Chemistry:Fluoroiodomethane
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Fluoro(iodo)methane | |
| Other names
Fluoroiodomethane
Fluoro-iodo-methane Fluoromethyl iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
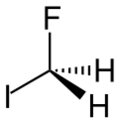
| CH2FI | |
| Molar mass | 159.93 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 53.4 °C (128.1 °F; 326.5 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H330 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Fluoroiodomethane is the halomethane with the formula FCH2I. Also classified as a fluoroiodocarbon (FIC), it is a colorless liquid. It is a reagent for the introduction of the fluoromethyl (FCH2) group.
Synthesis and uses
It is prepared by fluorination of methylene iodide.[1]
Its isotopomer [18F]fluoroiodomethane is used for fluoromethylation of radiopharmaceuticals.
Additional reading
- Zheng L.; Berridge M. S. (January 2000). "Synthesis of [18F]fluoromethyl iodide, a synthetic precursor for fluoromethylation of radiopharmaceuticals". Applied Radiation and Isotopes 52 (1): 55–61(7). doi:10.1016/S0969-8043(99)00061-5. PMID 10670923.
- Tedder, J. M.; Sloan, J. P.; Walton, J. C. (1975). "Free Radical Addition to Olefins, Part XVII. Addition of Fluoroiodomethane to Fluoroethylenes". Journal of the Chemical Society: 1846–1850.
References
- ↑ Landelle, Gregory; Paquin, Jean-Francois (2011). "Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01273. ISBN 978-0471936237.
 |

