Chemistry:Progesterone (medication)
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Prometrium, Utrogestan, Endometrin, others |
| Other names | P4; Pregnenedione; Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604017 |
| Routes of administration | • By mouth (capsule) • Sublingual (troche) • Topical (cream, gel) • Vaginal (capsule, tablet, gel, suppository, ring) • Rectal (suppository) • IM injection (oil solution) • SC injection (aq. soln.) • Intrauterine (IUD) |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Antimineralocorticoid; Neurosteroid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: <2.4%[3] Vaginal (micronized insert): 4–8%[4][5][6] |
| Metabolism | Mainly liver: • 5α- and 5β-reductase • 3α- and 3β-HSD • 20α- and 20β-HSD • Conjugation • 17α-Hydroxylase • 21-Hydroxylase • CYPs (e.g., CYP3A4) |
| Metabolites | • Dihydroprogesterones • Pregnanolones • Pregnanediols • 20α-Hydroxyprogesterone • 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone • Pregnanetriols • 11-Deoxycorticosterone (and glucuronide/sulfate conjugates) |
| Excretion | Bile and urine[7][8] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 314.469 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Specific rotation | [α]D25 = +172 to +182° (2% in dioxane, β-form) |
| Melting point | 126 °C (259 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Progesterone (P4) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone.[9] It is a progestogen and is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women.[9][10] It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders.[11][12][13][14] Progesterone can be taken by mouth, vaginally, and by injection into muscle or fat, among other routes.[9] A progesterone vaginal ring and progesterone intrauterine device used for birth control also exist in some areas of the world.[15][16]
Progesterone is well tolerated and often produces few or no side effects.[17] However, a number of side effects are possible, for instance mood changes.[17] If progesterone is taken by mouth or at high doses, certain central side effects including sedation, sleepiness, and cognitive impairment can also occur.[17][9] The medication is a naturally occurring progestogen and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor (PR), the biological target of progestogens like endogenous progesterone.[9] It opposes the effects of estrogens in various parts of the body like the uterus and also blocks the effects of the hormone aldosterone.[9][18] In addition, progesterone has neurosteroid effects in the brain.[9]
Progesterone was first isolated in pure form in 1934.[19][20] It first became available as a medication later that year.[21][22] Oral micronized progesterone (OMP), which allowed progesterone to be taken by mouth, was introduced in 1980.[22][11][23] A large number of synthetic progestogens, or progestins, have been derived from progesterone and are used as medications as well.[9] Examples include medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.[9] In 2020, it was the 158th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions.[24][25]
Medical uses
Hormone therapy
Menopause
Progesterone is used in combination with an estrogen as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in peri- and postmenopausal women.[9][26] It is used specifically to provide endometrial protection against unopposed estrogen-induced endometrial hyperplasia and cancer in women with intact uteruses.[9][26] A 2016 systematic review of endometrial protection with progesterone recommended 100 mg/day continuous oral progesterone, 200 mg/day cyclic oral progesterone, 45 to 100 mg/day cyclic vaginal progesterone, and 100 mg alternate-day vaginal progesterone.[18][27] Twice-weekly 100 mg vaginal progesterone was also recommended, but more research is needed on this dose and endometrial monitoring may be advised.[18][27] Transdermal progesterone was not recommended for endometrial protection.[18][27]
The REPLENISH trial was the first adequately powered study to show that continuous 100 mg/day oral progesterone with food provides adequate endometrial protection.[28][29][26][30] Cyclic 200 mg/day oral progesterone has also been found to be effective in the prevention of endometrial hyperplasia, for instance in the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Interventions (PEPI) trial.[28][31][27] However, the PEPI trial was not adequately powered to fully quantify endometrial hyperplasia or cancer risk.[28] No adequately powered studies have assessed endometrial protection with vaginal progesterone.[28] In any case, the Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE) found that cyclic 45 mg/day vaginal progesterone gel showed no significant difference from placebo in endometrial cancer rates.[28][18] Due to the vaginal first-pass effect, low doses of vaginal progesterone may allow for adequate endometrial protection.[11][32][9] Although not sufficiently powered, various other smaller studies have also found endometrial protection with oral or vaginal progesterone.[28][31][27][33] There is inadequate evidence for endometrial protection with transdermal progesterone cream.[18][11][34][35]
Oral progesterone has been found to significantly reduce hot flashes relative to placebo.[28][36] The combination of an estrogen and oral progesterone likewise reduces hot flashes.[28][26] Estrogen plus oral progesterone has been found to significantly improve quality of life.[28][26] The combination of an estrogen and 100 to 300 mg/day oral progesterone has been found to improve sleep outcomes.[28][26][36] Moreover, sleep was improved to a significantly better extent than estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate.[28] This may be attributable to the sedative neurosteroid effects of progesterone.[28] Reduction of hot flashes may also help to improve sleep outcomes.[28] Based on animal research, progesterone may be involved in sexual function in women.[37][38] However, very limited clinical research suggests that progesterone does not improve sexual desire or function in women.[39]
The combination of an estrogen and oral progesterone has been found to improve bone mineral density (BMD) to a similar extent as an estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate.[28] Progestogens, including progesterone, may have beneficial effects on bone independent of those of estrogens, although more research is required to confirm this notion.[40] The combination of an estrogen and oral or vaginal progesterone has been found to improve cardiovascular health in women in early menopause but not in women in late menopause.[28] Estrogen therapy has a favorable influence on the blood lipid profile, which may translate to improved cardiovascular health.[28][9] The addition of oral or vaginal progesterone has neutral or beneficial effects on these changes.[28][26][36] This is in contrast to various progestins, which are known to antagonize the beneficial effects of estrogens on blood lipids.[9][28] Progesterone, both alone and in combination with an estrogen, has been found to have beneficial effects on skin and to slow the rate of skin aging in postmenopausal women.[41][42]
In the French E3N-EPIC observational study, the risk of diabetes was significantly lower in women on menopausal hormone therapy, including with the combination of an oral or transdermal estrogen and oral progesterone or a progestin.[43]
Transgender women
Progesterone is used as a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women in combination with estrogens and antiandrogens.[44][10] However, the addition of progestogens to HRT for transgender women is controversial and their role is unclear.[44][10] Some patients and clinicians believe anecdotally that progesterone may enhance breast development, improve mood, and increase sex drive.[10] However, there is a lack of evidence from well-designed studies to support these notions at present.[10] In addition, progestogens can produce undesirable side effects, although bioidentical progesterone may be safer and better tolerated than synthetic progestogens like medroxyprogesterone acetate.[44][45]
Because some believe that progestogens are necessary for full breast development, progesterone is sometimes used in transgender women with the intention of enhancing breast development.[44][46][45] However, a 2014 review concluded the following on the topic of progesterone for enhancing breast development in transgender women:[46]
Our knowledge concerning the natural history and effects of different cross-sex hormone therapies on breast development in [transgender] women is extremely sparse and based on low quality of evidence. Current evidence does not provide evidence that progestogens enhance breast development in [transgender] women. Neither do they prove the absence of such an effect. This prevents us from drawing any firm conclusion at this moment and demonstrates the need for further research to clarify these important clinical questions.[46]
Data on menstruating women shows there is no correlation between water retention, and levels of progesterone or estrogen.[47] Despite this, some theorise progesterone might cause temporary breast enlargement due to local fluid retention, and may thus give a misleading appearance of breast growth.[48][49] Aside from a hypothetical involvement in breast development, progestogens are not otherwise known to be involved in physical feminization.[45][44]
Pregnancy support
Vaginally dosed progesterone is being investigated as potentially beneficial in preventing preterm birth in women at risk for preterm birth. The initial study by Fonseca suggested that vaginal progesterone could prevent preterm birth in women with a history of preterm birth.[50] According to a recent study, women with a short cervix that received hormonal treatment with a progesterone gel had their risk of prematurely giving birth reduced. The hormone treatment was administered vaginally every day during the second half of a pregnancy.[51] A subsequent and larger study showed that vaginal progesterone was no better than placebo in preventing recurrent preterm birth in women with a history of a previous preterm birth,[52] but a planned secondary analysis of the data in this trial showed that women with a short cervix at baseline in the trial had benefit in two ways: a reduction in births less than 32 weeks and a reduction in both the frequency and the time their babies were in intensive care.[53]
In another trial, vaginal progesterone was shown to be better than placebo in reducing preterm birth prior to 34 weeks in women with an extremely short cervix at baseline.[54] An editorial by Roberto Romero discusses the role of sonographic cervical length in identifying patients who may benefit from progesterone treatment.[55] A meta-analysis published in 2011 found that vaginal progesterone cut the risk of premature births by 42 percent in women with short cervixes.[56][57] The meta-analysis, which pooled published results of five large clinical trials, also found that the treatment cut the rate of breathing problems and reduced the need for placing a baby on a ventilator.[58]
Fertility support
Progesterone is used for luteal support in assisted reproductive technology (ART) cycles such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).[13][59] It is also used to correct luteal phase deficiency to prepare the endometrium for implantation in infertility therapy and is used to support early pregnancy.[60][61]
Birth control
A progesterone vaginal ring is available for birth control when breastfeeding in a number of areas of the world.[15] An intrauterine device containing progesterone has also been marketed under the brand name Progestasert for birth control, including previously in the United States .[62]
Gynecological disorders
Progesterone is used to control persistent anovulatory bleeding.[63][64][65] It is used in non-pregnant women with a delayed menstruation of one or more weeks, in order to allow the thickened endometrial lining to slough off. This process is termed a progesterone withdrawal bleed. Progesterone is taken orally for a short time (usually one week), after which it is discontinued and bleeding should occur.[citation needed]
Other uses
Progesterone is of unclear benefit for the reversal of mifepristone-induced abortion.[66] Evidence is insufficient to support use in traumatic brain injury.[67]
Progesterone has been used as a topical medication applied to the scalp to treat female and male pattern hair loss.[68][69][70][71][72] Variable effectiveness has been reported, but overall its effectiveness for this indication in both sexes has been poor.[69][70][73][72]
Breast pain
Progesterone is approved under the brand name Progestogel as a 1% topical gel for local application to the breasts to treat breast pain in certain countries.[74][75][11] It is not approved for systemic therapy.[76][74] It has been found in clinical studies to inhibit estrogen-induced proliferation of breast epithelial cells and to abolish breast pain and tenderness in women with the condition.[11] However, in one small study in women with cyclic breast pain it was ineffective.[77] Vaginal progesterone has also been found to be effective in the treatment of breast pain and tenderness.[77]
Premenstrual syndrome
Historically, progesterone has been widely used in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome.[78] A 2012 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence for or against the effectiveness of progesterone for this indication.[79] Another review of 10 studies found that progesterone was not effective for this condition, although it stated that insufficient evidence is available currently to make a definitive statement on progesterone in premenstrual syndrome.[78][80]
Catamenial epilepsy
Progesterone can be used to treat catamenial epilepsy by supplementation during certain periods of the menstrual cycle.[81]
Available forms
Progesterone is available in a variety of different forms, including oral capsules; sublingual tablets; vaginal capsules, tablets, gels, suppositories, and rings; rectal suppositories; oil solutions for intramuscular injection; and aqueous solutions for subcutaneous injection.[82][9] A 1% topical progesterone gel is approved for local application to the breasts to treat breast pain, but is not indicated for systemic therapy.[76][74] Progesterone was previously available as an intrauterine device for use in hormonal contraception, but this formulation was discontinued.[82] Progesterone is also limitedly available in combination with estrogens such as estradiol and estradiol benzoate for use by intramuscular injection.[83][84]
In addition to approved pharmaceutical products, progesterone is available in unregulated custom compounded and over-the-counter formulations like systemic transdermal creams and other preparations.[85][86][34][35][87] The systemic efficacy of transdermal progesterone is controversial and has not been demonstrated.[34][35][87]
Contraindications
