peroxisomes.[32] Tau proteins (the main components of neurofibrillary tangles) have been found in some glial cytoplasmic inclusions.[39]
Diagnosis
Clinical
Clinical diagnostic criteria were defined in 1998[40] and updated in 2007[41] and in 2022.[42] Certain signs and symptoms of MSA also occur with other disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, making the diagnosis more difficult.[43][44][45]
Features characteristic of OPCA include progressive cerebellar ataxia, leading to clumsiness in body movements, veering from midline when walking, wide-based stance, and falls without signs of paralysis or weakness.[46][47] Clinical presentation can vary greatly between patients, but mostly affects speech, balance and walking.[48] Other possible neurological problems include spasmodic dysphonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, rigidity, dysarthria, dysphagia and neck dystonic posture.[47] Dysarthria is characterized by increased pauses of irregular duration, impaired coordination of vocal pitch, prolonged syllables and an overall irregular speech rhythm.[49] Diagnosis may be based on a thorough medical exam; the presence of signs and symptoms; imaging studies; various laboratory tests; and an evaluation of the family history.[50]
Radiologic

Both MRI and CT scanning may show a decrease in the size of the cerebellum and pons in those with cerebellar features (MSA-C). The putamen is hypointense on T2-weighted MRI and may show an increased deposition of iron in the Parkinsonian (MSA-P) form. In MSA-C, a "hot cross bun" sign is sometimes found; it reflects atrophy of the pontocerebellar tracts that give T2 hyper intense signal intensity in the atrophic pons.
Pathologic
Pathological diagnosis can only be made at autopsy by finding abundant glial cytoplasmic inclusions (GCIs) on histological specimens of the central nervous system.[51]
Olivopontocerebellar atrophy can be used as a pathological term to describe degeneration of neurons in specific areas of the brain – the cerebellum, pons, and inferior olivary nucleus.[52] OPCA is present in several neurodegenerative syndromes, including inherited and non-inherited forms of ataxia (such as the hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia known as Machado–Joseph disease) and MSA, with which it is primarily associated.[52]
Contrary to most other synucleinopathies, which develop α-synuclein inclusions primarily in neuronal cell populations,[53] MSA presents with extensive pathological α-synuclein inclusions in the cytosol of oligodendrocytes (glial cytoplasmic inclusions), with limited pathology in neurons.[54] MSA also differs from other synucleinopathies in its regional pathological presentation, with α-synuclein positive inclusions detected predominantly in the striatum, midbrain, pons, medulla and cerebellum,[55][56] rather than the brainstem, limbic and cortical regions typically effected in Lewy inclusion diseases.[56] However, recent studies using novel, monoclonal antibodies specific for C-terminally truncated α-synuclein (αSynΔC) have now shown that neuronal α-synuclein pathology is more abundant than previously thought.[57][58] One group revealed robust α-synuclein pathology in the pontine nuclei and medullary inferior olivary nucleus upon histological analysis of neurological tissue from MSA patients.[57] Histopathological investigation on six cases of pathologically confirmed MSA, using antibodies directed at a variety of α-synuclein epitopes, revealed substantial variation in α-synuclein protein deposition across both cases and brain regions within cases, providing evidence for 'strains' of aggregated conformers that may differentially promote pathological prion-like spread.[59]
In 2020, researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston concluded that protein misfolding cyclic amplification could be used to distinguish between two progressive neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy, being the first process to give an objective diagnosis of Multiple System Atrophy instead of just a differential diagnosis.[60][61]
Classification
MSA is one of several neurodegenerative diseases known as synucleinopathies: they have in common an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in various parts of the brain. Other synucleinopathies include Parkinson's disease, the Lewy body dementias, and other more rare conditions.[62]
Old terminology
| Olivopontocerebellar atrophy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Multiple system atrophy – cerebellar subtype[63] |
 | |
