Chemistry:Lead carbonate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lead(II) carbonate
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| PbCO 3 | |
| Molar mass | 267.21 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 6.582 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 315 °C (599 °F; 588 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.00011 g/(100 mL) (20 °C) | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
1.46·10−13 |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol, ammonia; soluble in acid, alkali |
| −61.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.804[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H332, H360, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+312, P304+312, P304+340, P308+313, P312, P314, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lead(II) carbonate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula PbCO
3. It is a white solid with several practical uses, despite its toxicity.[2] It occurs naturally as the mineral cerussite.[3]
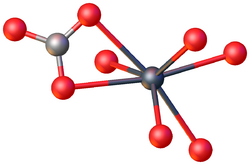
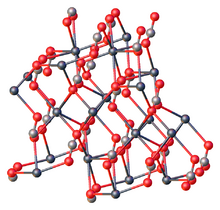
Structure
Like all metal carbonates, lead(II) carbonate adopts a dense, highly crosslinked structure consisting of intact CO2−
3 and metal cation sites. As verified by X-ray crystallography, the Pb(II) centers are seven-coordinate, being surrounded by multiple carbonate ligands. The carbonate centers are bonded bidentate to a single Pb and bridge to five other Pb sites.[4]
Production and use
Lead carbonate is manufactured by passing carbon dioxide into a cold dilute solution of lead(II) acetate, or by shaking a suspension of a lead salt more soluble than the carbonate with ammonium carbonate at a low temperature to avoid formation of basic lead carbonate.[2]
- Pb(CH
3COO)
2 + [NH
4]
2CO
3 → PbCO
3 + 2 [NH
4](CH
3COO)
Lead carbonate is used as a catalyst to polymerize formaldehyde to poly(oxymethylene). It improves the bonding of chloroprene to wire.[2]
Regulations
The supply and use of this compound is restricted in Europe.[5]
Other lead carbonates
A number of lead carbonates are known:
- White lead, a basic lead carbonate, 2PbCO
3 · Pb(OH)
2 - Shannonite, PbCO
3 · PbO - Plumbonacrite, 3PbCO
3 · Pb(OH)
2 · PbO[6] - PbCO
3 · 2PbO - Abellaite, NaPb
2(OH)(CO
3)
2 - Leadhillite, 2PbCO
3 · PbSO
4 · Pb(OH)
2
References
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN:0-07-049439-8
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Carr, Dodd S. (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_249.
- ↑ Inorganic Chemistry, Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman Elsevier 2001 ISBN:0-12-352651-5
- ↑ Sahl, Kurt (1974). "Verfeinerung der Kristallstruktur von Cerussit, PbCO3". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 139 (3–5): 215–222. doi:10.1524/zkri.1974.139.3-5.215. Bibcode: 1974ZK....139..215S.
- ↑ "EU law - EUR-Lex". http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/index.htm.
- ↑ S.V. Krivovichev and P.C. Burns, "Crystal chemistry of basic lead carbonates. II. Crystal structure of synthetic 'plumbonacrite'." Mineralogical Magazine, 64(6), pp. 1069-1075, December 2000. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-05-21. https://web.archive.org/web/20090521065308/http://www.nd.edu/~pburns/pcb075.pdf. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
External links
| H2CO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li2CO3, LiHCO3 |
BeCO3 | B | C | (NH4)2CO3, NH4HCO3 |
O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na2CO3, NaHCO3, Na3H(CO3)2 |
MgCO3, Mg(HCO3)2 |
Al2(CO3)3 | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K2CO3, KHCO3 |
CaCO3, Ca(HCO3)2 |
Sc | Ti | V | Cr | MnCO3 | FeCO3 | CoCO3 | NiCO3 | CuCO3 | ZnCO3 | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb2CO3 | SrCO3 | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag2CO3 | CdCO3 | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs2CO3, CsHCO3 |
BaCO3 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl2CO3 | PbCO3 | (BiO)2CO3 | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La2(CO3)3 | Ce2(CO3)3 | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2CO3 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |