Seven-dimensional cross product
In mathematics, the seven-dimensional cross product is a bilinear operation on vectors in seven-dimensional Euclidean space. It assigns to any two vectors a, b in a vector a × b also in .[1] Like the cross product in three dimensions, the seven-dimensional product is anticommutative and a × b is orthogonal both to a and to b. Unlike in three dimensions, it does not satisfy the Jacobi identity, and while the three-dimensional cross product is unique up to a sign, there are many seven-dimensional cross products. The seven-dimensional cross product has the same relationship to the octonions as the three-dimensional product does to the quaternions.
The seven-dimensional cross product is one way of generalising the cross product to other than three dimensions, and it is the only other bilinear product of two vectors that is vector-valued, orthogonal, and has the same magnitude as in the 3D case.[2] In other dimensions there are vector-valued products of three or more vectors that satisfy these conditions, and binary products with bivector results.
Multiplication table
| × | e1 | e2 | e3 | e4 | e5 | e6 | e7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e1 | 0 | e3 | −e2 | e5 | −e4 | −e7 | e6 |
| e2 | −e3 | 0 | e1 | e6 | e7 | −e4 | −e5 |
| e3 | e2 | −e1 | 0 | e7 | −e6 | e5 | −e4 |
| e4 | −e5 | −e6 | −e7 | 0 | e1 | e2 | e3 |
| e5 | e4 | −e7 | e6 | −e1 | 0 | −e3 | e2 |
| e6 | e7 | e4 | −e5 | −e2 | e3 | 0 | −e1 |
| e7 | −e6 | e5 | e4 | −e3 | −e2 | e1 | 0 |
The product can be given by a multiplication table, such as the one here. This table, due to Cayley,[3][4] gives the product of orthonormal basis vectors ei and ej for each i, j from 1 to 7. For example, from the table
The table can be used to calculate the product of any two vectors. For example, to calculate the e1 component of x × y the basis vectors that multiply to produce e1 can be picked out to give
This can be repeated for the other six components.
There are 480 such tables, one for each of the products satisfying the definition.[5] This table can be summarized by the relation[4]
where is a completely antisymmetric tensor with a positive value +1 when ijk = 123, 145, 176, 246, 257, 347, 365.
The top left 3 × 3 corner of this table gives the cross product in three dimensions.
Definition
The cross product on a Euclidean space V is a bilinear map from V × V to V, mapping vectors x and y in V to another vector x × y also in V, where x × y has the properties[1][6]
where (x·y) is the Euclidean dot product and |x| is the Euclidean norm. The first property states that the product is perpendicular to its arguments, while the second property gives the magnitude of the product. An equivalent expression in terms of the angle θ between the vectors[7] is[8]
which is the area of the parallelogram in the plane of x and y with the two vectors as sides.[9] A third statement of the magnitude condition is
if x × x = 0 is assumed as a separate axiom.[10]
Consequences of the defining properties
Given the properties of bilinearity, orthogonality and magnitude, a nonzero cross product exists only in three and seven dimensions.[2][8][10] This can be shown by postulating the properties required for the cross product, then deducing an equation which is only satisfied when the dimension is 0, 1, 3 or 7. In zero dimensions there is only the zero vector, while in one dimension all vectors are parallel, so in both these cases the product must be identically zero.
The restriction to 0, 1, 3 and 7 dimensions is related to Hurwitz's theorem, that normed division algebras are only possible in 1, 2, 4 and 8 dimensions. The cross product is formed from the product of the normed division algebra by restricting it to the 0, 1, 3, or 7 imaginary dimensions of the algebra, giving nonzero products in only three and seven dimensions.[11]
In contrast to the three-dimensional cross product, which is unique (apart from sign), there are many possible binary cross products in seven dimensions. One way to see this is to note that given any pair of vectors x and y and any vector v of magnitude |v| = |x||y| sin θ in the five-dimensional space perpendicular to the plane spanned by x and y, it is possible to find a cross product with a multiplication table (and an associated set of basis vectors) such that x × y = v. Unlike in three dimensions, x × y = a × b does not imply that a and b lie in the same plane as x and y.[8]
Further properties follow from the definition, including the following identities:
Other properties follow only in the three-dimensional case, and are not satisfied by the seven-dimensional cross product, notably,
Because the Jacobi Identity is not satisfied, the seven-dimensional cross product does not give R7 the structure of a Lie algebra.