| Sagittal section through right cerebellar hemisphere. The right olive has also been cut sagittally. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Historically, many terms were used to refer to this disorder, based on the predominant systems presented. These terms were discontinued by consensus in 1996 and replaced with MSA and its subtypes,[64] but awareness of these older terms and their definitions is helpful to understanding the relevant literature prior to 1996. These include striatonigral degeneration (SND), olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA), and Shy–Drager syndrome.[65] A table describing the characteristics and modern names of these conditions follows:
| Historical Name | Characteristics | Modern name and abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Striatonigral degeneration | predominating Parkinson's-like symptoms | MSA-P, "p" = parkinsonian subtype |
| Sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA) | characterized by progressive ataxia (an inability to coordinate voluntary muscular movements) of the gait and arms and dysarthria (difficulty in articulating words) | MSA-C, "c" = cerebellar dysfunction subtype |
| Shy-Drager syndrome | characterized by Parkinsonism plus a more pronounced failure of the autonomic nervous system.[66] | No modern equivalent – this terminology fell out of favour[67] and was not specified in the 2007 consensus paper.[41] The earlier consensus of 1998[40] referred to MSA-A, "a" = autonomic dysfunction subtype but this subtype is no longer used. |
The term olivopontocerebellar atrophy was originally coined by Joseph Jules Dejerine and André Thomas.[68][69] It was subdivided as:
| Number | OMIM | Alt. name | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPCA type 2 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 258300 | Fickler[70]-Winkler[71] type OPCA | autosomal recessive |
| OPCA type 5 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 164700 | OPCA with dementia and extrapyramidal signs | autosomal dominant |
Non-hereditary diseases formerly categorized as olivopontocerebellar atrophy have were reclassified as forms of MSA[72] as well as to four hereditary types, that have been currently reclassified as four different forms of spinocerebellar ataxia:
| Hereditary OPCA type | OPCA name | SCA # | Gene | OMIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPCA type 1 | "Menzel type OPCA" | SCA1 | ATXN1 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 164400 |
| OPCA type 2, autosomal dominant | "Holguin type OPCA" | SCA2 | ATXN2 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 183090 |
| OPCA type 3 | "OPCA with retinal degeneration" | SCA7 | ATXN7 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 164500 |
| OPCA type 4 | "Schut-Haymaker type OPCA" | SCA1 | ATXN1 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 164400 |
Current terminology
The current terminology and diagnostic criteria for the disease were established at a 2007 conference of experts and set forth in a position paper.[41] This Second Consensus Statement defines two categories of MSA, based on the predominant symptoms of the disease at the time of evaluation. These are:
Management
Supervision
Ongoing care from a neurologist specializing in movement disorders is recommended,[by whom?] because the complex symptoms of MSA are often not familiar to less-specialized neurologists. Hospice/homecare services can be very useful as disability progresses.
Drug therapy
Levodopa (L-Dopa), a drug used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, improves parkinsonian symptoms in a small percentage of MSA patients. A recent trial reported that only 1.5% of MSA patients experienced any improvement at all when taking levodopa, their improvement was less than 50%, and even that improvement was a transient effect lasting less than one year. Poor response to L-Dopa has been suggested as a possible element in the differential diagnosis of MSA from Parkinson's disease.[73]
The drug riluzole is ineffective in treating MSA or PSP.[10]
Rehabilitation
Physiotherapists can help to maintain the patient's mobility and will help to prevent contractures.[74] Instructing patients in gait training will help to improve their mobility and decrease their risk of falls.[75] A physiotherapist may also prescribe mobility aids such as a cane or a walker to increase the patient's safety.[75]
Early intervention of swallowing difficulties is particularly useful to allow for discussion around tube feeding further in the disease progression. At some point in the progression of the disease, fluid and food modification may be implemented.{{citation needed|date=December
Avoidance of postural hypotension
One particularly serious problem, the drop in blood pressure upon standing up (with risk of fainting and thus injury from falling), often responds to fludrocortisone, a synthetic mineralocorticoid.[76][77] Another common drug treatment is the alpha-agonist midodrine.[76]