Contraindications of progesterone include hypersensitivity to progesterone or progestogens, prevention of cardiovascular disease (a Black Box warning), thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic disorder, cerebral hemorrhage, impaired liver function or disease, breast cancer, reproductive organ cancers, undiagnosed vaginal bleeding, missed menstruations, miscarriage, or a history of these conditions.[88][89] Progesterone should be used with caution in people with conditions that may be adversely affected by fluid retention such as epilepsy, migraine headaches, asthma, cardiac dysfunction, and renal dysfunction.[88][89] It should also be used with caution in patients with anemia, diabetes mellitus, a history of depression, previous ectopic pregnancy, and unresolved abnormal Pap smear.[88][89] Use of progesterone is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.[89] However, the medication has been deemed usually safe in breastfeeding by the American Academy of Pediatrics, but should not be used during the first four months of pregnancy.[88] Some progesterone formulations contain benzyl alcohol, and this may cause a potentially fatal "gasping syndrome" if given to premature infants.[88]
Side effects
Progesterone is well tolerated, and many clinical studies have reported no side effects.[17] Side effects of progesterone may include abdominal cramps, back pain, breast tenderness, constipation, nausea, dizziness, edema, vaginal bleeding, hypotension, fatigue, dysphoria, depression, and irritability, among others.[17] Central nervous system depression, such as sedation and cognitive/memory impairment, can also occur.[17][9]
Vaginal progesterone may be associated with vaginal irritation, itchiness, and discharge, decreased libido, painful sexual intercourse, vaginal bleeding or spotting in association with cramps, and local warmth or a "feeling of coolness" without discharge.[17] Intramuscular injection may cause mild-to-moderate pain at the site of injection.[17] High intramuscular doses of progesterone have been associated with increased body temperature, which may be alleviated with paracetamol treatment.[17]
Progesterone lacks undesirable off-target hormonal activity, in contrast to various progestins.[9] As a result, it is not associated with androgenic, antiandrogenic, estrogenic, or glucocorticoid effects.[9] Conversely, progesterone can still produce side effects related to its antimineralocorticoid and neurosteroid activity.[9] Compared to the progestin medroxyprogesterone acetate, there are fewer reports of breast tenderness with progesterone.[17] In addition, the magnitude and duration of vaginal bleeding with progesterone are reported to be lower than with medroxyprogesterone acetate.[17]
Central depression
Progesterone can produce central nervous system depression as an adverse effect, particularly with oral administration or with high doses of progesterone.[9][17] These side effects may include drowsiness, sedation, sleepiness, fatigue, sluggishness, reduced vigor, dizziness, lightheadedness, confusion, and cognitive, memory, and/or motor impairment.[17][90][91] Limited available evidence has shown minimal or no adverse influence on cognition with oral progesterone (100–600 mg), vaginal progesterone (45 mg gel), or progesterone by intramuscular injection (25–200 mg).[92][28][17][93][94] However, high doses of oral progesterone (300–1200 mg), vaginal progesterone (100–200 mg), and intramuscular progesterone (100–200 mg) have been found to result in dose-dependent fatigue, drowsiness, and decreased vigor.[17][93][92][9][95][94][96] Moreover, high single doses of oral progesterone (1200 mg) produced significant cognitive and memory impairment.[17][95][94][9] Intravenous infusion of high doses of progesterone (e.g., 500 mg) has been found to induce deep sleep in humans.[97][98][99][100] Some individuals are more sensitive and can experience considerable sedative and hypnotic effects at lower doses of oral progesterone (e.g., 400 mg).[9][101]
Sedation and cognitive and memory impairment with progesterone are attributable to its inhibitory neurosteroid metabolites.[9] These metabolites occur to a greater extent with oral progesterone, and may be minimized by switching to a parenteral route.[9][102][103] Progesterone can also be taken before bed to avoid these side effects and to help with sleep.[90] The neurosteroid effects of progesterone are unique to progesterone and are not shared with progestins.[9]
Breast cancer
Breast cell proliferation has been found to be significantly increased by the combination of an oral estrogen plus cyclic medroxyprogesterone acetate in postmenopausal women but not by the combination of transdermal estradiol plus oral progesterone.[28] Studies of topical estradiol and progesterone applied to the breasts for 2 weeks have been found to result in highly pharmacological local levels of estradiol and progesterone.[28][104] These studies have assessed breast proliferation markers and have found increased proliferation with estradiol alone, decreased proliferation with progesterone, and no change in proliferation with estradiol and progesterone combined.[28] In the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Interventions (PEPI) trial, the combination of estrogen and cyclic oral progesterone resulted in a higher mammographic breast density than estrogen alone (3.1% vs. 0.9%) but a non-significantly lower breast density than the combination of estrogen and cyclic or continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (3.1% vs. 4.4–4.6%).[28] Higher breast density is a strong known risk factor for breast cancer.[105] Other studies have had mixed findings however.[106] A 2018 systematic review reported that breast density with an estrogen plus oral progesterone was significantly increased in three studies and unchanged in two studies.[106] Changes in breast density with progesterone appear to be less than with the compared progestins.[106]
In large short-term observational studies, estrogen alone and the combination of estrogen and oral progesterone have generally not been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.[28][107][108][27] Conversely, the combination of estrogen and almost any progestin, such as medroxyprogesterone acetate or norethisterone acetate, has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.[28][107][27][108][109] The only exception among progestins is dydrogesterone, which has shown similar risk to that of oral progesterone.[28] Breast cancer risk with estrogen and progestin therapy is duration-dependent, with the risk being significantly greater with more than 5 years of exposure relative to less than 5 years.[107] In contrast to shorter-term studies, the longer-term observations (>5 years) of the French E3N study showed significant associations of both estrogen plus oral progesterone and estrogen plus dydrogesterone with higher breast cancer risk, similarly to estrogen plus other progestogens.[28] Oral progesterone has very low bioavailability and has relatively weak progestogenic effects.[109][110] The delayed onset of breast cancer risk with estrogen plus oral progesterone is potentially consistent with a weak proliferative effect of oral progesterone on the breasts.[109][110] As such, a longer duration of exposure may be necessary for a detectable increase in breast cancer risk to occur.[109][110] In any case, the risk remains lower than that with most progestins.[28][108] A 2018 systematic review of progesterone and breast cancer concluded that short-term use (<5 years) of an estrogen plus progesterone is not associated with a significant increase in risk of breast cancer but that long-term use (>5 years) is associated with greater risk.[106] The conclusions for progesterone were the same in a 2019 meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer (CGHFBC).[111]
Most data on breast density changes and breast cancer risk are with oral progesterone.[106] Data on breast safety with vaginal progesterone are scarce.[106] The Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE) was a randomized controlled trial of about 650 postmenopausal women who used estradiol and 45 mg/day cyclic vaginal progesterone.[106][112] Incidence of breast cancer was reported as an adverse effect.[106][112] The absolute incidences were 10 cases in the estradiol plus vaginal progesterone group and 8 cases in the control group.[106][112] However, the study was not adequately powered for quantifying breast cancer risk.[106][112]
Blood clots
Whereas the combination of estrogen and a progestin is associated with increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) relative to estrogen alone, there is no difference in risk of VTE with the combination of estrogen and oral progesterone relative to estrogen alone.[110][113] Hence, in contrast to progestins, oral progesterone added to estrogen does not appear to increase coagulation or VTE risk.[110][113] The reason for the differences between progesterone and progestins in terms of VTE risk are unclear.[114][110][109] However, they may be due to very low progesterone levels and relatively weak progestogenic effects produced by oral progesterone.[110][109] In contrast to oral progesterone, non-oral progesterone—which can achieve much higher progesterone levels—has not been assessed in terms of VTE risk.[110][109]
Overdose
Progesterone is likely to be relatively safe in overdose. Levels of progesterone during pregnancy are up to 100-fold higher than during normal menstrual cycling, although levels increase gradually over the course of pregnancy.[115] Oral dosages of progesterone of as high as 3,600 mg/day have been assessed in clinical trials, with the main side effect being sedation.[116] There is a case report of progesterone misuse with an oral dosage of 6,400 mg per day.[117] Administration of as much as 500 mg progesterone by intravenous infusion in humans was uneventful in terms of toxicity, but did induce deep sleep, though the individuals were still able to be awakened with sufficient stimulation.[97][98][99][100]
Interactions
There are several notable drug interactions with progesterone. Certain selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline may increase the GABAA receptor-related central depressant effects of progesterone by enhancing its conversion into 5α-dihydroprogesterone and allopregnanolone via activation of 3α-HSD.[118] Progesterone potentiates the sedative effects of benzodiazepines and alcohol.[119] Notably, there is a case report of progesterone abuse alone with very high doses.[120] 5α-Reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride inhibit the conversion of progesterone into the inhibitory neurosteroid allopregnanolone, and for this reason, may have the potential to reduce the sedative and related effects of progesterone.[121][122][123]
Progesterone is a weak but significant agonist of the pregnane X receptor (PXR), and has been found to induce several hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP3A4, especially when concentrations are high, such as with pregnancy range levels.[124][125][126][127] As such, progesterone may have the potential to accelerate the metabolism of various medications.[124][125][126][127]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Progesterone is a progestogen, or an agonist of the nuclear progesterone receptors (PRs), the PR-A, PR-B, and PR-C.[9] In addition, progesterone is an agonist of the membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs), including the mPRα, mPRβ, mPRγ, mPRδ, and mPRϵ.[128][129] Aside from the PRs and mPRs, progesterone is a potent antimineralocorticoid, or antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor, the biological target of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone.[130][131] In addition to its activity as a steroid hormone, progesterone is a neurosteroid.[132] Among other neurosteroid activities, and via its active metabolites allopregnanolone and pregnanolone, progesterone is a potent positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, the major signaling receptor of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).[133]
The PRs are expressed widely throughout the body, including in the uterus, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes, breasts, fat, skin, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and in other areas of the brain.[9][134] In accordance, progesterone has numerous effects throughout the body.[9] Among other effects, progesterone produces changes in the female reproductive system, the breasts, and the brain.[9][134] Progesterone has functional antiestrogenic effects due to its progestogenic activity, including in the uterus, cervix, and vagina.[9] The effects of progesterone may influence health in both positive and negative ways.[9] In addition to the aforementioned effects, progesterone has antigonadotropic effects due to its progestogenic activity, and can inhibit ovulation and suppress gonadal sex hormone production.[9]
The activities of progesterone besides those mediated by the PRs and mPRs are also of significance.[9] Progesterone lowers blood pressure and reduces water and salt retention among other effects via its antimineralocorticoid activity.[9][135] In addition, progesterone can produce sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, euphoric, amnestic, cognitive-impairing, motor-impairing, anticonvulsant, and even anesthetic effects via formation of sufficiently high concentrations of its neurosteroid metabolites and consequent GABAA receptor potentiation in the brain.[17][90][91][136]
There are differences between progesterones and progestins, such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone, with implications for pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, as well as for efficacy, tolerability, and safety.[9]
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of progesterone are dependent on its route of administration. The medications is approved in the form of oil-filled capsules containing micronized progesterone for oral administration, termed oral micronized progesterone or OMP.[137] It is also available in the form of vaginal or rectal suppositories or pessaries, topical creams and gels,[138] oil solutions for intramuscular injection, and aqueous solutions for subcutaneous injection.[137][102][139]
Routes of administration that progesterone has been used by include oral, intranasal, transdermal/topical, vaginal, rectal, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intravenous injection.[102] Vaginal progesterone is available in the form of progesterone capsules, tablets or inserts, gels, suppositories or pessaries, and rings.[102]
The bioavailability of progesterone was commonly overestimated due to the immunoassay method of analysis failing to distinguish between progesterone itself and its metabolites.[140][109][110] Newer methods have adjusted the oral bioavailbility estimate from 6.2 to 8.6%[141] down to less than 2.4%.[3]
Chemistry
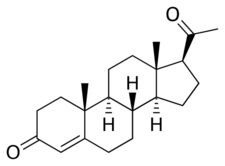
Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane steroid and is also known as pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione.[142][143] It has a double bond (4-ene) between the C4 and C5 positions and two ketone groups (3,20-dione), one at the C3 position and the other at the C20 position.[142][143] Due to its pregnane core and C4(5) double bond, progesterone is often abbreviated as P4. It is contrasted with pregnenolone, which has a C5(6) double bond and is often abbreviated as P5.
