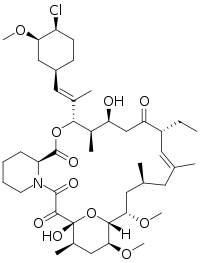
Chemistry:Pimecrolimus
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Elidel |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | low systemic absorption |
| Protein binding | 74%–87% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic CYP3A |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H68ClNO11 |
| Molar mass | 810.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Pimecrolimus is an immunomodulating agent[clarification needed] of the calcineurin inhibitor class used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). It is available as a topical cream, once marketed by Novartis (however, Galderma has been promoting the compound in Canada since early 2007) under the trade name Elidel.
Medical uses
It has been proven to be effective in various inflammatory skin diseases, e.g., seborrheic dermatitis,[1] cutaneous lupus erythematosus,[2] oral lichen planus,[3] vitiligo,[4] and psoriasis.[5][6] Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are both calcineurin inhibitors and function as immunosuppressants.[7]
Atopic dermatitis
If topical corticosteroids and moisturisers fail in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, short-term treatment with topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be tried. Both tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are effective and safe to use in AD.[8][9]
Side effects
In January 2006, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that Elidel packaging would be required to carry a black box warning regarding the potential increased risk of lymph node or skin cancer, as for the similar drug tacrolimus, whereas current practice by United Kingdom dermatologists is not to consider this a significant real concern and they are increasingly recommending the use of such new drugs.[10]
Importantly, although the FDA has approved updated black-box warning for tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, the recent report of the American Academy of Dermatology Association Task Force finds that there is no causal proof that topical immunomodulators cause lymphoma or nonmelanoma skin cancer, and systemic immunosuppression after short-term or intermittent long-term topical application seems an unlikely mechanism.[11] Another recent review of evidence concluded that postmarketing surveillance shows no evidence for this systemic immunosuppression or increased risk for any malignancy.[12] A 2023 systematic review and meta-analysis published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health further concluded with moderate-certainty evidence that the two drugs were not associated with any increased risk of cancer.[13] However, strong debates and controversies continue regarding the exact indications of immunomodulators and their duration of use in the absence of active controlled trials.[14] Dermatologists' and allergists' professional societies, the American Academy of Dermatology,[15] and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, have protested the inclusion of the black box warning. The AAAAI states "None of the information provided for the cases of lymphoma associated with the use of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus in AD indicate or suggest a causal relationship."[16]
Pharmacology
Pimecrolimus is an ascomycin macrolactam derivative. It has been shown in vitro that pimecrolimus binds to FKBP1A and also inhibits calcineurin.[citation needed] Thus pimecrolimus inhibits T-cell activation by inhibiting the synthesis and release of cytokines from T-cells. Pimecrolimus also prevents the release of inflammatory cytokines and mediators from mast cells.[citation needed]
Pimecrolimus, like tacrolimus, belongs to the ascomycin class of macrolactam immunosuppressives, acting by the inhibition of T-cell activation by the calcineurin pathway and inhibition of the release of numerous inflammatory cytokines, thereby preventing the cascade of immune and inflammatory signals.[17] Pimecrolimus has a similar mode of action to that of tacrolimus but is more selective, with no effect on dendritic (Langerhans) cells.[18] It has lower permeation through the skin than topical steroids or topical tacrolimus[19] although they have not been compared with each other for their permeation ability through mucosa. In addition, in contrast with topical steroids, pimecrolimus does not produce skin atrophy.[20]
References
- ↑ "Pimecrolimus cream, 1%, vs hydrocortisone acetate cream, 1%, in the treatment of facial seborrheic dermatitis: a randomized, investigator-blind, clinical trial". Archives of Dermatology 142 (8): 1066–1067. August 2006. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.8.1066. PMID 16924062.
- ↑ "Pimecrolimus 1% cream for cutaneous lupus erythematosus". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 51 (3): 407–410. September 2004. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.01.044. PMID 15337984.
