Astronomy:Gliese 208
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Orion |
| Right ascension | 05h 36m 30.991s[2] |
| Declination | +11° 19′ 40.33″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.80 - 9.05[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M0.0 Ve[4] |
| Variable type | RS CVn[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 21.772[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −2.811 ± 0.080[2] mas/yr Dec.: −56.368 ± 0.060[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 87.66 ± 0.29[2] mas |
| Distance | 37.2 ± 0.1 ly (11.41 ± 0.04 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 8.6 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.646[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.601[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.08[7] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,966[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.05[6] dex |
| Age | 2.7[6] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Gliese 208 (Gj 208) is a red dwarf star with an apparent magnitude of 8.9. It is 37 light years away in the constellation of Orion. It is an extremely wide binary with 2MASS J0536+1117, an M4 star 2.6 arcminutes away (at least 0.028 light years)
The spectral type of Gj 208 has variously been described between K6 and M1.[8][9][10] Two of the most recent observations give a statistically calculated spectral type of K7.9[6] or a more traditional classification of M0.0 Ve.[4] It is a cool dwarf star and probably a spectroscopic binary.[3]
Calculations from 2010 suggest that this star passed as close as 1.537 parsecs (5.0 light-years) from the Sun about 500,000 years ago.[11]
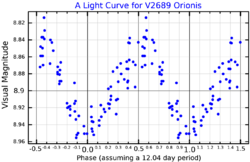
GJ 208 is an RS Canum Venaticorum variable, close binary systems which show small amplitude brightness changes caused by chromospheric activity. Its visual magnitude varies by about a quarter magnitude with a period of 12.285 days.[3]
References
- ↑ Kiraga, M. (March 2012). "ASAS Photometry of ROSAT Sources. I. Periodic Variable Stars Coincident with Bright Sources from the ROSAT All Sky Survey". Acta Astronomica 62 (1): 67–95. Bibcode: 2012AcA....62...67K. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2012AcA....62...67K. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Gaia Collaboration (2016). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Gaia DR1 (Gaia Collaboration, 2016)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: I/337. Originally Published in: Astron. Astrophys. 1337. Bibcode: 2016yCat.1337....0G.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lépine, Sébastien; Hilton, Eric J.; Mann, Andrew W.; Wilde, Matthew; Rojas-Ayala, Bárbara; Cruz, Kelle L.; Gaidos, Eric (2013). "A Spectroscopic Catalog of the Brightest (J < 9) M Dwarfs in the Northern Sky". The Astronomical Journal 145 (4): 102. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/4/102. Bibcode: 2013AJ....145..102L.
- ↑ Soubiran, C.; Jasniewicz, G.; Chemin, L.; Crifo, F.; Udry, S.; Hestroffer, D.; Katz, D. (2013). "The catalogue of radial velocity standard stars for Gaia. I. Pre-launch release". Astronomy & Astrophysics 552: A64. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220927. Bibcode: 2013A&A...552A..64S.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Mann, Andrew W.; Feiden, Gregory A.; Gaidos, Eric; Boyajian, Tabetha; von Braun, Kaspar (2015). "How to Constrain Your M Dwarf: Measuring Effective Temperature, Bolometric Luminosity, Mass, and Radius". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (1): 64. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/1/64. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804...64M.
- ↑ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 427 (1): 343–357. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M.
- ↑ Stephenson, C. B. (1986). "Dwarf K and M stars of high proper motion found in a hemispheric survey". Astronomical Journal 92: 139. doi:10.1086/114146. Bibcode: 1986AJ.....92..139S.
- ↑ Stephenson, C. B.; Sanduleak, N. (1975). "Dwarf K and M stars discovered on objective-prism plates". Astronomical Journal 80: 972. doi:10.1086/111829. Bibcode: 1975AJ.....80..972S.
- ↑ Skiff, B. A. (2014). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Spectral Classifications (Skiff, 2009-2016)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/Mk. Originally Published in: Lowell Observatory (October 2014) 1. Bibcode: 2014yCat....1.2023S.
- ↑ Bobylev, Vadim V. (March 2010). "Searching for Stars Closely Encountering with the Solar System". Astronomy Letters 36 (3): 220–226. doi:10.1134/S1063773710030060. Bibcode: 2010AstL...36..220B.
External links
- Wikisky image of HD 245409 (Gliese 208)
 |