Derivatives
A large number of progestins, or synthetic progestogens, have been derived from progesterone.[142][9] They can be categorized into several structural groups, including derivatives of retroprogesterone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, 17α-methylprogesterone, and 19-norprogesterone, with a respective example from each group including dydrogesterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, medrogestone, and promegestone.[9] The progesterone ethers quingestrone (progesterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether) and progesterone 3-acetyl enol ether are among the only examples that do not belong to any of these groups.[134][144] Another major group of progestins, the 19-nortestosterone derivatives, exemplified by norethisterone (norethindrone) and levonorgestrel, are not derived from progesterone but rather from testosterone.[9]
A variety of synthetic inhibitory neurosteroids have been derived from progesterone and its neurosteroid metabolites, allopregnanolone and pregnanolone.[142] Examples include alfadolone, alfaxolone, ganaxolone, hydroxydione, minaxolone, and renanolone.[142] In addition, C3 and C20 conjugates of progesterone, such as progesterone carboxymethyloxime (progesterone 3-(O-carboxymethyl)oxime; P4-3-CMO), P1-185 (progesterone 3-O-(L-valine)-E-oxime), EIDD-1723 (progesterone 20E-[O-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxime] sodium salt), EIDD-036 (progesterone 20-oxime; P4-20-O), and VOLT-02 (chemical structure unreleased), have been developed as water-soluble prodrugs of progesterone and its neurosteroid metabolites.[145][146][147][148][149][150]
Synthesis
Chemical syntheses of progesterone have been published.[151]
History
Discovery and synthesis
The hormonal action of progesterone was discovered in 1929.[19][20][152] Pure crystalline progesterone was isolated in 1934 and its chemical structure was determined.[19][20] Later that year, chemical synthesis of progesterone was accomplished.[20][153] Shortly following its chemical synthesis, progesterone began being tested clinically in women.[20][154]
Injections and implants
In 1933 or 1934, Schering introduced progesterone in oil solution as a medication by intramuscular injection under the brand name Proluton.[155][21][22][11][156] This was the first pharmaceutical formulation of progesterone to be marketed for medical use.[157] It was initially a corpus luteum extract, becoming pure synthesized progesterone only subsequently.[158][159][155][160] A clinical study of the formulation was published in 1933.[155][161][159] Multiple formulations of progesterone in oil solution for intramuscular injection, under the brand names Proluton, Progestin, and Gestone, were available by 1936.[158][162] A parenteral route was used because oral progesterone had very low activity and was thought to be inactive.[11][156][160] Progesterone was initially very expensive due to the large doses required.[163] However, with the start of steroid manufacturing from diosgenin in the 1940s, costs greatly decreased.[164]
Subcutaneous pellet implants of progesterone were first studied in women in the late 1930s.[165][166][167][168][169] They were the first long-acting progestogen formulation.[170] Pellets were reported to be extruded out of the skin within a few weeks at high rates, even when implanted beneath the deep fascia, and also produced frequent inflammatory reactions at the site of implantation.[171][167][172] In addition, they were absorbed too slowly and achieved unsatisfactorily low progesterone levels.[171] Consequently, they were soon abandoned, in favor of other preparations such as aqueous suspensions.[171][172][173][170] However, subcutaneous pellet implants of progesterone were later studied as a form of birth control in women in the 1980s and early 1990s, though no preparations were ultimately marketed.[174][175][176][177]
Aqueous suspensions of progesterone crystals for intramuscular injection were first described in 1944.[170][178][179][180] These preparations were on the market in the 1950s under a variety of brand names including Flavolutan, Luteosan, Lutocyclin M, and Lutren, among others.[181] Aqueous suspensions of steroids were developed because they showed much longer durations than intramuscular injection of steroids in oil solution.[182] However, local injection site reactions, which do not occur with oil solutions, have limited the clinical use of aqueous suspensions of progesterone and other steroids.[183][184][185] Today, a preparation with the brand name Agolutin Depot remains on the market in the Czech Republic and Slovakia.[186][187] A combined preparation of progesterone, estradiol benzoate, and lidocaine remains available with the brand name Clinomin Forte in Paraguay as well.[188] In addition to aqueous suspensions, water-in-oil emulsions of steroids were studied by 1949,[189][190][191] and long-acting emulsions of progesterone were introduced for use by intramuscular injection under the brand names Progestin and Di-Pro-Emulsion (with estradiol benzoate) by the 1950s.[181][192][193][194][195] Due to lack of standardization of crystal sizes, crystalline suspensions of steroids had marked variations in effect.[171] Emulsions were said to be even more unreliable.[171]
Macrocrystalline aqueous suspensions of progesterone as well as microspheres of progesterone were investigated as potential progestogen-only injectable contraceptives and combined injectable contraceptives (with estradiol) by the late 1980s and early 1990s but were never marketed.[196][197][198][199][200]
Aqueous solutions of water-insoluble steroids were first developed via association with colloid solubility enhancers in the 1940s.[201] An aqueous solution of progesterone for use by intravenous injection was marketed by Schering AG under the brand name Primolut Intravenous by 1962.[202][203] One of its intended uses was the treatment of threatened abortion, in which rapid-acting effect was desirable.[171] An aqueous solution of progesterone complexed with cyclodextrin to increase its water solubility was introduced for use by once-daily subcutaneous injection in Europe under the brand name Prolutex in the mid-2010s.[204][102]
In the 1950s, long-acting parenteral progestins such as hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and norethisterone enanthate were developed and introduced for use by intramuscular injection.[170][205][206] They lacked the need for frequent injections and the injection site reactions associated with progesterone by intramuscular injection and soon supplanted progesterone for parenteral therapy in most cases.[206][205][207]
Oral and sublingual
The first study of oral progesterone in humans was published in 1949.[208][209] It found that oral progesterone produced significant progestational effects in the endometrium in women.[208] Prior to this study, animal research had suggested that oral progesterone was inactive, and for this reason, oral progesterone had never been evaluated in humans.[208][209] A variety of other early studies of oral progesterone in humans were also published in the 1950s and 1960s.[209][210][211][212][213][214][215][216][217][218] These studies generally reported oral progesterone to be only very weakly active.[209][214][213] Oral non-micronized progesterone was introduced as a pharmaceutical medication around 1953, for instance as Cyclogesterin (1 mg estrogenic substances and 30 mg progesterone tablets) for menstrual disturbances by Upjohn, though it saw limited use.[219][220] Another preparation, which contained progesterone alone, was Synderone (trademark registered by Chemical Specialties in 1952).[221][222][223]
Sublingual progesterone in women was first studied in 1944 by Robert Greenblatt.[224][225][172][208][226][212] Buccal progesterone tablets were marketed by Schering under the brand name Proluton Buccal Tablets by 1949.[227] Sublingual progesterone tablets were marketed under the brand names Progesterone Lingusorbs and Progesterone Membrettes by 1951.[228][229][230] A sublingual tablet formulation of progesterone has been approved under the brand name Luteina in Poland and Ukraine and remains marketed today.[83][84]
Progesterone was the first progestogen that was found to inhibit ovulation, both in animals and in women.[231] Injections of progesterone were first shown to inhibit ovulation in animals between 1937 and 1939.[232][231][233][234] Inhibition of fertilization by administration of progesterone during the luteal phase was also demonstrated in animals between 1947 and 1949.[232] Ovulation inhibition by progesterone in animals was subsequently re-confirmed and expanded on by Gregory Pincus and colleagues in 1953 and 1954.[231][235][236] Findings on inhibition of ovulation by progesterone in women were first presented at the Fifth International Conference on Planned Parenthood in Tokyo, Japan in October 1955.[218][237] Three different research groups presented their findings on this topic at the conference.[218][237] They included Pincus (in conjunction with John Rock, who did not attend the conference); a nine-member Japanese group led by Masaomi Ishikawa; and the two-member team of Abraham Stone and Herbert Kupperman.[218][237][238][239][240] The conference marked the beginning of a new era in the history of birth control.[237] The results were subsequently published in scientific journals in 1956 in the case of Pincus and in 1957 in the case of Ishikawa and colleagues.[241][242][243] Rock and Pincus also subsequently described findings from 1952 that "pseudopregnancy" therapy with a combination of high doses of diethylstilbestrol and oral progesterone prevented ovulation and pregnancy in women.[215][244][245][246][247][248]
Unfortunately, the use of oral progesterone as a hormonal contraceptive was plagued by problems.[231][246] These included the large and by extension expensive doses required, incomplete inhibition of ovulation even at high doses, and a frequent incidence of breakthrough bleeding.[231][246] At the 1955 Tokyo conference, Pincus had also presented the first findings of ovulation inhibition by oral progestins in animals, specifically 19-nortestosterone derivatives like noretynodrel and norethisterone.[246][218] These progestins were far more potent than progesterone, requiring much smaller doses orally.[246][218] By December 1955, inhibition of ovulation by oral noretynodrel and norethisterone had been demonstrated in women.[246] These findings as well as results in animals were published in 1956.[249][250] Noretynodrel and norethisterone did not show the problems associated with oral progesterone—in the studies, they fully inhibited ovulation and did not produce menstruation-related side effects.[246] Consequently, oral progesterone was abandoned as a hormonal contraceptive in women.[231][246] The first birth control pills to be introduced were a noretynodrel-containing product in 1957 and a norethisterone-containing product in 1963, followed by numerous others containing a diversity of progestins.[251] Progesterone itself has never been introduced for use in birth control pills.[252]
More modern clinical studies of oral progesterone demonstrating elevated levels of progesterone and end-organ responses in women, specifically progestational endometrial changes, were published between 1980 and 1983.[253][254][255][256] Up to this point, many clinicians and researchers apparently still thought that oral progesterone was inactive.[256][257][258] It was not until almost half a century after the introduction of progesterone in medicine that a reasonably effective oral formulation of progesterone was marketed.[259] Micronization of progesterone and suspension in oil-filled capsules, which allowed progesterone to be absorbed several-fold more efficiently by the oral route, was first studied in the late 1970s and described in the literature in 1982.[260][255][261] This formulation, known as oral micronized progesterone (OMP), was then introduced for medical use under the brand name Utrogestan in France in 1982.[255][23][22][11] Subsequently, oral micronized progesterone was introduced under the brand name Prometrium in the United States in 1998.[141][262] By 1999, oral micronized progesterone had been marketed in more than 35 countries.[141] In 2019, the first combination of oral estradiol and progesterone was introduced under the brand name Bijuva in the United States.[263][264]
A sustained-release (SR) formulation of oral micronized progesterone, also known as "oral natural micronized progesterone sustained release" or "oral NMP SR", was marketed in India in 2012 under the brand name Gestofit SR.[265][266][267][83] Many additional brand names followed.[266][83] The preparation was originally developed in 1986 by a compounding pharmacy called Madison Pharmacy Associates in Madison, Wisconsin in the United States .[265][267]
Vaginal, rectal, and uterine
Vaginal progesterone suppositories were first studied in women by Robert Greenblatt in 1954.[268][172][269] Shortly thereafter, vaginal progesterone suppositories were introduced for medical use under the brand name Colprosterone in 1955.[270][172] Rectal progesterone suppositories were first studied in men and women by Christian Hamburger in 1965.[271][269] Vaginal and rectal progesterone suppositories were introduced for use under the brand name Cyclogest by 1976.[272][273][274] Vaginal micronized progesterone gels and capsules were introduced for medical use under brand names such as Utrogestan and Crinone in the early 1990s.[259][275] Progesterone was approved in the United States as a vaginal gel in 1997 and as a vaginal insert in 2007.[276][277] A progesterone contraceptive vaginal ring known as Progering was first studied in women in 1985 and continued to be researched through the 1990s.[278][279] It was approved for use as a contraceptive in lactating mothers in Latin America by 2004.[278] A second progesterone vaginal ring known as Fertiring was developed as a progesterone supplement for use during assisted reproduction and was approved in Latin America by 2007.[280][281]
Development of a progesterone-containing intrauterine device (IUD) for contraception began in the 1960s.[282] Incorporation of progesterone into IUDs was initially studied to help reduce the risk of IUD expulsion.[282] However, while addition of progesterone to IUDs showed no benefit on expulsion rates, it was unexpectedly found to induce endometrial atrophy.[282] This led in 1976 to the development and introduction of Progestasert, a progesterone-containing product and the first progestogen-containing IUD.[62][282][16] Unfortunately, the product had various problems that limited its use.[282][16][62] These included a short duration of efficacy of only one year, a high cost, a relatively high 2.9% failure rate, a lack of protection against ectopic pregnancy, and difficult and sometimes painful insertions that could necessitate use of a local anesthetic or analgesic.[282][16][62] As a result of these issues, Progestasert never became widely used, and was discontinued in 2001.[282][16][62] It was used mostly in the United States and France while it was marketed.[16]
Transdermal and topical
A topical gel formulation of progesterone, for direct application to the breasts as a local therapy for breast disorders such as breast pain, was introduced under the brand name Progestogel in Europe by 1972.[283] No transdermal formulations of progesterone for systemic use have been successfully marketed, in spite of efforts of pharmaceutical companies towards this goal.[34][11][284] The low potency of transdermal progesterone has thus far precluded it as a possibility.[285][286][287][103] Although no formulations of transdermal progesterone are approved for systemic use, transdermal progesterone is available in the form of creams and gels from custom compounding pharmacies in some countries, and is also available over-the-counter without a prescription in the United States.[34][35][87] However, these preparations are unregulated and have not been adequately characterized, with low and unsubstantiated effectiveness.[34][11]
Society and culture
Generic names
Progesterone is the generic name of the drug in English and its INN, USAN, USP, BAN, DCIT, and JAN, while progestérone is its name in French and its DCF.[83][142][143][288] It is also referred to as progesteronum in Latin, progesterona in Spanish and Portuguese, and progesteron in German.[83][143]
Brand names

Progesterone is marketed under a large number of brand names throughout the world.[83][143] Examples of major brand names under which progesterone has been marketed include Crinone, Crinone 8%, Cyclogest, Endogest, Endometrin, Estima, Geslutin, Gesterol, Gestone, Luteina, Luteinol, Lutigest, Lutinus, Microgest, Progeffik, Progelan, Progendo, Progering, Progest, Progestaject, Progestan, Progesterone, Progestin, Progestogel, Prolutex, Proluton, Prometrium, Prontogest, Strone, Susten, Utrogest, and Utrogestan.[83][143]
Availability
Progesterone is widely available in countries throughout the world in a variety of formulations.[83][84] Progesterone in the form of oral capsules; vaginal capsules, tablets/inserts, and gels; and intramuscular oil have widespread availability.[83][84] The following formulations/routes of progesterone have selective or more limited availability:[83][84]
- A tablet of micronized progesterone which is marketed under the brand name Luteina is indicated for sublingual administration in addition to vaginal administration and is available in Poland and Ukraine .[83][84]
- A progesterone suppository which is marketed under the brand name Cyclogest is indicated for rectal administration in addition to vaginal administration and is available in Cyprus, Hong Kong, India, Malaysia, Malta, Oman, Singapore, South Africa , Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, the United Kingdom , and Vietnam.[83][84]
- An aqueous solution of progesterone complexed with β-cyclodextrin for subcutaneous injection is marketed under the brand name Prolutex in the Czech Republic, Hungary, Italy, Poland , Portugal, Slovakia, Spain , and Switzerland .[83][84]
- A non-systemic topical gel formulation of progesterone for local application to the breasts to treat breast pain is marketed under the brand name Progestogel and is available in Belgium, Bulgaria, Colombia, Ecuador, France , Georgia, Germany , Hong Kong, Lebanon, Peru, Romania, Russia , Serbia, Switzerland , Tunisia, Venezuela, and Vietnam.[83][84] It was also formerly available in Italy, Portugal, and Spain , but was discontinued in these countries.[84]
- A progesterone intrauterine device was previously marketed under the brand name Progestasert and was available in Canada , France , the United States , and possibly other countries, but was discontinued.[84][289]
- Progesterone vaginal rings are marketed under the brand names Fertiring and Progering and are available in Chile , Ecuador, and Peru.[83][84]
- A sustained-release tablet formulation of oral micronized progesterone (also known as "oral natural micronized progesterone sustained release" or "oral NMP SR") is marketed in India under the brand names Lutefix Pro (CROSMAT Technology), Dubagest SR, Gestofit SR, and Susten SR, among many others.[265][290][291][292][293][294][295][267][83]
In addition to single-drug formulations, the following progesterone combination formulations are or have been marketed, albeit with limited availability:[83][84]
- A combination pack of progesterone capsules for oral use and estradiol gel for transdermal use is marketed under the brand name Estrogel Propak in Canada .[83][84]
- A combination pack of progesterone capsules and estradiol tablets for oral use is marketed in an under the brand name Duogestan in Belgium.[83][84]
- Progesterone and estradiol in an aqueous suspension for use by intramuscular injection is marketed under the brand name Cristerona FP in Argentina .[83][84]
- Progesterone and estradiol in microspheres in an oil solution for use by intramuscular injection is marketed under the brand name Juvenum in Mexico.[83][84][296]
- Progesterone and estradiol benzoate in an oil solution for use by intramuscular injection is marketed under the brand names Duogynon, Duoton Fort T P, Emmenovis, Gestrygen, Lutofolone, Menovis, Mestrolar, Metrigen Fuerte, Nomestrol, Phenokinon-F, Prodiol, Pro-Estramon-S, Proger F, Progestediol, and Vermagest and is available in Belize, Egypt, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Guatemala, Honduras, Italy, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mexico, Nicaragua, Taiwan, Thailand, and Turkey.[83][84]
- Progesterone and estradiol hemisuccinate in an oil solution for use by intramuscular injection is marketed under the brand name Hosterona in Argentina .[83][84]
- Progesterone and estrone for use by intramuscular injection is marketed under the brand name Synergon in Monaco.[83]
United States
(As of November 2016), progesterone is available in the United States in the following formulations:[82]
- Oral: Capsules: Prometrium (100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg)
- Vaginal: Tablets: Endometrin (100 mg); Gels: Crinone (4%, 8%)
- Intramuscular injection: Oil: Progesterone (50 mg/mL)
A 25 mg/mL concentration of progesterone oil for intramuscular injection and a 38 mg/device progesterone intrauterine device (Progestasert) have been discontinued.[82]
An oral combination formulation of micronized progesterone and estradiol in oil-filled capsules (brand name Bijuva) is marketed in the United States for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and endometrial hyperplasia.[297][263]
Progesterone is also available in unregulated custom preparations from compounding pharmacies in the United States.[85][86] In addition, transdermal progesterone is available over-the-counter in the United States, although the clinical efficacy of transdermal progesterone is controversial.[34][35][87]
Research
Progesterone was studied as a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive, but was never marketed.[196][197][198] Combinations of estradiol and progesterone as a macrocrystalline aqueous suspension and as an aqueous suspension of microspheres have been studied as once-a-month combined injectable contraceptives, but were likewise never marketed.[197][199]
Progesterone has been assessed for the suppression of sex drive and spermatogenesis in men.[298][299] In one study, 100 mg rectal suppositories of progesterone given five times per day for 9 days resulted in progesterone levels of 5.5 to 29 ng/mL and suppressed circulating testosterone and growth hormone levels by about 50% in men, but did not affect libido or erectile potency in this short treatment period.[298][300] In other studies, 50 mg/day progesterone by intramuscular injection for 10 weeks in men produced azoospermia, decreased testicular size, markedly suppressed libido and erectile potency, and resulted in minimal semen volume upon ejaculation.[298][299][301][302]
An oil and water nanoemulsion of progesterone (particles of <1 mm in diameter) using micellar nanoparticle technology for transdermal administration known as Progestsorb NE was under development by Novavax for use in menopausal hormone therapy in the 2000s.[303][304][305] However, development was discontinued in 2007 and the formulation was never marketed.[303]
See also
- Estradiol/progesterone
- Estradiol benzoate/progesterone
- Estradiol hemisuccinate/progesterone
References
- ↑ Handbook of Behavioral Neurobiology Volume 7 Reproduction (1st ed.). New York: Plenum Press. 6 December 2012. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-4684-4834-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=MoDrBwAAQBAJ&q=pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione;+abbreviated+as+P4&pg=PA189. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ↑ "Search Page - Drug and Health Product Register". 23 October 2014. https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/regulatory-decision-summary-detail.php?lang=en&linkID=RDS00517.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of crinone 8% administered vaginally versus Prometrium administered orally in postmenopausal women(3)". Fertility and Sterility 73 (3): 516–521. March 2000. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00553-1. PMID 10689005.