Non-drug treatments include "head-up tilt" (elevating the head of the whole bed by about 10 degrees), salt tablets or increasing salt in the diet, generous intake of fluids, and pressure (elastic) stockings. Avoidance of triggers of low blood pressure, such as hot weather, alcohol, and dehydration, are crucial.[77] The patient can be taught to move and transfer from sitting to standing slowly to decrease risk of falls and limit the effect of postural hypotension.[75] Instruction in ankle pumping helps to return blood in the legs to the systemic circulation.[75] Other preventative measures are raising the head of the bed by 8 in (20.3 cm), and the use of compression stockings and abdominal binders.[6]
Supine hypertension
In addition to orthostatic hypotension, supine hypertension, where the BP is excessively high lying down, is a frequent problem in multiple system atrophy. Treatment of one symptom can easily aggravate the other, and supine hypertension in such patients has been linked to the same cardiovascular complications as essential hypertension.[78]
Support
Prognosis
The average lifespan after the onset of symptoms in patients with MSA is 6–10 years.[4] Approximately 60% of patients require a wheelchair within five years of onset of the motor symptoms, and few patients survive beyond 12 years.[4] The disease progresses without remission at a variable rate. Those who present at an older age, those with parkinsonian features, and those with severe autonomic dysfunction have a poorer prognosis.[4] Those with predominantly cerebellar features and those who display autonomic dysfunction later have a better prognosis.[4]
Causes of death
The most common causes of death are sudden death and death caused by infections, which include urinary catheterization infections, feeding tube infections, and aspiration pneumonia. Some deaths are caused by cachexia, also known as wasting syndrome.[79]
Epidemiology
Multiple system atrophy is estimated to affect approximately 5 per 100,000 people. At autopsy, many patients diagnosed during life with Parkinson's disease are found actually to have MSA, suggesting that the actual incidence of MSA is higher than that estimate.[4] While some suggest that MSA affects slightly more men than women (1.3:1), others suggest that the two sexes are equally likely to be affected.[4][6][74] The condition most commonly presents in persons aged 50–60.[4]
Research
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy may delay the progression of neurological deficits in patients with MSA-cerebellar type.[80]
Notable cases
- Nikolai Andrianov was a Soviet/Russian gymnast who held the record for men for the most Olympic medals at 15 (7 gold medals, 5 silver medals, 3 bronze medals) until Michael Phelps surpassed him at the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics.[81]
- Todd J. Campbell (1956–2021), United States district judge and counsel to former Vice President Al Gore.[82]
- Singer and songwriter Johnny Cash wrote in his autobiography that he was diagnosed with Shy–Drager in 1997.[83]
- Ronald Green (1944–2012), American-Israeli basketball player[84]
- Joseph C. Howard Sr. (1922-2000) was the first African American to serve as a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of Maryland.[85]
- Kenneth More British actor, originally diagnosed with Parkinson's disease.
- Chef Kerry Simon died from complications of MSA.[86]
- David Colin Sherrington FRS (1945–2014), noted polymer chemist, who was diagnosed in 2012 and died from pneumonia two years later.
- Karsten Heuer (1968-2024) Canadian Biologist, Conservationist, Filmmaker and Author.
See also
References
- ↑ "Multiple system atrophy" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "Multiple System Atrophy-D Maybe Something Altogether–Different" (in en). https://practicalneurology.com/articles/2018-mar-apr/multiple-system-atrophy-d-maybe-something-altogetherdifferent.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies". Nature 557 (7706): 558–563. May 2018. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0104-4. PMID 29743672. Bibcode: 2018Natur.557..558P.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 "Multiple-system atrophy". The New England Journal of Medicine 372 (3): 249–263. January 2015. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1311488. PMID 25587949.
- ↑ "Multiple System Atrophy Clinical Presentation". https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1154583-clinical#b4.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Multiple system atrophy". Physical Therapy 79 (5): 488–494. May 1999. doi:10.1093/ptj/79.5.488. PMID 10331752.
- ↑ "Multiple system atrophy: cellular and molecular pathology". Molecular Pathology 54 (6): 419–426. December 2001. doi:10.1136/mp.54.6.419. PMID 11724918.
