Biology:SUMO protein
In molecular biology, SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) proteins are a family of small proteins that are covalently attached to and detached from other proteins in cells to modify their function. This process is called SUMOylation (sometimes written sumoylation). SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.[1]
SUMO proteins are similar to ubiquitin and are considered members of the ubiquitin-like protein family. SUMOylation is directed by an enzymatic cascade analogous to that involved in ubiquitination. In contrast to ubiquitin, SUMO is not used to tag proteins for degradation. Mature SUMO is produced when the last four amino acids of the C-terminus have been cleaved off to allow formation of an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal glycine residue of SUMO and an acceptor lysine on the target protein.
SUMO family members often have dissimilar names; the SUMO homologue in yeast, for example, is called SMT3 (suppressor of mif two 3). Several pseudogenes have been reported for SUMO genes in the human genome.
Function
SUMO modification of proteins has many functions. Among the most frequent and best studied are protein stability, nuclear-cytosolic transport, and transcriptional regulation. Typically, only a small fraction of a given protein is SUMOylated and this modification is rapidly reversed by the action of deSUMOylating enzymes. SUMOylation of target proteins has been shown to cause a number of different outcomes including altered localization and binding partners. The SUMO-1 modification of RanGAP1 (the first identified SUMO substrate) leads to its trafficking from cytosol to nuclear pore complex.[2][3] The SUMO modification of ninein leads to its movement from the centrosome to the nucleus.[4] In many cases, SUMO modification of transcriptional regulators correlates with inhibition of transcription.[5] One can refer to the GeneRIFs of the SUMO proteins, e.g. human SUMO-1,[6] to find out more.
There are 4 confirmed SUMO isoforms in humans; SUMO-1, SUMO-2, SUMO-3 and SUMO-4. At the amino acid level, SUMO1 is about 50% identical to SUMO2.[citation needed] SUMO-2/3 show a high degree of similarity to each other and are distinct from SUMO-1. SUMO-4 shows similarity to SUMO-2/3 but differs in having a Proline instead of Glutamine at position 90. As a result, SUMO-4 isn't processed and conjugated under normal conditions, but is used for modification of proteins under stress-conditions like starvation.[7] During mitosis, SUMO-2/3 localize to centromeres and condensed chromosomes, whereas SUMO-1 localizes to the mitotic spindle and spindle midzone, indicating that SUMO paralogs regulate distinct mitotic processes in mammalian cells.[8] One of the major SUMO conjugation products associated with mitotic chromosomes arose from SUMO-2/3 conjugation of topoisomerase II, which is modified exclusively by SUMO-2/3 during mitosis.[9] SUMO-2/3 modifications seem to be involved specifically in the stress response.[10] SUMO-1 and SUMO-2/3 can form mixed chains, however, because SUMO-1 does not contain the internal SUMO consensus sites found in SUMO-2/3, it is thought to terminate these poly-SUMO chains.[11] Serine 2 of SUMO-1 is phosphorylated, raising the concept of a 'modified modifier'.[12]
DNA damage response
Cellular DNA is regularly exposed to DNA damaging agents. A DNA damage response (DDR) that is well regulated and intricate is usually employed to deal with the potential deleterious effects of the damage. When DNA damage occurs, SUMO protein has been shown to act as a molecular glue to facilitate the assembly of large protein complexes in repair foci.[13] Also, SUMOylation can alter a protein's biochemical activities and interactions. SUMOylation plays a role in the major DNA repair pathways of base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, non-homologous end joining and homologous recombinational repair. [13] SUMOylation also facilitates error prone translation synthesis.
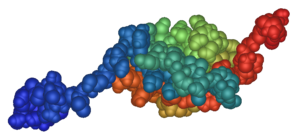
Structure
SUMO proteins are small; most are around 100 amino acids in length and 12 kDa in mass. The exact length and mass varies between SUMO family members and depends on which organism the protein comes from. Although SUMO has very little sequence identity with ubiquitin (less than 20%) at the amino acid level, it has a nearly identical structural fold. SUMO protein has a unique N-terminal extension of 10-25 amino acids which other ubiquitin-like proteins do not have. This N-terminal is found related to the formation of SUMO chains.[14]
The structure of human SUMO1 is depicted on the right. It shows SUMO1 as a globular protein with both ends of the amino acid chain (shown in red and blue) sticking out of the protein's centre. The spherical core consists of an alpha helix and a beta sheet. The diagrams shown are based on an NMR analysis of the protein in solution.
Prediction of SUMO attachment
Most SUMO-modified proteins contain the tetrapeptide consensus motif Ψ-K-x-D/E where Ψ is a hydrophobic residue, K is the lysine conjugated to SUMO, x is any amino acid (aa), D or E is an acidic residue. Substrate specificity appears to be derived directly from Ubc9 and the respective substrate motif. Currently available prediction programs are:
- SUMOplot - online free access software developed to predict the probability for the SUMO consensus sequence (SUMO-CS) to be engaged in SUMO attachment.[15] The SUMOplot score system is based on two criteria: 1) direct amino acid match to the SUMO-CS observed and shown to bind Ubc9, and 2) substitution of the consensus amino acid residues with amino acid residues exhibiting similar hydrophobicity. SUMOplot has been used in the past to predict Ubc9 dependent sites.