- ↑ "Dydrogesterone: pharmacological profile and mechanism of action as luteal phase support in assisted reproduction". Reproductive Biomedicine Online 38 (2): 249–259. February 2019. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.11.017. PMID 30595525.
- ↑ "Evaluating the clinical efficacy and safety of progestogens in the management of threatened and recurrent miscarriage in early pregnancy-A review of the literature". Indian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research 3 (2): 157. 2016. doi:10.5958/2394-2754.2016.00043.6. ISSN 2394-2746.
- ↑ "Progesterone pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics with 3 dosages and 2 regimens of an effervescent micronized progesterone vaginal insert". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 99 (11): 4241–4249. November 2014. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3937. PMID 24606090.
- ↑ "PROMETRIUM (progesterone, USP) Capsules 100 mg". Solvay Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 1998. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/1998/20843lbl.pdf.
- ↑ "Progesterone Injection USP in Sesame Oil for Intramuscular Use Only Rx Only". Watson Laboratories, Inc.. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. January 2007. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/017362s104lbl.pdf.
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 9.17 9.18 9.19 9.20 9.21 9.22 9.23 9.24 9.25 9.26 9.27 9.28 9.29 9.30 9.31 9.32 9.33 9.34 9.35 9.36 9.37 9.38 "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric 8 (Suppl 1): 3–63. August 2005. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 "Hormonal and Surgical Treatment Options for Transgender Women and Transfeminine Spectrum Persons". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America 40 (1): 99–111. March 2017. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2016.10.006. PMID 28159148.
- ↑ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 11.10 "Systemic progesterone therapy--oral, vaginal, injections and even transdermal?". Maturitas 79 (3): 248–255. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.07.009. PMID 25113944.
- ↑ "Clinical roles and applications of progesterone in reproductive medicine: an overview". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 94 (Suppl 161): 3–7. November 2015. doi:10.1111/aogs.12791. PMID 26443945.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Clinical use of progesterone in infertility and assisted reproduction". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 94 (Suppl 161): 17–27. November 2015. doi:10.1111/aogs.12770. PMID 26345161.
- ↑ "Use of progesterone supplement therapy for prevention of preterm birth: review of literatures". Obstetrics & Gynecology Science 60 (5): 405–420. September 2017. doi:10.5468/ogs.2017.60.5.405. PMID 28989916.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Contraception for Adolescent and Young Adult Women. Springer. 2014. p. 98. ISBN 9781461465799. https://books.google.com/books?id=vMQkBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA98.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 Chaudhuri (2007). Practice of Fertility Control: A Comprehensive Manual (7Th ed.). Elsevier India. pp. 153–. ISBN 978-81-312-1150-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=pzanxKlcU74C&pg=PA153.
- ↑ 17.00 17.01 17.02 17.03 17.04 17.05 17.06 17.07 17.08 17.09 17.10 17.11 17.12 17.13 17.14 17.15 17.16 "Progesterone: review of safety for clinical studies". Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 15 (5): 427–444. October 2007. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.15.5.427. PMID 17924777.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 "The impact of micronized progesterone on the endometrium: a systematic review". Climacteric 19 (4): 316–328. August 2016. doi:10.1080/13697137.2016.1187123. PMID 27277331.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Gynecologic Endocrinology. Springer Science & Business Media. 11 November 2013. pp. 9, 25–29, 139. ISBN 978-1-4613-2157-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=9vv2BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 Is Menstruation Obsolete?. Oxford University Press. 1999. pp. 31–. ISBN 978-0-19-513021-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=1ZzmCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA31.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 The Greatest Experiment Ever Performed on Women: Exploding the Estrogen Myth. Seven Stories Press. 4 January 2011. pp. 27–. ISBN 978-1-60980-062-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=HHm1qkcgFSUC&pg=PA27.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "Micronized progesterone: vaginal and oral uses". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 38 (4): 902–914. December 1995. doi:10.1097/00003081-199538040-00024. PMID 8616985.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "[Utrogestan]" (in fr). Soins. Gynecologie, Obstetrique, Puericulture, Pediatrie (16): 45–46. September 1982. PMID 6925387.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Progesterone - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Progesterone.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 26.5 26.6 "A combined, bioidentical, oral, 17β-estradiol and progesterone capsule for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause". Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 12 (8): 729–739. August 2019. doi:10.1080/17512433.2019.1637731. PMID 31282768.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 27.3 27.4 27.5 27.6 "The endometrial and breast safety of menopausal hormone therapy containing micronised progesterone: A short review". The Australian & New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 57 (1): 12–15. February 2017. doi:10.1111/ajo.12583. PMID 28251642.
- ↑ 28.00 28.01 28.02 28.03 28.04 28.05 28.06 28.07 28.08 28.09 28.10 28.11 28.12 28.13 28.14 28.15 28.16 28.17 28.18 28.19 28.20 28.21 28.22 28.23 28.24 28.25 28.26 28.27 "Evidence on the use of progesterone in menopausal hormone therapy". Climacteric 21 (4): 346–354. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1455657. PMID 29630427.
- ↑ "Will estradiol/progesterone capsules for oral use become the best choice for menopausal hormone therapy?". Climacteric 22 (6): 535–537. December 2019. doi:10.1080/13697137.2019.1663625. PMID 31612748.
- ↑ "Estradiol and progesterone bioavailability for moderate to severe vasomotor symptom treatment and endometrial protection with the continuous-combined regimen of TX-001HR (oral estradiol and progesterone capsules)". Menopause 26 (7): 720–727. July 2019. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001306. PMID 30694918.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "Progesterone, progestins and the endometrium in perimenopause and in menopausal hormone therapy". Climacteric 21 (4): 321–325. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1446932. PMID 29583028.
- ↑ "Vaginal progesterone and the vaginal first-pass effect". Climacteric 21 (4): 355–357. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1450856. PMID 29583019.
- ↑ "Micronized progesterone and its impact on the endometrium and breast vs. progestogens". Climacteric 15 (Suppl 1): 18–25. April 2012. doi:10.3109/13697137.2012.669584. PMID 22432812.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 34.3 34.4 34.5 34.6 "Treatment of postmenopausal women with topical progesterone creams and gels: are they effective?". Climacteric 17 (Suppl 2): 8–11. December 2014. doi:10.3109/13697137.2014.944496. PMID 25196424.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 "Percutaneous administration of progesterone: blood levels and endometrial protection". Menopause 12 (2): 232–237. March 2005. doi:10.1097/00042192-200512020-00019. PMID 15772572.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 "Progesterone for treatment of symptomatic menopausal women". Climacteric 21 (4): 358–365. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1472567. PMID 29962247.
- ↑ "Novel perspectives for progesterone in hormone replacement therapy, with special reference to the nervous system". Endocrine Reviews 28 (4): 387–439. June 2007. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0050. PMID 17431228.
- ↑ "Progesterone receptors: form and function in brain". Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 29 (2): 313–339. May 2008. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2008.02.001. PMID 18374402.
- ↑ "Hormones and Female Sexual Dysfunction: Beyond Estrogens and Androgens--Findings from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine". The Journal of Sexual Medicine 13 (3): 283–290. March 2016. doi:10.1016/j.jsxm.2015.12.014. PMID 26944460.
- ↑ "Progesterone for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in women". Climacteric 21 (4): 366–374. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1467400. PMID 29962257.
- ↑ "Skin aging and menopause : implications for treatment". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 4 (6): 371–378. 2003. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304060-00001. PMID 12762829.
- ↑ "Effects and side-effects of 2% progesterone cream on the skin of peri- and postmenopausal women: results from a double-blind, vehicle-controlled, randomized study". The British Journal of Dermatology 153 (3): 626–634. September 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06685.x. PMID 16120154.
- ↑ "17β-Estradiol and natural progesterone for menopausal hormone therapy: REPLENISH phase 3 study design of a combination capsule and evidence review". Maturitas 81 (1): 28–35. May 2015. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.02.266. PMID 25835751.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 44.4 World Professional Association for Transgender Health (September 2011), Standards of Care for the Health of Transsexual, Transgender, and Gender Nonconforming People, Seventh Version, http://www.wpath.org/uploaded_files/140/files/IJT%20SOC,%20V7.pdf
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 Principles of Transgender Medicine and Surgery. Routledge. 20 May 2016. pp. 170–. ISBN 978-1-317-51460-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=LwszDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA170.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 "Clinical review: Breast development in trans women receiving cross-sex hormones". The Journal of Sexual Medicine 11 (5): 1240–1247. May 2014. doi:10.1111/jsm.12487. PMID 24618412.
- ↑ "Fluid Retention over the Menstrual Cycle: 1-Year Data from the Prospective Ovulation Cohort". Obstetrics and Gynecology International 2011: 138451. 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/138451. PMID 21845193.
- ↑ Pathophysiology - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 25 June 2014. pp. 660–. ISBN 978-0-323-29317-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=i7jwAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA660. "Throughout the reproductive years, some women note swelling of the breast around the latter part of each menstrual cycle before the onset of menstruation. The water retention and subsequent swelling of breast tissue during this phase of the menstrual cycle are thought to be due to high levels of circulating progesterone stimulating the secretory cells of the breast."
- ↑ "Physiological changes associated with the menstrual cycle: a review". Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey 64 (1): 58–72. January 2009. doi:10.1097/OGX.0b013e3181932a37. PMID 19099613.
- ↑ "Prophylactic administration of progesterone by vaginal suppository to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women at increased risk: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 188 (2): 419–424. February 2003. doi:10.1067/mob.2003.41. PMID 12592250.
- ↑ "Hormone Is Said to Cut Risk of Premature Birth". The New York Times. 2 May 2011. https://www.nytimes.com/2011/05/03/health/research/03preemie.html.
- ↑ "Progesterone vaginal gel for the reduction of recurrent preterm birth: primary results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 30 (5): 687–696. October 2007. doi:10.1002/uog.5158. PMID 17899572.
- ↑ "Vaginal progesterone is associated with a decrease in risk for early preterm birth and improved neonatal outcome in women with a short cervix: a secondary analysis from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 30 (5): 697–705. October 2007. doi:10.1002/uog.5159. PMID 17899571.
- ↑ "Progesterone and the risk of preterm birth among women with a short cervix". The New England Journal of Medicine 357 (5): 462–469. August 2007. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa067815. PMID 17671254.
