Chemistry:Dicarbonate

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dicarbonate
| |
| Other names
Pyrocarbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| MeSH | pyrocarbonate |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 2O2− 5 | |
| Molar mass | 104.017 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |

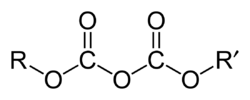
A dicarbonate, also known as a pyrocarbonate, is a chemical containing the divalent –O–C(=O)–O–C(=O)–O– or –C
2O
5– functional group, which consists of two carbonate groups sharing an oxygen atom. These compounds can be viewed as derivatives of the hypothetical compound dicarbonic acid, HO–C(=O)–O–C(=O)–OH or H
2C
2O
5. Two important organic compounds containing this group are dimethyl dicarbonate H
3C–C
2O
5–CH
3 and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (H
3C–)
3C–C
2O
5–C(–CH
3)
3.
It is one of the oxocarbon anions, consisting solely of oxygen and carbon. The anion has the formula −
O–C(=O)–O–C(=O)–O−
or C
2O2−
5. Dicarbonate salts are apparently unstable at ambient conditions, but can be made under pressure and may have a fleeting existence in carbonate solutions.[2]
The term dicarbonate is sometimes used erroneously to refer to bicarbonate, the common name of the hydrogencarbonate anion HCO−
3 or esters of the hydrogencarbonate functional group –O–C(=O)–OH. It is also sometimes used for chemicals that contain two carbonate units in their covalent structure or stoichiometric formula.
Inorganic salts
PbC
2O
5 (lead(II) dicarbonate) can be formed at 30 GPa and 2000K from PbCO3 and CO2. It forms white monoclinic crystals, with space group P21/c and four formula units per unit cell. At 30 GPa the unit cell has a=4.771 b=8.079 c=7.070 Å and β=91.32°. The unit cell volume is 272.4 Å3 and density 7.59.[3]
SrC
2O
5 (strontium dicarbonate) is very similar to the lead compound, and also has monoclinic structure with space group P21/c and four formula units per unit cell. At 30 GPa the unit cell has a=4.736 b=8.175 c=7.140 Å and β=91.34°. The unit cell volume is 276.3 Å3 and density 4.61.[3] The double Sr=O bonds have lengths of 1.22, 1.24, and 1.25 Å. The single Sr-O bonds have lengths of 1.36 and 1.41 Å. The angles subtended at the carbon atoms are slightly less than 120°, and the angle at the C-O-C is larger.[4]
See also
- Boc anhydride
- Tricarbonate
- Peroxodicarbonate
- Oxalate
- Pyrosulfate
- Peroxydisulfate
- Dithionate
- Trithionate
- Tetrathionate
- Pyrophosphate
- Polyphosphate
References
- ↑ Plácido García; Helge Willner; Maximiliano Burgos Paci; Gustavo A. Argüello; Thorsten Berends (2005). "Bis(trifluoromethyl)dicarbonate, CF3OC(O)OC(O)OCF3". J. Fluorine Chem. 126 (6): 984–990. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2005.05.002.
- ↑ Zeller, Klaus-Peter; Schuler, Paul; Haiss, Peter (2005). "The hidden equilibrium in aqueous sodium carbonate solutions: Evidence for the formation of the dicarbonate anion". Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005 (1): 168–172. doi:10.1002/ejic.200400445.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Spahr, Dominik; König, Jannes; Bayarjargal, Lkhamsuren; Luchitskaia, Rita; Milman, Victor; Perlov, Alexander; Liermann, Hanns-Peter; Winkler, Björn (22 June 2022). "Synthesis and Structure of Pb[C2O5]: An Inorganic Pyrocarbonate Salt". Inorganic Chemistry 61 (26): 9855–9859. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01507. PMID 35730801.
- ↑ Spahr, Dominik; König, Jannes; Bayarjargal, Lkhamsuren; Milman, Victor; Perlov, Alexander; Liermann, Hanns-Peter; Winkler, Björn (23 February 2022). "Sr[C2O5 ] is an Inorganic Pyrocarbonate Salt with [C 2 O 5 ] 2– Complex Anions". Journal of the American Chemical Society 144 (7): 2899–2904. doi:10.1021/jacs.2c00351. PMID 35134291.
 |