(ε, δ)-definition of limit
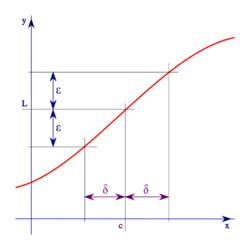
In calculus, the (ε, δ)-definition of limit ("epsilon–delta definition of limit") is a formalization of the notion of limit. The concept is due to Augustin-Louis Cauchy, who never gave a formal (ε, δ) definition of limit in his Cours d'Analyse, but occasionally used ε, δ arguments in proofs. It was first given as a formal definition by Bernard Bolzano in 1817, and the definitive modern statement was ultimately provided by Karl Weierstrass.[1][2] It provides rigor to the following informal notion: the dependent expression f(x) approaches the value L as the variable x approaches the value c if f(x) can be made as close as desired to L by taking x sufficiently close to c.
History
Although the Greeks examined limiting processes, such as the Babylonian method, they probably had no concept similar to the modern limit.[3] The need for the concept of a limit arose in the 1600s, when Pierre de Fermat attempted to find the slope of the tangent line at a point to the graph of a function such as . Using a non-zero but almost zero quantity , Fermat performed the following calculation:
The key to the above calculation is that since is non-zero, one can divide by , but since is close to 0, is essentially .[4] Quantities such as are called infinitesimals. The problem with this calculation is that mathematicians of the era were unable to rigorously define a quantity with properties of ,[5] even though it was common practice to 'neglect' higher power infinitesimals and this seemed to yield correct results.
This problem reappeared later in the 1600s at the center of the development of calculus, where calculations such as Fermat's are important to the calculation of derivatives. Isaac Newton first developed calculus via an infinitesimal quantity called a fluxion. He developed them in reference to the idea of an "infinitely small moment in time..."[6] However, Newton later rejected fluxions in favor of a theory of ratios that is close to the modern definition of the limit.[6] Moreover, Newton was aware that the limit of the ratio of vanishing quantities was not itself a ratio, as he wrote:
- Those ultimate ratios ... are not actually ratios of ultimate quantities, but limits ... which they can approach so closely that their difference is less than any given quantity...
Additionally, Newton occasionally explained limits in terms similar to the epsilon–delta definition.[7] Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz developed an infinitesimal of his own and tried to provide it with a rigorous footing, but it was still greeted with unease by some mathematicians and philosophers.[6]
Augustin-Louis Cauchy gave a definition of limit in terms of a more primitive notion he called a variable quantity. He never gave an epsilon–delta definition of limit (Grabiner 1981). Some of Cauchy's proofs contain indications of the epsilon–delta method. Whether or not his foundational approach can be considered a harbinger of Weierstrass's is a subject of scholarly dispute. Grabiner feels that it is, while Schubring (2005) disagrees.[dubious ][1] Nakane concludes that Cauchy and Weierstrass gave the same name to different notions of limit.[8][unreliable source?]
Eventually, Weierstrass and Bolzano are credited with providing a rigorous footing for calculus, in the form of the modern definition of the limit.[1][2] The need for reference to an infinitesimal was then removed,[6] and Fermat's computation turned into the computation of the following limit:
This is not to say that the limiting definition was free of problems as, although it removed the need for infinitesimals, it did require the construction of the real numbers by Richard Dedekind.[6] This is also not to say that infinitesimals have no place in modern mathematics, as later mathematicians were able to rigorously create infinitesimal quantities as part of the hyperreal number or surreal number systems. Moreover, it is possible to rigorously develop calculus with these quantities and they have other mathematical uses.[9]
Informal statement
A viable informal (that is, intuitive or provisional) definition is that a "function f approaches the limit L near a (symbolically, ) if we can make f(x) as close as we like to L by requiring that x be sufficiently close to, but unequal to, a."[10]
When we say that two things are close (such as f(x) and L or x and a), we mean that the difference (or distance) between them is small. When f(x), L, x, and a are real numbers, the difference/distance between two numbers is the absolute value of the difference of the two. Thus, when we say f(x) is close to L, we mean that |f(x) − L| is small. When we say that x and a are close, we mean that |x − a| is small.[11]
When we say that we can make f(x) as close as we like to L, we mean that for all non-zero distances, ε, we can make the distance between f(x) and L smaller than ε.[11]
When we say that we can make f(x) as close as we like to L by requiring that x be sufficiently close to, but, unequal to, a, we mean that for every non-zero distance ε, there is some non-zero distance δ such that if the distance between x and a is less than δ then the distance between f(x) and L is smaller than ε.[11]
The informal/intuitive aspect to be grasped here is that the definition requires the following internal conversation (which is typically paraphrased by such language as "your enemy/adversary attacks you with an ε, and you defend/protect yourself with a δ"): One is provided with any challenge ε > 0 for a given f, a, and L. One must answer with a δ > 0 such that 0 < |x − a| < δ implies that |f(x) − L| < ε. If one can provide an answer for any challenge, then one has proven that the limit exists.[12]
Precise statement and related statements
Precise statement for real-valued functions
The definition of the limit of a function is as follows:[11]
Let be a real-valued function defined on a subset of the real numbers. Let be a limit point of and let be a real number. We say that
if for every there exists a such that, for all , if , then .[13]
Symbolically:
If or , then the condition that is a limit point can be replaced with the simpler condition that c belongs to D, since closed real intervals and the entire real line are perfect sets.