- ↑ "Prevention of spontaneous preterm birth: the role of sonographic cervical length in identifying patients who may benefit from progesterone treatment". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 30 (5): 675–686. October 2007. doi:10.1002/uog.5174. PMID 17899585.
- ↑ "Vaginal progesterone reduces the rate of preterm birth in women with a sonographic short cervix: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 38 (1): 18–31. July 2011. doi:10.1002/uog.9017. PMID 21472815.
- ↑ "Hormone Treatment May Drastically Reduce Preterm Births". December 14, 2011. https://www.webmd.com/baby/news/20111214/hormone-treatment-may-drastically-reduce-preterm-births.
- ↑ "Progesterone helps cut risk of pre-term birth". Women's health. msnbc.com. 14 December 2011. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/45671241/ns/health-womens_health/#.TutW95hOERl.
- ↑ "Luteal phase support in in vitro fertilization". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 33 (2): 118–127. March 2015. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1545363. PMID 25734349.
- ↑ "Progesterone administration for luteal phase deficiency in human reproduction: an old or new issue?". Journal of Ovarian Research 8: 77. November 2015. doi:10.1186/s13048-015-0205-8. PMID 26585269.
- ↑ "The role of progesterone therapy in early pregnancy: from physiological role to therapeutic utility". Gynecological Endocrinology 33 (6): 421–424. June 2017. doi:10.1080/09513590.2017.1291615. PMID 28277122.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 62.2 62.3 62.4 Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2007. pp. 406–. ISBN 978-0-323-03309-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=fOPtaEIKvcIC&pg=PA406.
- ↑ "Evaluation and management of abnormal uterine bleeding in premenopausal women". American Family Physician 85 (1): 35–43. January 2012. PMID 22230306. https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0101/p35.pdf.
- ↑ "Progestogens with or without oestrogen for irregular uterine bleeding associated with anovulation". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012 (9): CD001895. September 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001895.pub3. PMID 22972055.
- ↑ "Abnormal uterine bleeding". The Medical Clinics of North America 79 (2): 329–344. March 1995. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)30071-2. PMID 7877394.
- ↑ "Continuing pregnancy after mifepristone and "reversal" of first-trimester medical abortion: a systematic review". Contraception 92 (3): 206–211. September 2015. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2015.06.001. PMID 26057457.
- ↑ "Progesterone for acute traumatic brain injury". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12 (12): CD008409. December 2016. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008409.pub4. PMID 28005271.
- ↑ "Androgenetic alopecia and its treatment. A historical overview". Hair Transplantation (Third ed.). Taylor & Francis. 1 February 1995. pp. 1–33. ISBN 978-0-8247-9363-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=_KxsAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 "Androgenetic alopecia. New approved and unapproved treatments". Dermatologic Clinics 18 (1): 47–61, viii. January 2000. doi:10.1016/S0733-8635(05)70146-7. PMID 10626111.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 "Androgenetic alopecia and hair growth promotion state of the art: present and future". Clinics in Dermatology 6 (4): 218–227. 1988. doi:10.1016/0738-081X(88)90090-9. PMID 3063373.
- ↑ "Hair loss in women". Handbook of hair in health and disease. Human Health Handbooks no. 1. 1. 2012. pp. 70–97. doi:10.3920/978-90-8686-728-8_4. ISBN 978-90-8686-728-8.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "The antiandrogens. When and how they should be used". Dermatologic Clinics 11 (1): 65–72. January 1993. doi:10.1016/S0733-8635(18)30283-3. PMID 8435919.
- ↑ "Hair loss and herbs for treatment". Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 12 (3): 210–222. September 2013. doi:10.1111/jocd.12051. PMID 23992163.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 74.2 The Premenstrual Syndrome: Proceedings of a workshop held during the Sixth International Congress of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynecology, Berlin, September 1980. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 51–53. ISBN 978-94-011-6255-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=0IAJBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA51.
- ↑ "Progestogens in menopausal hormone therapy". Przeglad Menopauzalny = Menopause Review 14 (2): 134–143. June 2015. doi:10.5114/pm.2015.52154. PMID 26327902.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Gynaecology E-Book: Expert Consult: Online and Print. Elsevier Health Sciences. 1 October 2010. pp. 417–. ISBN 978-0-7020-4838-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=Ylqqk9-5zUsC&pg=PA417.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 "Evaluation and management of breast pain". Mayo Clinic Proceedings 79 (3): 353–372. March 2004. doi:10.4065/79.3.353. PMID 15008609.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 "Premenstrual syndrome". American Family Physician 67 (8): 1743–1752. April 2003. PMID 12725453.
- ↑ "Progesterone for premenstrual syndrome". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012 (3): CD003415. March 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003415.pub4. PMID 22419287.
- ↑ "Efficacy of progesterone and progestogens in management of premenstrual syndrome: systematic review". BMJ 323 (7316): 776–780. October 2001. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7316.776. PMID 11588078.
- ↑ Complementary and Alternative Therapies for Epilepsy. Demos Medical Publishing. 1 January 2005. pp. 378–. ISBN 978-1-934559-08-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=WVUE-6Xdny4C&pg=PT378.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/.
- ↑ 83.00 83.01 83.02 83.03 83.04 83.05 83.06 83.07 83.08 83.09 83.10 83.11 83.12 83.13 83.14 83.15 83.16 83.17 83.18 83.19 83.20 83.21 83.22 83.23 83.24 "Progesterone". https://www.drugs.com/international/progesterone.html.
- ↑ 84.00 84.01 84.02 84.03 84.04 84.05 84.06 84.07 84.08 84.09 84.10 84.11 84.12 84.13 84.14 84.15 84.16 84.17 84.18 "Micromedex Products: Please Login". http://www.micromedexsolutions.com/micromedex2/librarian.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 "Compounded bioidentical hormone therapy: time for a reality check?". Menopause 22 (9): 919–920. September 2015. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000484. PMID 26035149.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 "Update on medical and regulatory issues pertaining to compounded and FDA-approved drugs, including hormone therapy". Menopause 23 (2): 215–223. February 2016. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000523. PMID 26418479.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 87.2 87.3 "Over-the-counter progesterone cream produces significant drug exposure compared to a food and drug administration-approved oral progesterone product". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 45 (6): 614–619. June 2005. doi:10.1177/0091270005276621. PMID 15901742.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 88.2 88.3 88.4 Drug Therapy in Nursing. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2009. pp. 1150–. ISBN 978-0-7817-6587-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=5zd_W_PUwvYC&pg=PA1150.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 89.3 Fundamental Pharmacology for Pharmacy Technicians. Cengage Learning. 29 October 2008. pp. 322–. ISBN 978-1-111-80040-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=bXkGAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA322.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 90.2 Menopause. ACP Press. 2007. p. 97. ISBN 978-1-930513-83-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=mPs5Ly71OCQC&pg=PA97.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Estrogen Effects in Psychiatric Disorders. Springer Science & Business Media. 27 December 2005. p. 179. ISBN 978-3-211-27063-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=L4YQ50SbBnsC&pg=PA179.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Progesterone and human cognition". Climacteric 21 (4): 333–340. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1476484. PMID 29852783.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 "The case for progesterone". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1052 (1): 152–169. June 2005. doi:10.1196/annals.1347.011. PMID 16024758. Bibcode: 2005NYASA1052..152S.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 94.2 "A placebo-controlled study of effects of oral progesterone on performance and mood". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 33 (3): 293–298. March 1992. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04038.x. PMID 1576050.
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 North American Menopause Society (2003). "Role of progestogen in hormone therapy for postmenopausal women: position statement of The North American Menopause Society". Menopause 10 (2): 113–132. doi:10.1097/00042192-200310020-00003. PMID 12627037.
- ↑ "Administration of progesterone produces mild sedative-like effects in men and women". Psychoneuroendocrinology 29 (3): 339–354. April 2004. doi:10.1016/s0306-4530(03)00033-7. PMID 14644065.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 "Various Other Effects of Progesterone". Pharmacology of the Endocrine System and Related Drugs: Progesterone, Progestational Drugs and Antifertility Agents. Pergamon Press. 30 January 1971. pp. 375–387. ISBN 9780080157450. https://books.google.com/books?id=lf1sAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ 98.0 98.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid945344 - ↑ 99.0 99.1 "The Role of Progestins and Progesterone in Brain Function and Behavior". Metabolic Effects of Gonadal Hormones and Contraceptive Steroids. Springer. 1969. pp. 649–667. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-1782-1_48. ISBN 978-1-4684-1784-5.
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 "Progesterone anesthesia in human subjects". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 14 (12): 1567–1569. December 1954. doi:10.1210/jcem-14-12-1567. PMID 13211793.
- ↑ "Sedative and hypnotic effects of oral administration of micronized progesterone may be mediated through its metabolites". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 159 (5): 1203–1209. November 1988. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(88)90448-6. PMID 3189454.
- ↑ 102.0 102.1 102.2 102.3 102.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid26342177 - ↑ 103.0 103.1 "Progesterone and progestins: applications in gynecology". Steroids 65 (10–11): 671–679. 2000. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(00)00123-9. PMID 11108875.
- ↑ "Progesterone concentrations--physiologic or pharmacologic?". Fertility and Sterility 65 (5): 1077–1078. May 1996. doi:10.1016/s0015-0282(16)58295-8. PMID 8612843.
- ↑ "Hormone therapy, mammographic density, and breast cancer risk". Maturitas 64 (1): 20–26. September 2009. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.07.009. PMID 19709825.
- ↑ 106.00 106.01 106.02 106.03 106.04 106.05 106.06 106.07 106.08 106.09 "The impact of micronized progesterone on breast cancer risk: a systematic review". Climacteric 21 (2): 111–122. April 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2017.1421925. PMID 29384406.
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 107.2 "Estradiol therapy and breast cancer risk in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Gynecological Endocrinology 33 (2): 87–92. February 2017. doi:10.1080/09513590.2016.1248932. PMID 27898258.
- ↑ 108.0 108.1 108.2 "Progestogens in postmenopausal hormone therapy and the risk of breast cancer". Maturitas 77 (4): 311–317. April 2014. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.01.001. PMID 24485796.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 109.2 109.3 109.4 109.5 109.6 109.7 "Progesterone--promoter or inhibitor of breast cancer". Climacteric 16 (Suppl 1): 54–68. August 2013. doi:10.3109/13697137.2013.768806. PMID 23336704.
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 110.2 110.3 110.4 110.5 110.6 110.7 110.8 "Menopausal hormone therapy: a better and safer future". Climacteric 21 (5): 454–461. October 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1439915. PMID 29526116.
- ↑ Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer (September 2019). "Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence". Lancet 394 (10204): 1159–1168. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31709-X. PMID 31474332.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 112.2 112.3 "Vascular Effects of Early versus Late Postmenopausal Treatment with Estradiol". The New England Journal of Medicine 374 (13): 1221–1231. March 2016. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1505241. PMID 27028912.
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 "Progestogens and venous thromboembolism in menopausal women: an updated oral versus transdermal estrogen meta-analysis". Climacteric 21 (4): 341–345. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1446931. PMID 29570359.
- ↑ "Progestogens used in postmenopausal hormone therapy: differences in their pharmacological properties, intracellular actions, and clinical effects". Endocrine Reviews 34 (2): 171–208. April 2013. doi:10.1210/er.2012-1008. PMID 23238854.
- ↑ Knobil and Neill's Physiology of Reproduction. Academic Press. 15 November 2014. pp. 2289, 2386. ISBN 978-0-12-397769-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=I1ACBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA2386.
- ↑ "Progesterone co-administration in patients discontinuing long-term benzodiazepine therapy: effects on withdrawal severity and taper outcome". Psychopharmacology 117 (4): 424–429. February 1995. doi:10.1007/bf02246214. PMID 7604143.
- ↑ "Dependency on progesterone in woman with self-diagnosed premenstrual syndrome". Lancet 347 (9009): 1182. April 1996. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90639-x. PMID 8609776.
- ↑ "Neurosteroid biosynthesis regulates sexually dimorphic fear and aggressive behavior in mice". Neurochemical Research 33 (10): 1990–2007. October 2008. doi:10.1007/s11064-008-9718-5. PMID 18473173.
- ↑ "Physiological doses of progesterone potentiate the effects of triazolam in healthy, premenopausal women". Psychopharmacology 215 (3): 429–439. June 2011. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2206-7. PMID 21350928.
- ↑ "Progesterone abuse". Reactions Weekly 599 (1): 9. 1996. doi:10.2165/00128415-199605990-00031. ISSN 1179-2051.
- ↑ "The dark side of 5α-reductase inhibitors' therapy: sexual dysfunction, high Gleason grade prostate cancer and depression". Korean Journal of Urology 55 (6): 367–379. June 2014. doi:10.4111/kju.2014.55.6.367. PMID 24955220.
- ↑ "The biological activity of 3alpha-hydroxysteroid oxido-reductase in the spinal cord regulates thermal and mechanical pain thresholds after sciatic nerve injury". Neurobiology of Disease 30 (1): 30–41. April 2008. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.12.001. PMID 18291663.
- ↑ "Medroxyprogesterone acetate antagonizes the effects of estrogen treatment on social and sexual behavior in female macaques". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 89 (6): 2998–3006. June 2004. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-032086. PMID 15181090.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 "Isoform-specific regulation of cytochromes P450 expression by estradiol and progesterone". Drug Metabolism and Disposition 41 (2): 263–269. February 2013. doi:10.1124/dmd.112.046276. PMID 22837389.
- ↑ 125.0 125.1 Tactics in Contemporary Drug Design. Springer. 8 December 2014. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-3-642-55041-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=j2HEBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA161.
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 Principles of Gender-specific Medicine. Gulf Professional Publishing. 2004. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-0-12-440906-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=TiLxa8nPbLkC&pg=PA146.