- ↑ [unreliable medical source?]"Synucleinopathy with features of both multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 33 (1): 126–129. February 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00817.x. PMID 17239015.
- ↑ "Atypical multiple system atrophy is a new subtype of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: frontotemporal lobar degeneration associated with α-synuclein". Acta Neuropathologica 130 (1): 93–105. July 2015. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1442-z. PMID 25962793.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Riluzole treatment, survival and diagnostic criteria in Parkinson plus disorders: the NNIPPS study". Brain 132 (Pt 1): 156–171. January 2009. doi:10.1093/brain/awn291. PMID 19029129.
- ↑ "Reduced genital sensitivity in female patients with multiple system atrophy of parkinsonian type". Movement Disorders 18 (4): 430–432. April 2003. doi:10.1002/mds.10384. PMID 12671951.
- ↑ Stępnicki (2018-08-20). "Current Concepts and Treatments of Schizophrenia". Molecules 23 (8): 2087. doi:10.3390/molecules23082087. ISSN 1420-3049. PMID 30127324.
- ↑ "Chapter 7: Movement disorders". Clinical Neurology (6th ed.). Lange: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2005. pp. 241–45. ISBN 978-0-07-142360-1.
- ↑ "Role of Neuroimaging on Differentiation of Parkinson's Disease and Its Related Diseases". Yonago Acta Medica 61 (3): 145–155. September 2018. doi:10.33160/yam.2018.09.001. PMID 30275744. "Parkinsonian syndromes are a group of movement disorders characterized by classical motor symptoms such as tremors, bradykinesia, and rigidity. They are most frequently due to primary neurodegenerative disease, resulting in the loss of dopaminergic nerve terminals along the nigrostriatal pathway, similar to idiopathic PD, MSA, PSP, CBD, and DLB.".
- ↑ "Evolution of Cerebellum". Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. Springer. 2009. pp. 1240–1243. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29678-2_3124. ISBN 978-3-540-23735-8.
- ↑ "Autonomic nervous system" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "Hypotension". https://www.lecturio.com/concepts/hypotension/.
- ↑ Nursing diagnosis handbook: an evidence-based guide to planning care (9th ed.). Maryland Heights, Mo: Mosby. 2010. ISBN 978-0-323-07150-5.
- ↑ "Early bladder dysfunction in multiple system atrophy: who seek shall find". Clin Auton Res 29 (6): 625–6. 2019. doi:10.1007/s10286-019-00648-2. PMID 1705345.
- ↑ "A guideline for the management of bladder dysfunction in Parkinson's disease and other gait disorders". Neurourol Urodyn 35 (5): 551–63. 2016. doi:10.1002/nau.22764. PMID 25810035.
- ↑ "Overview of male sexual dysfunction.". UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate. 2018.
- ↑ "Constipation". https://www.lecturio.com/concepts/constipation/.
- ↑ "REM sleep behavior disorder is related to striatal monoaminergic deficit in MSA". Neurology 61 (1): 29–34. July 2003. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000073745.68744.94. PMID 12847152.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "What is multiple system atrophy?". https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/multiple-system-atrophy.
- ↑ "Cognitive impairment in patients with multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy". Brain 133 (Pt 8): 2382–2393. August 2010. doi:10.1093/brain/awq158. PMID 20576697.
- ↑ "Copy number loss of (src homology 2 domain containing)-transforming protein 2 (SHC2) gene: discordant loss in monozygotic twins and frequent loss in patients with multiple system atrophy". Molecular Brain 4: 24. June 2011. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-4-24. PMID 21658278. "Copy number loss of SHC2 strongly indicates a causal link to MSA.".
- ↑ "SHC2 gene copy number in multiple system atrophy (MSA)". Clinical Autonomic Research 24 (1): 25–30. February 2014. doi:10.1007/s10286-013-0216-8. PMID 24170347.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "RFC1 Intronic Repeat Expansions Absent in Pathologically Confirmed Multiple Systems Atrophy". Movement Disorders 35 (7): 1277–1279. July 2020. doi:10.1002/mds.28074. PMID 32333430.