- seeSUMO - uses random forests and support vector machines trained on the data collected from the literature[16]
- SUMOsp - uses PSSM to score potential SUMOylation peptide stites. It can predict sites followed the ψKXE motif and unusual SUMOylation sites contained other non-canonical motifs.[17]
- JASSA - online free access predictor of SUMOylation sites (classical and inverted consensus) and SIMs (SUMO interacting motif). JASSA uses a scoring system based on a Position Frequency Matrix derived from the alignment of experimental SUMOylation sites or SIMs. Novel features were implemented towards a better evaluation of the prediction, including identification of database hits matching the query sequence and representation of candidate sites within the secondary structural elements and/or the 3D fold of the protein of interest, retrievable from deposited PDB files.[18]
SUMO attachment (SUMOylation)
SUMO attachment to its target is similar to that of ubiquitin (as it is for the other ubiquitin-like proteins such as NEDD 8). The SUMO precursor has some extra amino acids that need to be removed, therefore a C-terminal peptide is cleaved from the SUMO precursor by a protease (in human these are the SENP proteases or Ulp1 in yeast) to reveal a di-glycine motif. The obtained SUMO then becomes bound to an E1 enzyme (SUMO Activating Enzyme (SAE)) which is a heterodimer (subunits SAE1 and SAE2). It is then passed to an E2, which is a conjugating enzyme (Ubc9). Finally, one of a small number of E3 ligating proteins attaches it to the protein. In yeast, there are four SUMO E3 proteins, Cst9,[19] Mms21, Siz1 and Siz2. While in ubiquitination an E3 is essential to add ubiquitin to its target, evidence suggests that the E2 is sufficient in SUMOylation as long as the consensus sequence is present. It is thought that the E3 ligase promotes the efficiency of SUMOylation and in some cases has been shown to direct SUMO conjugation onto non-consensus motifs. E3 enzymes can be largely classed into PIAS proteins, such as Mms21 (a member of the Smc5/6 complex) and Pias-gamma and HECT proteins. On Chromosome 17 of the human genome, SUMO2 is near SUMO1+E1/E2 and SUMO2+E1/E2, among various others. Some E3's, such as RanBP2, however, are neither.[20] Recent evidence has shown that PIAS-gamma is required for the SUMOylation of the transcription factor yy1 but it is independent of the zinc-RING finger (identified as the functional domain of the E3 ligases). SUMOylation is reversible and is removed from targets by specific SUMO proteases. In budding yeast, the Ulp1 SUMO protease is found bound at the nuclear pore, whereas Ulp2 is nucleoplasmic. The distinct subnuclear localisation of deSUMOylating enzymes is conserved in higher eukaryotes.[21]
DeSUMOylation
SUMO can be removed from its substrate, which is called deSUMOylation. Specific proteases mediate this procedure (SENP in human or Ulp1 and Ulp2 in yeast).[14]
Role in protein purification
Recombinant proteins expressed in E. coli may fail to fold properly, instead forming aggregates and precipitating as inclusion bodies.[22] This insolubility may be due to the presence of codons read inefficiently by E. coli, differences in eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes, or lack of appropriate molecular chaperones for proper protein folding.[23] In order to purify such proteins it may be necessary to fuse the protein of interest with a solubility tag such as SUMO or MBP (maltose-binding protein) to increase the protein's solubility.[23] SUMO can later be cleaved from the protein of interest using a SUMO-specific protease such as Ulp1 peptidase.[23]
Human SUMO proteins
See also
- Ubiquitin
- Prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein
References
- ↑ "SUMO: a history of modification". Molecular Cell 18 (1): 1–12. April 2005. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.03.012. PMID 15808504.
- ↑ "A novel ubiquitin-like modification modulates the partitioning of the Ran-GTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 between the cytosol and the nuclear pore complex". The Journal of Cell Biology 135 (6 Pt 1): 1457–70. December 1996. doi:10.1083/jcb.135.6.1457. PMID 8978815.
- ↑ "A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2". Cell 88 (1): 97–107. January 1997. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81862-0. PMID 9019411.
- ↑ "SUMO-1 modification of centrosomal protein hNinein promotes hNinein nuclear localization". Life Sciences 78 (10): 1114–20. February 2006. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.06.021. PMID 16154161. http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/196401/1/903.pdf.
- ↑ "Something about SUMO inhibits transcription". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 15 (5): 536–41. October 2005. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2005.07.004. PMID 16095902.
- ↑ SUMO1 SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae)
- ↑ "A stress-dependent SUMO4 SUMOylation of its substrate proteins". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 375 (3): 454–9. October 2008. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.028. PMID 18708028.
- ↑ "SUMO-2/3 modification and binding regulate the association of CENP-E with kinetochores and progression through mitosis". Molecular Cell 29 (6): 729–41. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.013. PMID 18374647.