Coordinate expressions
To define a particular cross product, an orthonormal basis {ej} may be selected and a multiplication table provided that determines all the products {ei × ej}. One possible multiplication table is described in the Example section, but it is not unique.[5] Unlike three dimensions, there are many tables because every pair of unit vectors is perpendicular to five other unit vectors, allowing many choices for each cross product.
Once we have established a multiplication table, it is then applied to general vectors x and y by expressing x and y in terms of the basis and expanding x × y through bilinearity.
| × | e1 | e2 | e3 | e4 | e5 | e6 | e7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e1 | 0 | e4 | e7 | −e2 | e6 | −e5 | −e3 |
| e2 | −e4 | 0 | e5 | e1 | −e3 | e7 | −e6 |
| e3 | −e7 | −e5 | 0 | e6 | e2 | −e4 | e1 |
| e4 | e2 | −e1 | −e6 | 0 | e7 | e3 | −e5 |
| e5 | −e6 | e3 | −e2 | −e7 | 0 | e1 | e4 |
| e6 | e5 | −e7 | e4 | −e3 | −e1 | 0 | e2 |
| e7 | e3 | e6 | −e1 | e5 | −e4 | −e2 | 0 |
Using e1 to e7 for the basis vectors a different multiplication table from the one in the Introduction, leading to a different cross product, is given with anticommutativity by[8]
More compactly this rule can be written as
with i = 1...7 modulo 7 and the indices i, i + 1 and i + 3 allowed to permute evenly. Together with anticommutativity this generates the product. This rule directly produces the two diagonals immediately adjacent to the diagonal of zeros in the table. Also, from an identity in the subsection on consequences,
which produces diagonals further out, and so on.
The ej component of cross product x × y is given by selecting all occurrences of ej in the table and collecting the corresponding components of x from the left column and of y from the top row. The result is:
As the cross product is bilinear the operator x×– can be written as a matrix, which takes the form[citation needed]
The cross product is then given by
Different multiplication tables
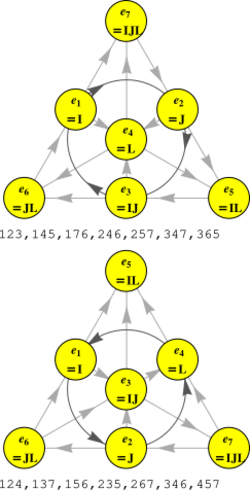
Two different multiplication tables have been used in this article, and there are more.[5][12] These multiplication tables are characterized by the Fano plane,[13][14] and these are shown in the figure for the two tables used here: at top, the one described by Sabinin, Sbitneva, and Shestakov, and at bottom that described by Lounesto. The numbers under the Fano diagrams (the set of lines in the diagram) indicate a set of indices for seven independent products in each case, interpreted as ijk → ei × ej = ek. The multiplication table is recovered from the Fano diagram by following either the straight line connecting any three points, or the circle in the center, with a sign as given by the arrows. For example, the first row of multiplications resulting in e1 in the above listing is obtained by following the three paths connected to e1 in the lower Fano diagram: the circular path e2 × e4, the diagonal path e3 × e7, and the edge path e6 × e1 = e5 rearranged using one of the above identities as:
or
also obtained directly from the diagram with the rule that any two unit vectors on a straight line are connected by multiplication to the third unit vector on that straight line with signs according to the arrows (sign of the permutation that orders the unit vectors).
It can be seen that both multiplication rules follow from the same Fano diagram by simply renaming the unit vectors, and changing the sense of the center unit vector. Considering all possible permutations of the basis there are 480 multiplication tables and so 480 cross products like this.[14]
Using geometric algebra
The product can also be calculated using geometric algebra. The product starts with the exterior product, a bivector valued product of two vectors:
This is bilinear, alternate, has the desired magnitude, but is not vector valued. The vector, and so the cross product, comes from the product of this bivector with a trivector. In three dimensions up to a scale factor there is only one trivector, the pseudoscalar of the space, and a product of the above bivector and one of the two unit trivectors gives the vector result, the dual of the bivector.