- ↑ 127.0 127.1 Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 24 January 2012. pp. 164–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Sd6ot9ul-bUC&pg=PA164.
- ↑ "Membrane estrogen receptors - is it an alternative way of estrogen action?". Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 64 (2): 129–142. April 2013. PMID 23756388.
- ↑ "Estrogen biology: new insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 389 (1–2): 71–83. May 2014. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.02.002. PMID 24530924.
- ↑ "Pharmacological and functional characterization of human mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor ligands". European Journal of Pharmacology 247 (2): 145–154. October 1993. doi:10.1016/0922-4106(93)90072-H. PMID 8282004.
- ↑ "Conception and pharmacodynamic profile of drospirenone". Steroids 68 (10–13): 891–905. November 2003. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2003.08.008. PMID 14667981.
- ↑ "Progesterone as a neuroactive neurosteroid, with special reference to the effect of progesterone on myelination". Steroids 65 (10–11): 605–612. 2000. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(00)00173-2. PMID 11108866.
- ↑ "Neuroactive steroids". FASEB Journal 6 (6): 2311–2322. March 1992. doi:10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1347506. PMID 1347506.
- ↑ 134.0 134.1 134.2 Endocrine Pharmacology: Physiological Basis and Therapeutic Applications. CUP Archive. 1980. pp. 264, 274. ISBN 978-0-521-22673-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=W6M9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA264.
- ↑ "Drospirenone--a new progestogen with antimineralocorticoid activity, resembling natural progesterone". The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care 5 (Suppl 3): 17–24. December 2000. doi:10.1080/14730782.2000.12288986. PMID 11246598.
- ↑ "Allopregnanolone and mood disorders". Progress in Neurobiology 113: 88–94. February 2014. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.07.005. PMID 23978486.
- ↑ 137.0 137.1 Zutshi (2005). Hormones in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Jaypee Brothers, Medical Publishers. pp. 74–75. ISBN 978-81-8061-427-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=IBxBbaDjXw0C&pg=PA75. "It has been observed that micronized progesterone has no suppressive effects on high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C). Jensen et al have proved that oral micronized progesterone has no adverse effect on serum lipids. These preparations have the same antiestrogenic and antimineralocorticoid effect but no androgenic action. It does not affect aldosterone synthesis, blood pressure, carbohydrate metabolism or mood changes. No side effects have been reported as far as lipid profile, coagulation factors and blood pressure are concerned."[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Making the Estrogen Decision. McGraw-Hill Professional. 1999. p. 22. ISBN 9780879836962. https://books.google.com/books?id=d3IP-dmpoNsC&q=progesterone+%22skin+cream%22+liver&pg=PA22.
- ↑ Progesterone - Drugs.com, https://www.drugs.com/pro/progesterone.html, retrieved 23 August 2015
- ↑ "Pharmacology of Progestogens". Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie-Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 8 (1): 157–177. 2011. http://www.kup.at/kup/pdf/10168.pdf.
- ↑ 141.0 141.1 141.2 "Oral micronized progesterone". Clinical Therapeutics 21 (1): 41–60; discussion 1–2. January 1999. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(00)88267-3. PMID 10090424.
- ↑ 142.0 142.1 142.2 142.3 142.4 142.5 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 1024–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA1024.
- ↑ 143.0 143.1 143.2 143.3 143.4 143.5 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 880–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA880.
- ↑ "The bioassay of progesterone". Endocrinology 61 (5): 528–533. November 1957. doi:10.1210/endo-61-5-528. PMID 13480263.
- ↑ "Effects of 3-hydrazone modification on the metabolism and protein binding of progesterone". International Journal of Pharmaceutics 65 (1–2): 109–114. 1990. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(90)90015-V. ISSN 0378-5173.
- ↑ "Evaluating the neurotherapeutic potential of a water-soluble progesterone analog after traumatic brain injury in rats". Neuropharmacology 109: 148–158. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.05.017. PMID 27267687.
- ↑ Guthrie DA, Lockwood MA, Natchus MG, Liotta DC, Stein DG, Sayeed I, "Progesterone phosphate analogs and uses related thereto", US patent 9802978, issued 31 October 2017, assigned to Emory University.
- ↑ "Development and screening of water-soluble analogues of progesterone and allopregnanolone in models of brain injury". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52 (19): 6012–6023. October 2009. doi:10.1021/jm900712n. PMID 19791804.
- ↑ "Water-soluble progesterone analogues are effective, injectable treatments in animal models of traumatic brain injury". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 3 (5): 362–366. May 2012. doi:10.1021/ml200303r. PMID 24900479.
- ↑ "Progesterone conjugate - Levolta Pharmaceuticals". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800041522.
- ↑ Die Gestagene. Springer-Verlag. 27 November 2013. pp. 5–. ISBN 978-3-642-99941-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=t8GpBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA5.
- ↑ The Menstrual Cycle. Routledge. 7 March 2008. pp. 49–. ISBN 978-1-134-71411-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=7HQBAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA49.
- ↑ Premenstrual Syndrome: Ethical and Legal Implications in a Biomedical Perspective. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 274–. ISBN 978-1-4684-5275-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=HTLoBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA274.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMVJain2018 - ↑ 155.0 155.1 155.2 Die Gestagene. Springer-Verlag. 27 November 2013. pp. 1027–. ISBN 978-3-642-99941-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=t8GpBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA1027.
- ↑ 156.0 156.1 The Drug Book. New York, New York: Sterling Publishing. 2013. pp. 186. ISBN 9781402782640.
- ↑ Use of Progestogens in Clinical Practice of Obstetrics and Gynecology. JP Medical Ltd. 31 July 2018. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-93-5270-218-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=VrpEDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA3.
- ↑ 158.0 158.1 "Sex Hormone Therapy in Gynæcology". Edinburgh Medical Journal 43 (11): 680–695. November 1936. PMID 29648134.
- ↑ 159.0 159.1 "Therapeutics with Hormones of the Ovary". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 27 (7): 849–863. 1934. doi:10.1177/003591573402700711. ISSN 0035-9157.
- ↑ 160.0 160.1 "Endocrinology: A Synopsis of Normal and Pathologic Physiology, Diagnostic Procedures, and Therapy". Medical Clinics of North America 28 (5): 1232–1276. 1944. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)36180-6. ISSN 0025-7125.
- ↑ "Die Behandlung der Amenorrhöe mit Hohen Dosen der Ovarialhormone". Klinische Wochenschrift 12 (40): 1557–1562. 1933. doi:10.1007/BF01765673. ISSN 0023-2173.
- ↑ "Hormones in the Treatment of Menstrual Disturbances". British Medical Journal 1 (3979): 763–765. April 1937. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.3979.763. PMID 20780598.
- ↑ "The Use of Hormones in Obstetrics and Gynæcology". Postgraduate Medical Journal 13 (141): 234–240. July 1937. doi:10.1136/pgmj.13.141.234. PMID 21313067.
- ↑ This Man's Pill: Reflections on the 50th Birthday of the Pill. Oxford University Press. 2003. pp. 21–. ISBN 978-0-19-860695-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=J4VSAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA21.
- ↑ "A clinical study of progesterone therapy by pellet implantation". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 41 (4): 687–693. 1941. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(41)90665-8. ISSN 0002-9378.
- ↑ "Implantation of Sex Hormone Tablets in Man". British Medical Bulletin 1 (2): 21–22. 1943. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070135. ISSN 1471-8391.
- ↑ 167.0 167.1 "Absorption of Pellets of Progesterone". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 5 (1): 38–39. 1945. doi:10.1210/jcem-5-1-38. ISSN 0021-972X.
- ↑ "Indications for hormonal pellets in the therapy of endocrine and gynecic disorders". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 57 (2): 294–301. February 1949. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(49)90429-9. PMID 18123090.
- ↑ "Absorption of hormone implants in man". Lancet 2 (6676): 229–232. August 1951. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(51)93237-0. PMID 14862159.
- ↑ 170.0 170.1 170.2 170.3 "Therapie mit Depotgestagenen". Moderne Entwicklungen auf dem Gestagengebiet. Symposion der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Endokrinologie. Springer. 1960. pp. 87–92. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-25301-4_11. ISBN 978-3-662-23272-9.
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 171.2 171.3 171.4 171.5 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSchering1962 - ↑ 172.0 172.1 172.2 172.3 172.4 "The use of newer progestational preparations in clinical practice". The Medical Clinics of North America 41 (2): 587–603. March 1957. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)34457-1. PMID 13407238.
- ↑ "Endocrine Therapy in Gynaecology and Obstetrics". BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 51 (1): 51–63. 1944. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1944.tb07317.x. ISSN 1470-0328.
- ↑ "The place of progesterone in human contraception". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 27 (4–6): 991–994. 1987. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(87)90179-8. PMID 3320572.
- ↑ "Contraception with progestogens and progesterone during lactation". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 40 (4–6): 705–710. 1991. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(91)90294-F. PMID 1835650.
- ↑ "Fertility regulation in nursing women. II. Comparative performance of progesterone implants versus placebo and copper T". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 144 (2): 201–208. September 1982. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(82)90628-7. PMID 7114130.
- ↑ "Fertility regulation in nursing women. VI. Contraceptive effectiveness of a subdermal progesterone implant". Contraception 30 (4): 311–325. October 1984. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(84)80023-2. PMID 6509984.
- ↑ "Progesterone in aqueous crystalline suspension versus progesterone in oil; comparison by withdrawal bleeding tests in the human female". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 12 (11): 1445–1453. November 1952. doi:10.1210/jcem-12-11-1445. PMID 12999984.
- ↑ "Depotwirkung von Kristallsuspensionen weiblicher Sexualhormone (Ovocyclin- und Lutocyclin-Kristallampullen). Experimentelle und theoretische Grundlagen". Helvetica Physiologica et Pharmacologica Acta 2: 515–532. 1944. ISSN 0367-6242. OCLC 499306481. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=9741975641705488663.
- ↑ "Administration of progesterone in the form of microcrystals". Endocrinology 38 (3): 214–215. March 1946. doi:10.1210/endo-38-3-214. PMID 21025113.
- ↑ 181.0 181.1 Konservative Therapie der Frauenkrankheiten: Anzeigen, Grenzen und Methoden Einschliesslich der Rezeptur. Springer-Verlag. 8 March 2013. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-3-7091-5694-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Hte1BgAAQBAJ&pg=PA20.
- ↑ "The Modification of the Duration of Drug Action". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 11 (S1): 54T–66T. 1959. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1959.tb10412.x. ISSN 0022-3573.
- ↑ "Hormonal therapy in cancer of the breast. III. Effect of progesterone on clinical course and hormonal excretion". Cancer 5 (2): 275–277. March 1952. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(195203)5:2<275::aid-cncr2820050213>3.0.co;2-h. PMID 14905411.
- ↑ "Progesterone and estrogen requirements to induce and maintain decidua". Fertility and Sterility 4 (1): 63–75. 1953. doi:10.1016/s0015-0282(16)31145-1. PMID 13021207.
- ↑ Estrogens and Progestogens in Clinical Practice. Churchill Livingstone. 1998. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-443-04706-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=eO5qAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "Progesterone: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects". https://www.drugs.com/international/agolutin.html.
- ↑ "Agolutin Depot Label". http://www.sukl.cz/download/spc/SPC14550.pdf.
- ↑ "Clinomin Forte Label". http://www.indufar.com.py/files/shares/prospectos/400000154.pdf.
- ↑ "The effect of sex hormones in some organic solvents; emulsified in water". Acta Endocrinologica 2 (4): 396–404. 1949. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0020396. PMID 18140399.
- ↑ "Relative duration of action of natural and synthetic estrogens administered parenterally in women with estrogen deficiency". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 12 (1): 28–35. January 1952. doi:10.1210/jcem-12-1-28. PMID 14907837.
- ↑ "Some Data on Emulsions of Steroid Hormones". Ciba Foundation Symposium - Steroid Hormone Administration (Book II of Colloquia on Endocrinology, Vol. 3). Novartis Foundation Symposia. John Wiley & Sons. 1952. pp. 254–262. doi:10.1002/9780470715154.ch2. ISBN 9780470715154.
- ↑ Therapie der Haut- und Geschlechtskrankheiten. Springer-Verlag. 14 March 2013. pp. 508–. ISBN 978-3-642-94850-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=txrUBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA508.
- ↑ Praktische Endokrinologie. G. Thieme. 1960. p. 295. https://books.google.com/books?id=QhdsAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "Simultaneous treatment of secondary amenorrhoea with oestrogen and progesterone". Acta Endocrinologica 6 (1): 67–89. 1951. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0060067. PMID 14810456.
- ↑ "Neue Spezialitäten". Klinische Wochenschrift 36 (17): 833. 1958. doi:10.1007/BF01481957. ISSN 0023-2173.
- ↑ 196.0 196.1 "Steroid Injectable Contraception: Current Concepts and Perspectives". Contraception: newer pharmacological agents, devices, and delivery systems. M. Dekker. 1992. pp. 41–70. ISBN 978-0-8247-8700-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=L5NsAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ 197.0 197.1 197.2 "Recent experience with and future directions of contraceptive implants and injectable contraceptives". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology 5 (6): 805–814. December 1993. doi:10.1097/00001703-199312000-00016. PMID 8286694.
- ↑ 198.0 198.1 "Injectable and implantable contraceptives". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology 4 (4): 536–543. August 1992. doi:10.1097/00001703-199208000-00008. PMID 1387011.
- ↑ 199.0 199.1 "Pharmacokinetics of once-a-month injectable contraceptives". Contraception 49 (4): 347–359. April 1994. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90032-9. PMID 8013219.