- ↑ "Biallelic expansion of an intronic repeat in RFC1 is a common cause of late-onset ataxia". Nature Genetics 51 (4): 649–658. April 2019. doi:10.1038/s41588-019-0372-4. PMID 30926972.
- ↑ "Papp-Lantos inclusions and the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: an update". Acta Neuropathologica 119 (6): 657–667. June 2010. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0672-3. PMID 20309568.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 "Review: Multiple system atrophy: emerging targets for interventional therapies". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 42 (1): 20–32. February 2016. doi:10.1111/nan.12304. PMID 26785838.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 "Multiple system atrophy: advances in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment". Lancet Neurology 23 (12): 1252-1266. December 2024. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00396-X. PMID 39577925.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 "Multiple System Atrophy: An oligodendroglioneural synucleinopathy". Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 62 (3): 1141-1179. March 2018. doi:10.3233/JAD-170397. PMID 28984582.
- ↑ "NACP/alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in fibrillary components of neuronal and oligodendroglial cytoplasmic inclusions in the pontine nuclei in multiple system atrophy". Acta Neuropathologica 96 (5): 439–444. November 1998. doi:10.1007/s004010050917. PMID 9829806.
- ↑ "Genetic variants of the alpha-synuclein gene SNCA are associated with multiple system atrophy". PLOS ONE 4 (9). September 2009. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007114. PMID 19771175. Bibcode: 2009PLoSO...4.7114A.
- ↑ "Proteopathic strains and the heterogeneity of neurodegenerative diseases". Annual Review of Genetics 50: 329–346. November 2016. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-034943. PMID 27893962.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 "Sabotage by the brain's supporting cells helps fuel neurodegeneration". Nature 557 (7706): 499-500. May 2018. doi:10.1038/d41586-018-04988-3. PMID 29777188.
- ↑ "Oligodendrocytes Prune Axons Containing α-Synuclein Aggregates In Vivo: Lewy Neurites as Precursors of Glial Cytoplasmic Inclusions in Multiple System Atrophy?". Biomolecules 13 (2): 269. February 2023. doi:10.3390/biom13020269. PMID 36830639.
- ↑ "Co-localization of alpha-synuclein and phosphorylated tau in neuronal and glial cytoplasmic inclusions in a patient with multiple system atrophy of long duration". Acta Neuropathologica 101 (3): 285–293. March 2001. doi:10.1007/s004010000292. PMID 11307630.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 "Consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 163 (1): 94–98. February 1999. doi:10.1016/s0022-510x(98)00304-9. PMID 10223419.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 "Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy". Neurology 71 (9): 670–676. August 2008. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000324625.00404.15. PMID 18725592.
- ↑ "The Movement Disorder Society Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple System Atrophy". Movement Disorders 37 (6): 1131–48. 2022. doi:10.1002/mds.29005. PMID 35445419.
- ↑ "Multiple System Atrophy / Shy Drager Syndrome". Vanderbilt Autonomic Dysfunction Center. http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/root/vumc.php?site=adc&doc=4791.
- ↑ "multiple system atrophy overview". Medscape (WebMD LLC). 2018-09-24. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1154074-overview#a2.
- ↑ "When DLB, PD, and PSP masquerade as MSA: an autopsy study of 134 patients". Neurology 85 (5): 404–412. August 2015. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000001807. PMID 26138942.
- ↑ Landers, M; Adams M; Acosta K; Fox A. (2009). "Challenge-oriented gait and balance training in sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy: a case study.". J Neurol Phys Ther 33 (3): 160–168. doi:10.1097/npt.0b013e3181b511f4. PMID 19809395.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Berciano, J; Boesch S; Pérez-Ramos JM; Wenning GK (2006). "Olivopontocerebellar atrophy: toward a better nosological definition.". Mov. Disord. 21 (10): 1607–13. doi:10.1002/mds.21052. PMID 16874757.