A similar calculation is done is seven dimensions, except as trivectors form a 35-dimensional space there are many trivectors that could be used, though not just any trivector will do. The trivector that gives the same product as the above coordinate transform is
This is combined with the exterior product to give the cross product
where is the left contraction operator from geometric algebra.[8][15]
Relation to the octonions
Just as the 3-dimensional cross product can be expressed in terms of the quaternions, the 7-dimensional cross product can be expressed in terms of the octonions. After identifying with the imaginary octonions (the orthogonal complement of the real line in ), the cross product is given in terms of octonion multiplication by
Conversely, suppose V is a 7-dimensional Euclidean space with a given cross product. Then one can define a bilinear multiplication on as follows:
The space with this multiplication is then isomorphic to the octonions.[16]
The cross product only exists in three and seven dimensions as one can always define a multiplication on a space of one higher dimension as above, and this space can be shown to be a normed division algebra. By Hurwitz's theorem such algebras only exist in one, two, four, and eight dimensions, so the cross product must be in zero, one, three or seven dimensions. The products in zero and one dimensions are trivial, so non-trivial cross products only exist in three and seven dimensions.[17][18]
The failure of the 7-dimension cross product to satisfy the Jacobi identity is due to the nonassociativity of the octonions. In fact,
where [x, y, z] is the associator.
Rotations
In three dimensions the cross product is invariant under the action of the rotation group, SO(3), so the cross product of x and y after they are rotated is the image of x × y under the rotation. But this invariance is not true in seven dimensions; that is, the cross product is not invariant under the group of rotations in seven dimensions, SO(7). Instead it is invariant under the exceptional Lie group G2, a subgroup of SO(7).[8][16]
Generalizations
Nonzero binary cross products exist only in three and seven dimensions. Further products are possible when lifting the restriction that it must be a binary product.[19][20] We require the product to be multi-linear, alternating, vector-valued, and orthogonal to each of the input vectors ai. The orthogonality requirement implies that in n dimensions, no more than n − 1 vectors can be used. The magnitude of the product should equal the volume of the parallelotope with the vectors as edges, which can be calculated using the Gram determinant. The conditions are
- orthogonality: for .
- the Gram determinant:
The Gram determinant is the squared volume of the parallelotope with a1, ..., ak as edges.
With these conditions a non-trivial cross product only exists:
- as a binary product in three and seven dimensions
- as a product of n − 1 vectors in n ≥ 3 dimensions, being the Hodge dual of the exterior product of the vectors
- as a product of three vectors in eight dimensions
One version of the product of three vectors in eight dimensions is given by where v is the same trivector as used in seven dimensions, is again the left contraction, and w = −ve12...7 is a 4-vector.
There are also trivial products. As noted already, a binary product only exists in 7, 3, 1 and 0 dimensions, the last two being identically zero. A further trivial 'product' arises in even dimensions, which takes a single vector and produces a vector of the same magnitude orthogonal to it through the left contraction with a suitable bivector. In two dimensions this is a rotation through a right angle.
As a further generalization, we can loosen the requirements of multilinearity and magnitude, and consider a general continuous function (where is endowed with the Euclidean inner product and ) which is only required to satisfy the following two properties:
- The cross product is always orthogonal to all the input vectors.
- If the input vectors are linearly independent, then the cross product is nonzero.
Under these requirements, the cross product only exists (I) for , (II) for , (III) for , and (IV) for any .[1]
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 WS Massey (1983). "Cross products of vectors in higher dimensional Euclidean spaces". The American Mathematical Monthly (Mathematical Association of America) 90 (10): 697–701. doi:10.2307/2323537.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 WS Massey (1983). "Cross products of vectors in higher dimensional Euclidean spaces". The American Mathematical Monthly 90 (10): 697–701. doi:10.2307/2323537. "If one requires only three basic properties of the cross product ... it turns out that a cross product of vectors exists only in 3-dimensional and 7-dimensional Euclidean space.".
- ↑ G Gentili, C Stoppato, DC Struppa and F Vlacci (2009). "Recent developments for regular functions of a hypercomplex variable". Hypercomplex analysis (Conference on quaternionic and Clifford analysis; proceedings ed.). Birkhäuser. p. 168. ISBN 978-3-7643-9892-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=H-5v6pPpyb4C&pg=PA168.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lev Vasilʹevitch Sabinin; Larissa Sbitneva; I. P. Shestakov (2006). "§17.2 Octonion algebra and its regular bimodule representation". Non-associative algebra and its applications. CRC Press. p. 235. ISBN 0-8247-2669-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=_PEWt18egGgC&pg=PA235.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Rafał Abłamowicz; Pertti Lounesto; Josep M. Parra (1996). "§ Four octonionic basis numberings". Clifford algebras with numeric and symbolic computations. Birkhäuser. p. 202. ISBN 0-8176-3907-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=OpbY_abijtwC&pg=PA202.