- ↑ "A pilot study on the assessment of a progesterone/estradiol sustained release as once-a-month-injectable contraceptive". Contraception 44 (1): 45–59. July 1991. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(91)90105-o. PMID 1893701.
- ↑ "Aqueous solutions of steroid hormones". Acta Endocrinologica 4 (2): 179–191. 1950. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0040179. PMID 15432051.
- ↑ Basic Sex Hormone Therapy. Schering A.G.. 1962. p. 93,96. https://books.google.com/books?id=uJrIvQEACAAJ. "Intravenous: The intravenous injection of sex hormones is restricted mainly to specific circumstances where a speedy elevation of hormone levels is required, for example, in treatment of threatened abortion. [...] Crystalline Suspension: With crystalline suspensions the crystalline size governs the rate of absorption and therefore the duration of action. The lack of standardisation of crystalline size in commercial products plus the limits imposed by needle bore, introduces marked variations in effect. The results from emulsified forms are even more unreliable. [...] Hormone Pellets for Implantation: The subcutaneous implantation of sterile tablets was the first means of achieving prolonged action. Such possible factors as encapsulation or extrusion and diminished absorption as the surface area of the pellet is reduced, may be a drawback. Implantation of testosterone (about eight 100 mg. pellets), repeated 6-monthly, is a satisfactory treatment for eunuchoidism and implantation of oestradiol (a 50 mg. pellet remains active for about a year or more) is sometimes a useful procedure. The implantation of progesterone is best discarded altogether; extrusion of pellets (even when placed beneath the deep fascia) and slowness of absorption, in relation to metabolic requirements, make it unsatisfactory and the new depot hormones should be given preference. [...] Sex Hormone Preparations of Schering A.G. Berlin [...] Trade Name: Primolut intravenous. Chemical Description: Progesterone in aqueous solution. Packing: Ampoules of 1 c. c. = 20 mg."
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedCurrMedDrugs1962 - ↑ "Progesterone - IBSA". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800048238.
- ↑ 205.0 205.1 "Physiologic and Clinical Aspects of Ovarian Hormones". Archives of Dermatology 89 (6): 846–857. June 1964. doi:10.1001/archderm.1964.01590300074022. PMID 14164973.
- ↑ 206.0 206.1 "Synthetic Progestational Agents". Molecular Modification in Drug Design. Advances in Chemistry. 45. American Chemical Society. 1964. pp. 190–203. doi:10.1021/ba-1964-0045.ch016. ISBN 0-8412-0046-7.
- ↑ "Practically Applicable Results of Twenty Years of Research in Endocrinology". Progress in Drug Research / Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. 12. Birkhäuser. 1968. 137–164. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-7065-8_3. ISBN 978-3-0348-7067-2.
- ↑ 208.0 208.1 208.2 208.3 "Progesterone; a comparison of intramuscular, oral and sublingual routes of administration". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 9 (8): 736–742. August 1949. doi:10.1210/jcem-9-8-736. PMID 18133494.
- ↑ 209.0 209.1 209.2 209.3 "Physiologic effectiveness of oral progesterone". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 10 (8): 886–896. August 1950. doi:10.1210/jcem-10-8-886. PMID 15436649.
- ↑ "Menstrual arrhythmias; oral estrogen and progesterone therapy". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 64 (1): 148–154. July 1952. doi:10.1016/s0002-9378(16)38745-2. PMID 14933526.
- ↑ "Cyclic oral therapy of menstrual disorders". Fertility and Sterility 3 (4): 328–333. 1952. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)30965-7. PMID 12980155.
- ↑ 212.0 212.1 "Progesterone metabolism. II. Pregnanediol excretion following oral, sublingual and parenteral administration of progesterone". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 13 (9): 1043–1053. September 1953. doi:10.1210/jcem-13-9-1043. PMID 13084722.
- ↑ 213.0 213.1 "Comparison of progesterone preparations in secondary amenorrhea". Fertility and Sterility 5 (4): 374–381. 1954. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)31687-9. PMID 13183192.
- ↑ 214.0 214.1 "Progesterone in problems of sterility; diagnostic and therapeutic use". Fertility and Sterility 8 (2): 131–46; discussion, 146–8. 1957. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)32642-5. PMID 13405054.
- ↑ 215.0 215.1 "Synthetic progestins in the normal human menstrual cycle". Recent Progress in Hormone Research 13: 323–39; discussion 339–46. 1957. PMID 13477811. https://www.popline.org/node/476326. Retrieved 2 May 2019.
- ↑ "Large-dose oral progesterone therapy in menstrual disorders". Obstetrics and Gynecology 11 (1): 115–118. January 1958. PMID 13504644. https://journals.lww.com/greenjournal/Citation/1958/01000/Large_Dose_Oral_Progesterone_Therapy_in_Menstrual.23.aspx.
- ↑ "Hormonal therapy in carcinoma of the breast.I. Effect of oral progesterone on clinical course and metabolism of nitrogen and selected electrolytes and steroids". Cancer 13 (4): 757–763. 1960. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(196007/08)13:4<757::AID-CNCR2820130417>3.0.CO;2-9. ISSN 0008-543X.
- ↑ 218.0 218.1 218.2 218.3 218.4 218.5 Contraceptive Diplomacy: Reproductive Politics and Imperial Ambitions in the United States and Japan. Stanford University Press. 9 January 2018. pp. 188–191, 243. ISBN 978-1-5036-0441-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=FvJFDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT188.
- ↑ "Modern medicinals in review". American Journal of Pharmacy and the Sciences Supporting Public Health 125 (2): 49–69. February 1953. PMID 13030701. "Cyclogesterin. A relatively new approach to progesterone therapy, Cyclogesterin establishes that this hormone can be effective by the oral route. Primarily indicated to induce menstruation in secondary amenorrhea by oral therapy, it contains 30 mg. of progesterone and 1 mg. of mixed natural estrogens per tablet. One tablet is given three times daily for five consecutive days and therapy is stopped. Menstruation follows in one to six days in the non-pregnant patient. The product is manufactured by the Upjohn Company.".
- ↑ Modern Drug Encyclopedia and Therapeutic Index. Yorke Medical Group. 1958. p. 299. https://books.google.com/books?id=a83GAAAAIAAJ.
- ↑ "Delay of menses: test of progestational efficacy in induction of pseudopregnancy". Obstetrics and Gynecology 19: 730–735. June 1962. PMID 13901505.
- ↑ "Clomiphene Citrate in the Management of Anovulatory Uterine Bleeding1". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 24 (9): 863–866. September 1964. doi:10.1210/jcem-24-9-863. PMID 14216475.
- ↑ United States. Patent Office (1955). Official Gazette of the United States Patent Office. U.S. Patent Office.. pp. 2–. https://books.google.com/books?id=FKnNAAAAMAAJ&pg=RA2-PA80.
- ↑ "Sublingual Absorption of Progesterone and Anhydrohydroxyprogesterone". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 4 (4): 156–158. 1944. doi:10.1210/jcem-4-4-156. ISSN 0021-972X.
- ↑ "Perlingual Absorption of Progesterone and Anhydrohydroxyprogesterone1,2". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 4 (7): 321–325. 1944. doi:10.1210/jcem-4-7-321. ISSN 0021-972X.
- ↑ "Recovery of pregnanediol from urine following administration of oral anhydrohydroxyprogesterone, buccal progesterone, and intramuscular progesterone". Obstetrics and Gynecology 2 (1): 68–72. July 1953. PMID 13073082.
- ↑ "New Prescription Products". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (Practical Pharmacy Ed.) 10 (4): 198–206. 1949. doi:10.1016/S0095-9561(16)31795-9. ISSN 0095-9561.
- ↑ Remington's Practice of Pharmacy: A Treatise on the Preparing, Standardizing, and Dispensing of Official and Extemporaneous Pharmaceutical Products, with Descriptions of Medicinal Substances, Their Properties, Uses and Doses. Also a Guide to Other Professional Services Rendered by the Pharmacist in Connection with Community Health. Intended for the Use of Pharmacists and Physicians and as a Textbook for Students. Mack Publishing Company. 1951. pp. 936–937. https://books.google.com/books?id=2u8jAQAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Dermatological Formulary: A Guide for Medical Students and Resident Physicians in Dermatology. Educational Publishers. 1951. p. 155. https://books.google.com/books?id=1m-C5uGARQEC.
- ↑ Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Ärzte und Medizinalbeamte: Wirkstoffgruppen II Chemikalien und Drogen (A-AL). Springer-Verlag. 1969. pp. 178–. ISBN 978-3-662-25655-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=a2a0BgAAQBAJ&pg=PA178.
- ↑ 231.0 231.1 231.2 231.3 231.4 231.5 Drugs Used in Control of Reproduction. Advances in Pharmacology. 3. Academic Press. 1964. pp. 285–313. doi:10.1016/S1054-3589(08)61115-1. ISBN 9780120329038. "The original observation of Makepeace et al. (1937) that progesterone inhibited ovulation in the rabbit was substantiated by Pincus and Chang (1953). In women, 300 mg of progesterone per day taken orally resulted in ovulation inhibition in 80% of cases (Pincus, 1956). The high dosage and frequent incidence of breakthrough bleeding limited the practical application of the method. Subsequently, the utilization of potent 19-norsteroids, which could be given orally, opened the field to practical oral contraception."
- ↑ 232.0 232.1 "Development of the oral contraceptives". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 132 (2): 217–219. September 1978. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(78)90928-6. PMID 356615.
- ↑ "The effect of progestin and progesterone on ovulation in the rabbit". American Journal of Physiology. Legacy Content 119 (3): 512–516. 1937. doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1937.119.3.512. ISSN 0002-9513.
- ↑ "Action of progesterone on the gonadotropic activity of the pituitary". American Journal of Physiology. Legacy Content 127 (1): 192–198. 1939. doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1939.127.1.192. ISSN 0002-9513.
- ↑ "The effects of progesterone and related compounds on ovulation and early development in the rabbit". Acta Physiologica Latino Americana 3 (2–3): 177–183. 1953. PMID 13138262.
- ↑ "Effects of progesterone and related compounds on mating and pregnancy in the rat". Fertility and Sterility 5 (3): 282–293. 1954. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)31628-4. PMID 13162007.
- ↑ 237.0 237.1 237.2 237.3 "Probable mode of action of oral contraceptives". British Medical Journal 2 (5475): 1394–1399. December 1965. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5475.1394. PMID 5848673. "At the Fifth International Conference on Planned Parenthood in Tokyo, Pincus (1955) reported an ovulation inhibition by progesterone or norethynodrel1 taken orally by women. This report indicated the beginning of a new era in the history of contraception. [...] That the cervical mucus might be one of the principal sites of action was suggested by the first studies of Pincus (1956, 1959) and of Ishikawa et al. (1957). These investigators found that no pregnancies occurred in women treated orally with large doses of progesterone, though ovulation was inhibited only in some 70% of the cases studied. [...] The mechanism of protection in this method—and probably in that of Pincus (1956) and of Ishikawa et al. (1957)—must involve an effect on the cervical mucus and/or endometrium and Fallopian tubes.".
- ↑ "Some Effects of Progesterone and Related Compounds upon Reproduction and Early Development in Mammals". The Fifth International Conference on Planned Parenthood: Theme, Overpopulation and Family Planning: Report of the Proceedings, 24-29 October, 1955, Tokyo, Japan. International Planned Parenthood Federation. 1955. pp. 175–184. https://books.google.com/books?id=d5oTAQAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "The Effects of Progesterone on Ovulation: A Preliminary Report". The Fifth International Conference on Planned Parenthood: Theme, Overpopulation and Family Planning: Report of the Proceedings, 24-29 October, 1955, Tokyo, Japan. International Planned Parenthood Federation. 1955. p. 185. https://www.popline.org/node/472171. Retrieved 2 May 2019. "The results of testing the effects of progesterone on ovulation in 13 patients at the Margaret Sanger Research Bureau are presented. The patients had normal menstrual cycles and showed clear evidence of ovulation. Each patient was given 1000 [mg] of [oral] progesterone daily during the midperiod for 10 or 12 days during 16 cycles. Ovulation was inhibited in 6 cycles. No disturbance in menstrual rhythm was observed. 3 of 12 patients with longstanding infertility histories became pregnant within 2–4 months after the cessation of progesterone therapy."
- ↑ "Some Effects of Progesterone and Related Compounds upon Reproduction and Early Development in Mammals". The Fifth International Conference on Planned Parenthood: Theme, Overpopulation and Family Planning: Report of the Proceedings, 24-29 October, 1955, Tokyo, Japan. International Planned Parenthood Federation. 1955. pp. 186–187. https://books.google.com/books?id=d5oTAQAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "Some effects of progesterone and related compounds upon reproduction and early development in mammals". Acta Endocrinologica. Supplementum 23 (Suppl 28): 18–36. 1956. doi:10.1530/acta.0.023S018. PMID 13394044.
- ↑ "Unknown". J. Jap. Family Plann. Ass. 2: 51–56.
- ↑ Progestational Agents and the Control of Fertility. Vitamins & Hormones. 17. Academic Press. 1959. 307–324. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(08)60274-5. ISBN 9780127098173. "Ishikawa et al. (1957) employing the same regime of progesterone administration also observed suppression of ovulation in a proportion of the cases taken to laparotomy. Although sexual intercourse was practised freely by the subjects of our experiments and those of Ishikawa el al., no pregnancies occurred. Since ovulation presumably took place in a proportion of cycles, the lack of any pregnancies may be due to chance, but Ishikawa et al. (1957) have presented data indicating that in women receiving oral progesterone the cervical mucus becomes impenetrable to sperm."
- ↑ "The history of steroidal contraceptive development: the progestins". Perspectives in Biology and Medicine 36 (3): 347–362. 1993. doi:10.1353/pbm.1993.0054. PMID 8506121.
