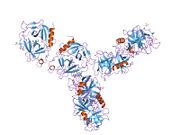
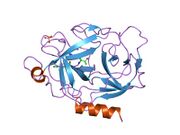
Biology:Granzyme A
Granzyme A (GzmA, EC 3.4.21.78, CTLA3, HuTPS, T-cell associated protease 1, cytotoxic T lymphocyte serine protease, TSP-1, T-cell derived serine proteinase) is a tryptase[1][2][3] and is one of the five granzymes encoded in the human genome.[4][5][6] In humans, GzmA is encoded by the GZMA gene in proximity to the GZMK gene on chromosome 5. This enzyme is present in cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) granules.
GzmA cleaves proteins after arginine or lysine basic residues. In CTL-targeted cells, it activates caspase-independent programmed cell death pathways that are unique and parallel to that of Granzyme B, although some substrates such as PARP-1[7] and lamin B[8] are shared with Granzyme B. Substrates of GzmA include Pro-IL-1β,[9] NDUFS3,[10] SET, APE1, and Ku70 among others. In vitro studies suggest that GzmA may have less cytotoxic capabilities than GzmB.[11][12]
In colorectal cancer, GzmA was associated with promotion of cancer development, which may be due to activation of inflammation-inducing cytokines from macrophages.[13]
See also
- GZMA
- GZMK
- GZMB
- GZMH
References
- ↑ "Purification and characterization of a T cell specific serine proteinase (TSP-1) from cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes". The EMBO Journal 5 (12): 3267–74. December 1986. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04638.x. PMID 3545816.
- ↑ "Cloning and chromosomal assignment of a human cDNA encoding a T cell- and natural killer cell-specific trypsin-like serine protease". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 85 (4): 1184–8. February 1988. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.4.1184. PMID 3257574. Bibcode: 1988PNAS...85.1184G.
- ↑ "Human and murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte serine proteases: subsite mapping with peptide thioester substrates and inhibition of enzyme activity and cytolysis by isocoumarins". Biochemistry 30 (8): 2217–27. February 1991. doi:10.1021/bi00222a027. PMID 1998680.
- ↑ "Characterization of three serine esterases isolated from human IL-2 activated killer cells". J Immunol 141 (9): 3142–7. Nov 1988. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.141.9.3142. PMID 3262682.
- ↑ "Identification of granzyme A isolated from cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-granules as one of the proteases encoded by CTL-specific genes". FEBS Lett 208 (1): 84–8. Dec 1986. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(86)81537-X. PMID 3533635.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GZMA granzyme A (granzyme 1, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated serine esterase 3)". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3001.
- ↑ Zhu, Pengcheng; Martinvalet, Denis; Chowdhury, Dipanjan; Zhang, Dong; Schlesinger, Ann; Lieberman, Judy (2009-08-06). "The cytotoxic T lymphocyte protease granzyme A cleaves and inactivates poly(adenosine 5'-diphosphate-ribose) polymerase-1". Blood 114 (6): 1205–1216. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-12-195768. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 19506301.
- ↑ Zhang, D.; Beresford, P. J.; Greenberg, A. H.; Lieberman, J. (2001-05-08). "Granzymes A and B directly cleave lamins and disrupt the nuclear lamina during granule-mediated cytolysis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98 (10): 5746–5751. doi:10.1073/pnas.101329598. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 11331782. Bibcode: 2001PNAS...98.5746Z.
- ↑ Irmler, M.; Hertig, S.; MacDonald, H. R.; Sadoul, R.; Becherer, J. D.; Proudfoot, A.; Solari, R.; Tschopp, J. (1995-05-01). "Granzyme A is an interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme". The Journal of Experimental Medicine 181 (5): 1917–1922. doi:10.1084/jem.181.5.1917. ISSN 0022-1007. PMID 7722467.
- ↑ Martinvalet, Denis; Dykxhoorn, Derek M.; Ferrini, Roger; Lieberman, Judy (2008-05-16). "Granzyme A cleaves a mitochondrial complex I protein to initiate caspase-independent cell death". Cell 133 (4): 681–692. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.032. ISSN 1097-4172. PMID 18485875.
- ↑ Martinvalet, Denis; Walch, Michael; Jensen, Danielle; Thiery, Jerome; Lieberman, Judy (Oct 29, 2009). "Response: Granzyme A: cell death–inducing protease, proinflammatory agent, or both?". Blood 114 (8): 3969–3970. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-08-233577.