- ↑ "Randomized trial of pimecrolimus cream versus triamcinolone acetonide paste in the treatment of oral lichen planus". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 57 (5): 806–813. November 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.06.022. PMID 17658663.
- ↑ "Topical pimecrolimus in the treatment of vitiligo". European Journal of Dermatology 17 (1): 55–61. 2007. doi:10.1684/ejd.2007.0093. PMID 17324829.
- ↑ "1% pimecrolimus, 0.005% calcipotriol, and 0.1% betamethasone in the treatment of intertriginous psoriasis: a double-blind, randomized controlled study". Archives of Dermatology 142 (9): 1138–1143. September 2006. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.9.1138. PMID 16983001.
- ↑ "Pimecrolimus 1% cream in the treatment of facial psoriasis: a 16-week open-label study". Dermatology 216 (2): 133–136. 2008. doi:10.1159/000111510. PMID 18216475.
- ↑ "The use of topical tacrolimus and pimecrolimus to treat psoriasis: a review". Dermatology Online Journal 10 (1): 3. July 2004. doi:10.5070/D35ZK7V6CS. PMID 15347485.
- ↑ "Topical tacrolimus for atopic dermatitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015 (7): CD009864. July 2015. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009864.pub2. PMID 26132597.
- ↑ "Cancer risk with topical calcineurin inhibitors, pimecrolimus and tacrolimus, for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet. Child & Adolescent Health 7 (1): 13–25. January 2023. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00283-8. PMID 36370744.
- ↑ "Advice to dermatologists re topical tacrolimus" (DOC). British Association of Dermatologists. December 2002. http://www.bad.org.uk/healthcare/guidelines/Advice_re_topical_tacrolimus.doc.
- ↑ "The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. Report of the American Academy of Dermatology Association Task Force". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 54 (5): 818–823. May 2006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.01.054. PMID 16635663.
- ↑ "Safety of topical calcineurin inhibitors in atopic dermatitis: evaluation of the evidence". Current Allergy and Asthma Reports 6 (4): 270–274. July 2006. doi:10.1007/s11882-006-0059-7. PMID 16822378.
- ↑ "Cancer risk with topical calcineurin inhibitors, pimecrolimus and tacrolimus, for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis" (in English). The Lancet. Child & Adolescent Health 7 (1): 13–25. January 2023. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00283-8. PMID 36370744.
- ↑ "Topical calcineurin inhibitors labeling: putting the "box" in perspective". Archives of Dermatology 142 (9): 1233–1235. September 2006. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.9.1233. PMID 16983018.
- ↑ "Statement Regarding FDA Decision On Two Eczema Medications By American Academy Of Dermatology". http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/21091.php.
- ↑ "Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 115 (6): 1249–1253. June 2005. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.04.006. PMID 15940142. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7802521.
- ↑ "Systemic exposure, tolerability, and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in atopic dermatitis patients". Archives of Disease in Childhood 88 (11): 969–973. November 2003. doi:10.1136/adc.88.11.969. PMID 14612358.
- ↑ "Pimecrolimus does not affect Langerhans cells in murine epidermis". The British Journal of Dermatology 149 (4): 853–857. October 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05559.x. PMID 14616380.
- ↑ "Percutaneous absorption of drugs used in atopic eczema: pimecrolimus permeates less through skin than corticosteroids and tacrolimus". International Journal of Pharmaceutics 269 (1): 29–35. January 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.07.013. PMID 14698574.
- ↑ "A randomized controlled trial of pimecrolimus cream 1% in adolescents and adults with head and neck atopic dermatitis and intolerant of, or dependent on, topical corticosteroids". The British Journal of Dermatology 157 (5): 954–959. November 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08192.x. PMID 17935515.
External links
- FDA News
- NPS RADAR
- Article about American Academy of Dermatology speaking out against black box warning
- Report of the Calcineurin Task Force of the ACAAI and AAAAI
 |