- ↑ "Olivopontocerebellar atrophy - PubMed Health". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001765/.
- ↑ Hähnel, Tom; Nemitz, Anna; Schön, Katja; Berger, Luise; Vogel, Annemarie; Gruber, Doreen; Schnalke, Nils; Bräuer, Stefan et al. (2025-05-03). "Speech Differences between Multiple System Atrophy and Parkinson's Disease" (in en). Movement Disorders Clinical Practice 12 (9): 1391–1396. doi:10.1002/mdc3.70094. ISSN 2330-1619. PMID 40317624.
- ↑ "Olivopontocerebellar atrophy | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7250/olivopontocerebellar-atrophy.
- ↑ "Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome)". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 94 (1–3): 79–100. December 1989. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(89)90219-0. PMID 2559165.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "NINDS Olivopontocerebellar Atrophy Information Page". http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/opca/opca.htm.
- ↑ "Molecular mechanisms of alpha-synuclein neurodegeneration". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 1792 (7): 616–624. July 2009. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.09.013. PMID 18955133.
- ↑ "Multiple system atrophy: cellular and molecular pathology". Molecular Pathology 54 (6): 419–426. December 2001. doi:10.1136/mp.54.6.419. PMID 11724918.
- ↑ "The spectrum of pathological involvement of the striatonigral and olivopontocerebellar systems in multiple system atrophy: clinicopathological correlations". Brain 127 (Pt 12): 2657–2671. December 2004. doi:10.1093/brain/awh303. PMID 15509623.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 "Converging Patterns of α-Synuclein Pathology in Multiple System Atrophy". Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 77 (11): 1005–1016. November 2018. doi:10.1093/jnen/nly080. PMID 30203094.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 "Robust α-synuclein pathology in select brainstem neuronal populations is a potential instigator of multiple system atrophy". Acta Neuropathologica Communications 9 (1). May 2021. doi:10.1186/s40478-021-01173-y. PMID 33941284.
- ↑ "Disease-, region- and cell type specific diversity of α-synuclein carboxy terminal truncations in synucleinopathies". Acta Neuropathologica Communications 9 (1). August 2021. doi:10.1186/s40478-021-01242-2. PMID 34454615.
- ↑ "Dissecting α-synuclein inclusion pathology diversity in multiple system atrophy: implications for the prion-like transmission hypothesis". Laboratory Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology 99 (7): 982–992. July 2019. doi:10.1038/s41374-019-0198-9. PMID 30737468.
- ↑ "Method Can Distinguish Parkinson's Disease From multiple system atrophy" (in en). Diagnostics from Technology Networks. https://www.technologynetworks.com/diagnostics/news/method-can-distinguish-parkinsons-disease-from-multiple-system-atrophy-330385.
- ↑ "Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy". Nature 578 (7794): 273–277. February 2020. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-1984-7. PMID 32025029. Bibcode: 2020Natur.578..273S.
- ↑ "The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On". Journal of Parkinson's Disease 7 (s1): S51–S69. 2017. doi:10.3233/JPD-179005. PMID 28282814.
- ↑ "Multiple system atrophy – cerebellar subtype: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia" (in en). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000758.htm.
- ↑ The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology (May 1996). "Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy.". Neurology 46 (5): 1470. doi:10.1212/wnl.46.5.1470. PMID 8628505.
- ↑ "The neuropathology, pathophysiology and genetics of multiple system atrophy". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 38 (1): 4–24. February 2012. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01234.x. PMID 22074330.
- ↑ "A neurological syndrome associated with orthostatic hypotension: a clinical-pathologic study". Archives of Neurology 2 (5): 511–527. May 1960. doi:10.1001/archneur.1960.03840110025004. PMID 14446364.
- ↑ "Farewell to the "Shy-Drager syndrome"". Annals of Internal Medicine 125 (1): 74–75. July 1996. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-125-1-199607010-00012. PMID 8644992.