- ↑ Metkar, Sunil S.; Menaa, Cheikh; Pardo, Julian; Wang, Baikun; Wallich, Reinhard; Freudenberg, Marina; Kim, Stephen; Raja, Srikumar M. et al. (2008-11-14). "Human and mouse granzyme A induce a proinflammatory cytokine response". Immunity 29 (5): 720–733. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.014. ISSN 1097-4180. PMID 18951048.
- ↑ Santiago, Llipsy; Castro, Marta; Sanz-Pamplona, Rebeca; Garzón, Marcela; Ramirez-Labrada, Ariel; Tapia, Elena; Moreno, Víctor; Layunta, Elena et al. (2020-07-07). "Extracellular Granzyme A Promotes Colorectal Cancer Development by Enhancing Gut Inflammation". Cell Reports 32 (1): 107847. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107847. ISSN 2211-1247. PMID 32640217. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32640217/.
Further reading
- "Granzyme A binding to target cell proteins. Granzyme A binds to and cleaves nucleolin in vitro". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (22): 14703–8. 1991. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)98743-0. PMID 1860869.
- "Human cytotoxic lymphocyte tryptase. Its purification from granules and the characterization of inhibitor and substrate specificity". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (26): 13215–22. 1988. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)37694-4. PMID 3047119.
- "Comparative molecular model building of two serine proteinases from cytotoxic T lymphocytes". Proteins 4 (3): 190–204. 1989. doi:10.1002/prot.340040306. PMID 3237717.
- "Cloning and chromosomal assignment of a human cDNA encoding a T cell- and natural killer cell-specific trypsin-like serine protease". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (4): 1184–8. 1988. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.4.1184. PMID 3257574. Bibcode: 1988PNAS...85.1184G.
- "Characterization of granzymes A and B isolated from granules of cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocytes". J. Immunol. 141 (10): 3471–7. 1988. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.141.10.3471. PMID 3263427.
- "Loss of cytotoxic T lymphocyte function in Chediak-Higashi syndrome arises from a secretory defect that prevents lytic granule exocytosis". J. Immunol. 154 (11): 6122–31. 1995. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.154.11.6122. PMID 7751653.
- "Close co-localization of CD4 and a serine esterase tryptase TL2 on the cell-surface of human monocytoid and CD4+ lymphoid cells". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 201 (3): 1390–5. 1994. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.1857. PMID 7912927.
- "The human granzyme A (HFSP, CTLA3) gene maps to 5q11-q12 and defines a new locus of the serine protease superfamily". Genomics 18 (2): 401–3. 1994. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1483. PMID 8288245.
- "Recombinant human granzyme A binds to two putative HLA-associated proteins and cleaves one of them". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (17): 9285–90. 1997. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.17.9285. PMID 9256474. Bibcode: 1997PNAS...94.9285B.
- "Extracellular granzymes A and B in humans: detection of native species during CTL responses in vitro and in vivo". J. Immunol. 160 (7): 3610–6. 1998. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.160.7.3610. PMID 9531325.
- "Granzymes A and B directly cleave lamins and disrupt the nuclear lamina during granule-mediated cytolysis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (10): 5746–51. 2001. doi:10.1073/pnas.101329598. PMID 11331782. Bibcode: 2001PNAS...98.5746Z.
- "Granzyme A activates an endoplasmic reticulum-associated caspase-independent nuclease to induce single-stranded DNA nicks". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (46): 43285–93. 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108137200. PMID 11555662.
- "HMG2 Interacts with the Nucleosome Assembly Protein SET and Is a Target of the Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Protease Granzyme A". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (8): 2810–20. 2002. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.8.2810-2820.2002. PMID 11909973.
- "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. 2003. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M.
- "Cleaving the oxidative repair protein Ape1 enhances cell death mediated by granzyme A". Nat. Immunol. 4 (2): 145–53. 2003. doi:10.1038/ni885. PMID 12524539.
- "Granzyme A: the road less traveled". Nat. Immunol. 4 (2): 106–8. 2003. doi:10.1038/ni0203-106. PMID 12555094.
- "Catalog of 680 variations among eight cytochrome p450 ( CYP) genes, nine esterase genes, and two other genes in the Japanese population". J. Hum. Genet. 48 (5): 249–70. 2003. doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0021-7. PMID 12721789.
- "The oligomeric structure of human granzyme A is a determinant of its extended substrate specificity". Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 (7): 527–34. 2003. doi:10.1038/nsb944. PMID 12819769.
External links
- Granzyme+A at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |