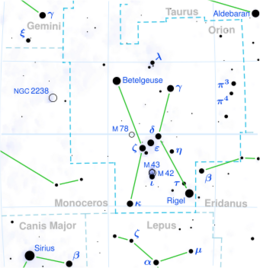
Astronomy:Rho Orionis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Orion |
| Right ascension | 05h 13m 17.48015s[1] |
| Declination | +02° 51′ 40.5479″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +4.44[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K0 III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.13[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.19[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +40.5[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +0.83[1] mas/yr Dec.: +3.91[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.32 ± 0.94[1] mas |
| Distance | approx. 350 ly (approx. 110 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.65[5] |
| Details[6] | |
| Mass | 2.67 M☉ |
| Radius | 25[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 251 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.4[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,533 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.06[8] dex |
| Age | 650 Myr |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Period (P) | 1031.4 days |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 6.9 mas[note 1] |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.1 |
| Inclination (i) | 122.8° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 242.6° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2426182.46 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 17.9° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 8.70 km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Rho Orionis, Latinised from ρ Orionis, is the Bayer designation for an orange-hued binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Orion. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.44.[2] The star shows an annual parallax shift of 9.32 mas due to the orbital motion of the Earth, which provides a distance estimate of roughly 350 light-years from the Sun. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +40.5 km/s.[4] About 2.6 million years ago, Rho Orionis made its perihelion passage at a distance of around 10 light-years (3.1 parsecs).[10]
This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system with an orbital period of 2.8 years and an eccentricity of 0.1.[9] The visible component is an evolved giant star of type K with a stellar classification of K0 III.[3] Its measured angular diameter is 2.19±0.02 mas,[11] which, at its estimated distance yields a physical size of about 25 times the radius of the Sun.[7] It has 2.67 times the mass of the Sun and is about 650 million years old. The star is radiating 251 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,533 K.[6]
Notes
- ↑ This is the photocentric semi-major axis, from the motion shown by the observed "star" relative to distant objects, and in practice relative to the barycentre. This is always smaller than the orbital semi-major axis, dramatically smaller when the primary star is much more massive than the secondary or when it is not much brighter.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999). "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars, Vol. 5". Michigan Spectral Survey 05: 0. Bibcode: 1999MSS...C05....0H.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Famaey, B.; Jorissen, A.; Luri, X.; Mayor, M.; Udry, S.; Dejonghe, H.; Turon, C. (2005). "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters". Astronomy and Astrophysics 430: 165. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272. Bibcode: 2005A&A...430..165F.
- ↑ Smith, Graeme H.; Shetrone, Matthew D. (2000). "CaII K Emission-Line Asymmetry among Red Giants Detected by the ROSAT Satellite". The Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 112 (776): 1320. doi:10.1086/316634. Bibcode: 2000PASP..112.1320S.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Luck, R. Earle (2015). "Abundances in the Local Region. I. G and K Giants". The Astronomical Journal 150 (3): 88. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/3/88. Bibcode: 2015AJ....150...88L.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lang, Kenneth R. (2006), Astrophysical formulae, Astronomy and astrophysics library, 1 (3rd ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 3-540-29692-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=OvTjLcQ4MCQC&pg=PA41. The radius (R*) is given by:
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Soubiran, C.; Le Campion, J.-F.; Cayrel de Strobel, G.; Caillo, A. (June 2010), "The PASTEL catalogue of stellar parameters", Astronomy and Astrophysics 515: A111, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014247, Bibcode: 2010A&A...515A.111S.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Ren, S. (2013), "Hipparcos Photocentric Orbits of 72 Single-lined Spectroscopic Binaries", The Astronomical Journal 145 (3): 81, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/3/81, Bibcode: 2013AJ....145...81R
- ↑ Bailer-Jones, C. A. L. (March 2015), "Close encounters of the stellar kind", Astronomy & Astrophysics 575: 13, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201425221, A35, Bibcode: 2015A&A...575A..35B.
- ↑ Richichi, A.; Percheron, I.; Khristoforova, M. (February 2005), "CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics 431 (2): 773–777, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042039, Bibcode: 2005A&A...431..773R
 |