- ↑ "SUMO-2/3 regulates topoisomerase II in mitosis". The Journal of Cell Biology 163 (3): 477–87. November 2003. doi:10.1083/jcb.200304088. PMID 14597774.
- ↑ "Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (9): 6252–8. March 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6252. PMID 10692421.
- ↑ "In vivo identification of human small ubiquitin-like modifier polymerization sites by high accuracy mass spectrometry and an in vitro to in vivo strategy". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 7 (1): 132–44. January 2008. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700173-MCP200. PMID 17938407.
- ↑ "Phosphorylation of SUMO-1 occurs in vivo and is conserved through evolution". Journal of Proteome Research 7 (9): 4050–7. September 2008. doi:10.1021/pr800368m. PMID 18707152.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Genome maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the role of SUMO and SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases". Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (5): 2242–2261. 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1369. PMID 28115630.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Geiss-Friedlander, Ruth; Melchior, Frauke (December 2007). "Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on" (in en). Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 8 (12): 947–956. doi:10.1038/nrm2293. ISSN 1471-0080. PMID 18000527. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrm2293.
- ↑ Gramatikoff K. et al. In Frontiers of Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals, Science Press (2004) 4: pp.181-210.
- ↑ "Predicting protein SUMOylation sites from sequence features". Amino Acids 43 (1): 447–55. July 2012. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-1100-2. PMID 21986959.
- ↑ Ren, Jian; Gao, Xinjiao; Jin, Changjiang; Zhu, Mei; Wang, Xiwei; Shaw, Andrew; Wen, Longping; Yao, Xuebiao et al. (2009). "Systematic study of protein SUMOylation: Development of a site-specific predictor of SUMOsp 2.0". Proteomics 9 (12): 3409–3412. doi:10.1002/pmic.200800646. PMID 19504496.
- ↑ "JASSA: a comprehensive tool for prediction of SUMOylation sites and SIMs". Bioinformatics 31 (21): 3483–91. November 2015. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv403. PMID 26142185.
- ↑ "SUMO modifications control assembly of synaptonemal complex and polycomplex in meiosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Genes & Development 20 (15): 2067–81. August 2006. doi:10.1101/gad.1430406. PMID 16847351.
- ↑ "The RanBP2 SUMO E3 ligase is neither HECT- nor RING-type". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 11 (10): 984–91. October 2004. doi:10.1038/nsmb834. PMID 15378033.
- ↑ "Modification in reverse: the SUMO proteases". Trends in Biochemical Sciences 32 (6): 286–95. June 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.05.002. PMID 17499995.
- ↑ Burgess, Richard; Deutscher, Murray (2009). Guide to Protein Purification. Methods in Enzymology. 463 (2nd ed.). pp. 259–282. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(09)63017-2.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Kuo, Dennis; Nie, Minghua; Courey, Albert (2014). Protein Affinity Tags. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols). New York, NY: Humana Press. pp. 71–80. ISBN 978-1-4939-1034-2. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263294849.
Further reading
- "Mutual interactions between the SUMO and ubiquitin systems: a plea of no contest". Trends in Cell Biology 15 (10): 525–32. October 2005. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2005.08.002. PMID 16125934.
- "Something about SUMO inhibits transcription". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 15 (5): 536–41. October 2005. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2005.07.004. PMID 16095902.
- "SUMO wrestling with type 1 diabetes". Journal of Molecular Medicine 83 (7): 504–13. July 2005. doi:10.1007/s00109-005-0645-5. PMID 15806321.
- "Modification with SUMO. A role in transcriptional regulation". EMBO Reports 4 (2): 137–42. February 2003. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor738. PMID 12612601.
- "SUMO fusion technology for enhanced protein expression and purification in prokaryotes and eukaryotes". Heterologous Gene Expression in E.coli. Methods in Molecular Biology. 705. 2011. pp. 15–30. doi:10.1007/978-1-61737-967-3_2. ISBN 978-1-61737-966-6.
- "Global SUMOylation on active chromatin is an acute heat stress response restricting transcription". Genome Biology 16 (1): 153–72. Jul 2015. doi:10.1186/s13059-015-0717-y. PMID 26259101.
- "Waves of sumoylation support transcription dynamics during adipocyte differentiation". Nucleic Acids Research 50 (3): 1351–1369. January 2022. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac027. PMID 35100417.
- "SUMOylation regulates the protein network and chromatin accessibility at glucocorticoid receptor-binding sites". Nucleic Acids Research 49 (4): 1951–1971. Feb 2021. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab032. PMID 33524141.
External links
- SUMO1 homology group from HomoloGene
- human SUMO proteins on ExPASy: SUMO1 SUMO2 SUMO3 SUMO4
Programs for prediction SUMOylation:
- SUMOplot Analysis Program — predicts and scores SUMOylation sites in your protein (by Abgent)
- seeSUMO - prediction of SUMOylation sites
- SUMOsp - prediction of SUMOylation sites
- JASSA - Predicts and scores SUMOylation sites and SIM (SUMO interacting motif)
Research laboratories
 |