- ↑ "History of oral contraception". The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care 15 (Suppl 2): S12–S18. December 2010. doi:10.3109/13625187.2010.513071. PMID 21091163.
- ↑ 246.0 246.1 246.2 246.3 246.4 246.5 246.6 246.7 Colonialism, Catholicism, and Contraception: A History of Birth Control in Puerto Rico. University of North Carolina Press. 10 October 2017. pp. 106–112. ISBN 978-1-4696-4001-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0fs4DwAAQBAJ&pg=PT106. "[...] Still, neither of the two researchers was completely satisfied with the results. Progesterone tended to cause "premature menses," or breakthrough bleeding, in approximately 20 percent of the cycles, an occurrence that disturbed the patients and worried Rock.17 in addition, Pincus was concerned about the failure to inhibit ovulation in all the cases. Only large doses of orally administered progesterone could insure the suppression of ovulation, and these doses were expensive. The mass use of this regimen as a birth control method was thus seriously imperiled.18 [...]"
- ↑ The Fertility Doctor: John Rock and the Reproductive Revolution. JHU Press. 31 October 2008. pp. 333–. ISBN 978-1-4214-0208-6. https://archive.org/details/fertilitydoctorj0000mars. "43. The first study used progesterone continuously rather than cyclically. Women began by taking 5 mg of stilbestrol and 50 mg of progesterone, increasing the dose of stilbestrol by 5 mg and of progesterone by 50 mg every two weeks. By the end of twelve weeks, women were taking 30 mg stilbestrol and 300 mg of progesterone. If they had vaginal bleeding at any time, the doses were increased. "Pseudopregnancy," typescript, 15 July 1954, GP-LC. Rock also summarizes his early studies in John Rock, Celso-Ramon Garcia, and Gregory Pincus, "Synthetic Progestins in the Normal Human Menstrual Cycle," Recent Progress in Hormone Research, vol. 13 (New York: Academic Press, 1957), 323-24."
- ↑ On the Pill: A Social History of Oral Contraceptives, 1950-1970. Johns Hopkins University Press. 14 September 2001. ISBN 978-1-4214-0371-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=jqbmtSPMfXYC. "In the early 1950s, independent of Pincus's work in Worcester, Rock successfully induced pregnancy in previously infertile women by treating them for several months with estrogen and progesterone. Although the steroids prevented pregnancy during the course of therapy, some of the women conceived when the treatment ended; this phenomenon became known as the "Rock rebound effect."58 When Pincus learned of Rock's work, he asked the physician to join forces in the hunt for an ovulation inhibitor, and Rock agreed. Pincus suggested two changes in the experimental regimen: use only progesterone (estrogen promoted cancer in laboratory animals) and administer the hormone for twenty days each month (to allow a period of menstruation). Rock achieved the same rate of success in curing infertility (about 15%), but a significant problem remained: tests indicated that about 15 percent of the women ovulated while taking the progesterone.59 Pincus and Rock needed to find an orally active compound that would completely inhibit ovulation. It was time to test the 19-nor steroids in humans. [...]"
- ↑ "Effects of certain 19-nor steroids on reproductive processes in animals". Science 124 (3227): 890–891. November 1956. doi:10.1126/science.124.3227.890-a. PMID 13380400. Bibcode: 1956Sci...124..890P.
- ↑ "Effects of certain 19-nor steroids on the normal human menstrual cycle". Science 124 (3227): 891–893. November 1956. doi:10.1126/science.124.3227.891. PMID 13380401. Bibcode: 1956Sci...124..891R.
- ↑ Sexual Chemistry: A History of the Contraceptive Pill. Yale University Press. 2010. pp. 75–. ISBN 978-0-300-16791-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=_i-s4biQs7MC&pg=PA75.
- ↑ "History of oral contraceptive drugs and their use worldwide". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 27 (1): 3–12. February 2013. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2012.11.004. PMID 23384741.
- ↑ "Absorption and metabolism of oral progesterone". British Medical Journal 280 (6217): 825–827. March 1980. doi:10.1136/bmj.280.6217.825. PMID 7370683.
- ↑ "Oral progesterone". British Medical Journal 282 (6274): 1476. May 1981. doi:10.1136/bmj.282.6274.1476-a. PMID 6784875.
- ↑ 255.0 255.1 255.2 "[The bioavailability of natural progesterone given by mouth. Measurement of steroid concentrations in plasma, endometrium and breast tissue]" (in fr). Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction 11 (3): 355–363. 1982. PMID 7119381.
- ↑ 256.0 256.1 "Dose dependent effects of oral progesterone on the oestrogenised postmenopausal endometrium". British Medical Journal 287 (6401): 1241–1245. October 1983. doi:10.1136/bmj.287.6401.1241. PMID 6315123.
- ↑ "Biliary excretion and intestinal metabolism of progesterone and estrogens in man". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 13 (2): 231–244. February 1980. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(80)90196-X. PMID 6991820. "It is generally accepted that orally administered progesterone has little biological effect.".
- ↑ "Even oral progesterone may be effective". JAMA 245 (14): 1394. April 1981. doi:10.1001/jama.1981.03310390003001. PMID 7193749.
- ↑ 259.0 259.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSauer2013 - ↑ "The history of natural progesterone, the never-ending story". Climacteric 21 (4): 308–314. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1462792. PMID 29806794.
- ↑ "Absorption of oral progesterone is influenced by vehicle and particle size". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 161 (4): 948–951. October 1989. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(89)90759-X. PMID 2801843.
- ↑ "Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations: 019781". Food and Drug Administration. 2 July 2010. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/docs/obdetail.cfm?Appl_No=019781&TABLE1=OB_Rx.
- ↑ 263.0 263.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid25944519 - ↑ "TherapeuticsMD Announces FDA Approval of TX-001HR: BIJUVA™ (Estradiol and Progesterone) Capsules for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Vasomotor Symptoms Due to Menopause". https://ir.therapeuticsmd.com/news-releases/news-release-details/therapeuticsmd-announces-fda-approval-tx-001hr-bijuvatm.
- ↑ 265.0 265.1 265.2 "Natural Micronized Progesterone Sustained Release (SR) and Luteal Phase: Role Redefined!!". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 10 (2): QE01–QE04. February 2016. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/17278.7212. PMID 27042538.
- ↑ 266.0 266.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedHaleemKhan2015 - ↑ 267.0 267.1 267.2 "A pharmacokinetic study of micronized natural progesterone extended release tablets". Restore Health. 1997. https://pharmacysolutionsonline.com/progesterone-even-release-tablets.php.
- ↑ "The physiologic effectiveness of progesterone vaginal suppositories". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 14 (12): 1564–1567. December 1954. doi:10.1210/jcem-14-12-1564. PMID 13211792.
- ↑ 269.0 269.1 "Absorption from the vagina". Drug Metabolism Reviews 14 (2): 137–168. 1983. doi:10.3109/03602538308991387. PMID 6301793.
- ↑ "NEW Prescription Products". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (Practical Pharmacy Ed.) 16 (3): 193–200. 1955. doi:10.1016/S0095-9561(16)33664-7. ISSN 0095-9561.
- ↑ "Administration of Progesterone in the Form of Suppositories". Acta Endocrinologica 49 (3_Suppl): S101. 1965. doi:10.1530/acta.0.049S101. ISSN 0804-4643.
- ↑ Unlisted Drugs. Unlisted Drugs. 1976. p. 360. https://books.google.com/books?id=nxdtAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ The Belfast Gazette. H.M. Stationery Office. January 1977. p. 158. https://books.google.com/books?id=YoNw_AGBEH8C.
- ↑ Organic-chemical Drugs and Their Synonyms. Akademie-Verlag. 1978. p. 872. https://books.google.com/books?id=4QMkAQAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Biennial Review of Infertility. Springer Science & Business Media. 7 June 2011. pp. 84–85. ISBN 978-1-4419-8456-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=4LgOGlCK_FMC&pg=PA84.
- ↑ "Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations: 020701". Food and Drug Administration. 2 July 2010. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/docs/obdetail.cfm?Appl_No=020701&TABLE1=OB_Rx.
- ↑ "Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations: 022057". Food and Drug Administration. 2 July 2010. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/docs/obdetail.cfm?Appl_No=022057&TABLE1=OB_Rx.
- ↑ 278.0 278.1 "Pros and Cons of Vaginal Rings for Contraceptive Hormone Delivery". American Journal of Drug Delivery 2 (4): 241–250. 2004. doi:10.2165/00137696-200402040-00004. ISSN 1175-9038.
- ↑ "Development of controlled release systems over the past 50years in the area of contraception". Journal of Controlled Release 240: 235–241. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.043. PMID 26732558.
- ↑ "Contraception – Update and Trends". J. Reproduktionsmed. Endokrinol 4 (6): 337–357. 2007. ISSN 1810-2107. https://www.kup.at/kup/pdf/6827.pdf.
- ↑ Drug Delivery: Fundamentals and Applications, Second Edition. CRC Press. 15 September 2016. pp. 294–. ISBN 978-1-4822-1772-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=TERnDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA294.
- ↑ 282.0 282.1 282.2 282.3 282.4 282.5 282.6 "Mirena (Levonorgestrel intrauterine system): a successful novel drug delivery option in contraception". Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 61 (10): 808–812. August 2009. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.04.022. PMID 19445984.
- ↑ Journal de gynécologie, obstétrique et biologie de la reproduction. Masson. 1972. pp. 198, 214, 327. https://books.google.com/books?id=NjH9dmzFBfsC.
- ↑ "Transdermal delivery of steroids". Contraception 39 (1): 1–20. January 1989. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(89)90012-7. PMID 2642780.
- ↑ "Transdermal drug delivery: clinical considerations for the obstetrician-gynecologist". Obstetrics and Gynecology 105 (5 Pt 1): 953–961. May 2005. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000161958.70059.db. PMID 15863530.
- ↑ "The Use of Progesterone in Clinical Practice: Evaluation of its Efficacy in Diverse Indications Using Different Routes of Administration". Current Drug Therapy 1 (2): 211–219. 2006. doi:10.2174/157488506776930923.
- ↑ "Different routes of progesterone administration and polycystic ovary syndrome: a review of the literature". Gynecological Endocrinology 21 (2): 119–127. August 2005. doi:10.1080/09513590500170049. PMID 16109599.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 31 October 1999. pp. 232–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=mqaOMOtk61IC&pg=PA232.
- ↑ Innovation in Clinical Practice: The Dynamics of Medical Technology Development. National Academies. 1991. pp. 195–. NAP:13513. https://books.google.com/books?id=MZkrAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA195.
- ↑ "Prescription event monitoring study to assess the safety profile of oral natural micronized progesterone sustained release in India". International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences 3 (4): 975. 2014. doi:10.5958/2319-5886.2014.00034.4. ISSN 2319-5886.
- ↑ "Changing Indian Market Trends of NMP: A Review". International Journal of Pharma Research & Review 4 (3): 28–30. March 2015.
- ↑ "Luteal Phase Support: Why, When and How". Pan Asian Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1 (2): 79–83. 2018. https://pajog.com/prints/Luteal%20Phase%20Support%20Why%20When%20and%20How.pdf.
- ↑ "Open-label, Prospective, Investigator Initiated Study to Assess the Clinical Role of Oral Natural or Synthetic Progesterone During Stimulated IUI Cycles for Unexplained Infertility". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 10 (1): QC08–QC10. January 2016. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/17058.7106. PMID 26894126.
- ↑ "A Drug Utilisation Surveillance Study to Assess the Clinical Utility and Safety of Oral Natural Micronized Progesterone SR in High Risk Pregnancies: NAP-DELAY Study". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2018. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2018/34886.12118. ISSN 2249-782X.
- ↑ "Current Concepts in Management of Preterm Labour - A Review Article". Indian Obstetrics and Gynaecology 5 (2). April–June 2015. https://iog.org.in/index.php/iog/article/view/192.
- ↑ "Estradiol/progesterone injection - Laboratorios Carnot". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800044558.
- ↑ "Estradiol/progesterone - TherapeuticsMD". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800038089.
- ↑ 298.0 298.1 298.2 Sex Hormone Pharmacology. Academic Press. 1976. pp. 341–342. ISBN 978-0-12-137250-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=zt5sAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ 299.0 299.1 "The influence of pharmaceutical compounds on male fertility". Andrologia 8 (3): 203–235. 1976. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.1976.tb02137.x. PMID 793446.
- ↑ "Reduced plasma testosterone and LH in young men during progesterone administration". Journal of Reproduction and Fertility 26 (2): 263–265. August 1971. doi:10.1530/jrf.0.0260263. PMID 5558416.
- ↑ "Effects of progestational compounds on the reproductive processes of the human male". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 71 (5): 649–665. July 1958. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb54641.x. PMID 13583821.
- ↑ "Effects of progesterone and synthetic progestins on the reproductive physiology of normal men". Federation Proceedings 18: 1057–1065. December 1959. PMID 14400846.
- ↑ 303.0 303.1 "Progesterone topical - Novavax". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800017094.
- ↑ Plunkett's Nanotechnology & MEMS Industry Almanac. Plunkett Research, Ltd.. March 2004. pp. 265–. ISBN 978-1-59392-004-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=Bu8MFtGR_iEC&pg=PT265.
- ↑ "Form 10-K Novavax, inc.". https://ir.novavax.com/static-files/af4f0b93-c3f2-442b-9da5-f3ee0c63f844.
Further reading
- "Oral micronized progesterone. Bioavailability pharmacokinetics, pharmacological and therapeutic implications--a review". Contraception 36 (4): 373–402. October 1987. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(87)90088-6. PMID 3327648.
- "Systemic progesterone therapy--oral, vaginal, injections and even transdermal?". Maturitas 79 (3): 248–255. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.07.009. PMID 25113944.
 |