- ↑ Mappings are restricted to be bilinear by (Massey 1993) and Robert B Brown; Alfred Gray (1967). "Vector cross products". Commentarii Mathematici Helvetici (Birkhäuser Basel) 42 (1/December): 222–236. doi:10.1007/BF02564418..
- ↑ Francis Begnaud Hildebrand (1992). Methods of applied mathematics (Reprint of Prentice-Hall 1965 2nd ed.). Courier Dover Publications. p. 24. ISBN 0-486-67002-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=17EZkWPz_eQC&pg=PA24.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 Lounesto, pp. 96–97
- ↑ Kendall, M. G. (2004). A Course in the Geometry of N Dimensions. Courier Dover Publications. p. 19. ISBN 0-486-43927-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=_dFJ6pSzRLkC&pg=PA19.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Z.K. Silagadze (2002). "Multi-dimensional vector product". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General 35 (23): 4949–4953. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/35/23/310. Bibcode: 2002JPhA...35.4949S.
- ↑ Nathan Jacobson (2009). Basic algebra I (Reprint of Freeman 1974 2nd ed.). Dover Publications. pp. 417–427. ISBN 978-0-486-47189-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=_K04QgAACAAJ.
- ↑ Further discussion of the tables and the connection of the Fano plane to these tables is found here: Tony Smith. "Octonion products and lattices". http://www.tony5m17h.net/480op.html.
- ↑ Rafał Abłamowicz; Bertfried Fauser (2000). Clifford Algebras and Their Applications in Mathematical Physics: Algebra and physics. Springer. p. 26. ISBN 0-8176-4182-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=yvCC94xzJG8C&pg=PA26.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Jörg Schray; Corinne A. Manogue (1996). "Octonionic representations of Clifford algebras and triality". Foundations of Physics 26 (1/January): 17–70. doi:10.1007/BF02058887. Bibcode: 1996FoPh...26...17S. Available as ArXive preprint Figure 1 is located here.
- ↑ Bertfried Fauser (2004). "§18.4.2 Contractions". Clifford algebras: applications to mathematics, physics, and engineering. Birkhäuser. pp. 292 ff. ISBN 0-8176-3525-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=b6mbSCv_MHMC&pg=PA292.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 John C. Baez (2002). "The Octonions". Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 39 (2): 145–205. doi:10.1090/s0273-0979-01-00934-x. http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/octonions/oct.pdf.
- ↑ Elduque, Alberto (2004). Vector cross products. http://www.unizar.es/matematicas/algebra/elduque/Talks/crossproducts.pdf.
- ↑ Darpö, Erik (2009). "Vector product algebras". Bulletin of the London Mathematical Society 41 (5): 898–902. doi:10.1112/blms/bdp066. See also: Real vector product algebras.
- ↑ Lounesto, §7.5: Cross products of k vectors in , p. 98
- ↑ Jean H. Gallier (2001). "Problem 7.10 (2)". Geometric methods and applications: for computer science and engineering. Springer. p. 244. ISBN 0-387-95044-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=CTHaW9ft1ZMC&pg=PA244.
References
- Brown, Robert B.; Gray, Alfred (1967). "Vector cross products". Commentarii Mathematici Helvetici 42 (1): 222–236. doi:10.1007/BF02564418.
- Lounesto, Pertti (2001). Clifford algebras and spinors. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-00551-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=kOsybQWDK4oC.
- Silagadze, Z.K. (2002). "Multi-dimensional vector product". J Phys A 35 (23): 4949–4953. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/35/23/310. Bibcode: 2002JPhA...35.4949S. Also available as ArXiv reprint arXiv:math.RA/0204357.
- Massey, W.S. (1983). "Cross products of vectors in higher dimensional Euclidean spaces". The American Mathematical Monthly 90 (10): 697–701. doi:10.2307/2323537.