Chemistry:Hexamidine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
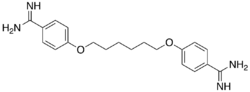
4,4′-[Hexane-1,6-diylbis(oxy)]di(benzene-1-carboximidamide) | |
| Other names
4-[6-(4-carbamimidoylphenoxy)hexoxy]benzamidine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 354.446 |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | D08AC04 (WHO) R01AX07 (WHO) R02AA18 (WHO) S01AX08 (WHO) S03AA05 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexamidine is an antiseptic and disinfectant. Hexomedine is the trade name of a diisethionate solution (1/1.000) of hexamidine.[1] Hexamidine is used primarily as its diisethionate salt, which is more water-soluble than the dihydrochloride. The dihydrochloride was first synthesized and patented as a trypanocide for May & Baker in 1939. Its amoebicidal properties emerged in the 1990s. The exact mechanism of its biocidal action is unknown, but presumed similar to quaternary ammonium compounds, involving binding to the negatively charged lipid membranes of pathogens. Hexamidine and its shorter congener, propamidine, are used as antiseptics and preservatives in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. They are particularly used for the topical treatment of acanthamoebiasis (Acanthamoeba keratitis).[2]
References
- ↑ "Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Hexamidine and Hexamidine Diisethionate". International Journal of Toxicology 26 (3_suppl): 79–88. 2007. doi:10.1080/10915810701663168. PMID 18273451.
- ↑ Parisi, N. (2017), "Hexamidine salts - applications in skin health and personal care products", International Journal of Cosmetic Science 39 (4): 361–365, doi:10.1111/ics.12392, PMID 28129440, http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1540352/1/PDF.pdf
 |