- ↑ synd/1903 at Who Named It? - "Dejerine-Thomas atrophy"
- ↑ J. J. Dejerine, A. Thomas. L'atrophie olivo-ponto-cérébelleuse. Nouvelle iconographie de la Salpêtrière, Paris, 1900, 13: 330-370. 1912, 25: 223-250.
- ↑ Fickler, A. Klinische und pathologisch-anatomische Beitraege zu den Erkrankungen des Kleinhirns. Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk. 41: 306-375, 1911.
- ↑ Winkler, C. A case of olivo-pontine cerebellar atrophy and our conceptions of neo- and palaio-cerebellum. Schweiz. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 13: 684-702, 1923.
- ↑ MeSH Result
- ↑ "Pharmacodynamics of a low subacute levodopa dose helps distinguish between multiple system atrophy with predominant Parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurology 263 (2): 250–256. February 2016. doi:10.1007/s00415-015-7961-7. PMID 26566913.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 "Multiple system atrophy". The Lancet. Neurology 3 (2): 93–103. February 2004. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00662-8. PMID 14747001.
"Erratum". Lancet Neurol 3 (3): 137. March 2004. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00695-7. - ↑ 75.0 75.1 75.2 75.3 "Multiple system atrophy: pathophysiology, treatment and nursing care". Nursing Standard 22 (22): 50–6; quiz 58. 2008. doi:10.7748/ns2008.02.22.22.50.c6359. PMID 18333558.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Multiple system atrophy (MSA) mayoclinic.org, accessed 20 May 2018
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 "Management of Orthostatic Hypotension" (in en-US). Continuum 26 (1): 154–177. February 2020. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000816. PMID 31996627.
- ↑ Palma, Jose-Alberto; Redel-Traub, Gabriel; Porciuncula, Angelo; Samaniego-Toro, Daniela; Millar Vernetti, Patricio; Lui, Yvonne W.; Norcliffe-Kaufmann, Lucy; Kaufmann, Horacio (June 2020). "The impact of supine hypertension on target organ damage and survival in patients with synucleinopathies and neurogenic orthostatic hypotension" (in en). Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 75 (75): 97–104. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.04.011. PMID 32516630.
- ↑ "Causes of death in multiple system atrophy". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 78 (3): 327–329. March 2007. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.103929. PMID 17308296.
- ↑ "A randomized trial of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple system atrophy". Annals of Neurology 72 (1): 32–40. July 2012. doi:10.1002/ana.23612. PMID 22829267. https://ir.ymlib.yonsei.ac.kr/handle/22282913/89525.
- ↑ "Olympic Legend Andrianov Dies at 58" (in en-gb). International Gymnast Magazine Online. http://www.intlgymnast.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2414:olympic-legend-andrianov-dies-at-58-&catid=2:news&Itemid=53.
- ↑ "Former U.S. District Judge Todd Campbell, longtime Nashville legal mind and adviser to a vice president, dead at 64". https://www.tennessean.com/story/news/2021/04/11/former-us-district-judge-todd-campbell-dies/7150314002/.
- ↑ Cash: The Autobiography. New York, NY, USA: HarperCollins Publishers. 1998. pp. 400–403. ISBN 978-0-06-101357-7. https://archive.org/details/cashautobiograph00cash.
- ↑ "Ronald Green Obituary". July 26, 2012. https://www.legacy.com/amp/obituaries/herald/158753446.
- ↑ "Standing up for justice". Baltimore AFRO-American. 2000-09-30. http://www.house.gov/cummings/articles/art00_37.htm.
- ↑ "Kerry Simon, Las Vegas 'Iron Chef' winner, dies at 60". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/ap-kerry-simon-las-vegas-iron-chef-winner-dies-at-60-2015-9?IR=T.
External links
- Medical Textbook: "Multiple System Atrophy" edited by Gregor Wenning and Alessandra Fanciulli
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
ca:Síndrome de Shy-Drager es:Síndrome de Shy-Drager pt:Síndrome de Shy-Drager ro:Sindromul Shy-Drager sl:Shy-Dragerjev sindrom
 |