Precise statement for functions between metric spaces
The definition can be generalized to functions that map between metric spaces. These spaces come with a function, called a metric, that takes two points in the space and returns a real number that represents the distance between the two points.[14] The generalized definition is as follows:[15]
Suppose is defined on a subset of a metric space with a metric and maps into a metric space with a metric . Let be a limit point of and let be a point of .
We say that
if for every , there exists a such that for all , if , then .
Since is a metric on the real numbers, one can show that this definition generalizes the first definition for real functions.[16]
Negation of the precise statement
The logical negation of the definition is as follows:[17]
Suppose is defined on a subset of a metric space with a metric and maps into a metric space with a metric . Let be a limit point of and let be a point of .
We say that
if there exists an such that for all there is an such that and .
We say that does not exist if for all , .
For the negation of a real valued function defined on the real numbers, simply set .
Precise statement for limits at infinity
The precise statement for limits at infinity is as follows:
Suppose is real-valued that is defined on a subset of the real numbers that contains arbitrarily large values. We say that
if for every , there is a real number such that for all , if then .[18]
It is also possible to give a definition in general metric spaces.[citation needed]
One-sided limits
The standard definition does not allow us to define limits at points of discontinuity. For this, one-sided limits are useful. We can formally define the limit "from the right" as
and the limit "from the left" as
Worked examples
Example 1
We will show that
- .
We let be given. We need to find a such that implies .
Since sine is bounded above by 1 and below by −1,
Thus, if we take , then implies , which completes the proof.
Example 2
Let us prove the statement that
for any real number .
Let be given. We will find a such that implies .
We start by factoring:
We recognize that is the term bounded by so we can presuppose a bound of 1 and later pick something smaller than that for .[19]
So we suppose . Since holds in general for real numbers and , we have
Thus,
Thus via the triangle inequality,
Thus, if we further suppose that
then
In summary, we set
So, if , then
Thus, we have found a such that implies . Thus, we have shown that
for any real number .
Example 3
Let us prove the statement that
This is easily shown through graphical understandings of the limit, and as such serves as a strong basis for introduction to proof. According to the formal definition above, a limit statement is correct if and only if confining to units of will inevitably confine to units of . In this specific case, this means that the statement is true if and only if confining to units of 5 will inevitably confine
to units of 12. The overall key to showing this implication is to demonstrate how and must be related to each other such that the implication holds. Mathematically, we want to show that
Simplifying, factoring, and dividing 3 on the right hand side of the implication yields
which immediately gives the required result if we choose
Thus the proof is completed. The key to the proof lies in the ability of one to choose boundaries in , and then conclude corresponding boundaries in , which in this case were related by a factor of 3, which is entirely due to the slope of 3 in the line
Continuity
A function f is said to be continuous at c if it is both defined at c and its value at c equals the limit of f as x approaches c:
The definition for a continuous function can be obtained from the definition of a limit by replacing with , to ensure that f is defined at c and equals the limit.
A function f is said to be continuous on an interval I if it is continuous at every point c of I.
Comparison with infinitesimal definition
Keisler proved that a hyperreal definition of limit reduces the logical quantifier complexity by two quantifiers.[20] Namely, converges to a limit L as tends to a if and only if the value is infinitely close to L for every infinitesimal e. (See Microcontinuity for a related definition of continuity, essentially due to Cauchy.)
Infinitesimal calculus textbooks based on Robinson's approach provide definitions of continuity, derivative, and integral at standard points in terms of infinitesimals. Once notions such as continuity have been thoroughly explained via the approach using microcontinuity, the epsilon–delta approach is presented as well. Karel Hrbáček argues that the definitions of continuity, derivative, and integration in Robinson-style non-standard analysis must be grounded in the ε–δ method, in order to cover also non-standard values of the input.[21] Błaszczyk et al. argue that microcontinuity is useful in developing a transparent definition of uniform continuity, and characterize the criticism by Hrbáček as a "dubious lament".[22] Hrbáček proposes an alternative non-standard analysis, which (unlike Robinson's) has many "levels" of infinitesimals, so that limits at one level can be defined in terms of infinitesimals at the next level.[23]
Family of formal limit definitions
There is not a single definition of limit - there is a whole family of definitions. This is due to the presence of infinity, and the concept of limits "from the right" and "from the left". The limit itself can be a finite value, , or . The value approached by can also be a finite value, , or , and if it is a finite value, it can be approached from the left or the right. Typically, each combination is given its own definition, like this:
| Notation | Def. | Example | |||||||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Grabiner, Judith V. (March 1983), "Who Gave You the Epsilon? Cauchy and the Origins of Rigorous Calculus", The American Mathematical Monthly 90 (3): 185–194, doi:10.2307/2975545, http://www.mr-ideahamster.com/classes/assets/a_evepsilon.pdf, retrieved 2009-05-01
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cauchy, A.-L. (1823), "Septième Leçon – Valeurs de quelques expressions qui se présentent sous les formes indéterminées Relation qui existe entre le rapport aux différences finies et la fonction dérivée", Résumé des leçons données à l'école royale polytechnique sur le calcul infinitésimal, Paris, http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k90196z/f45n5.capture, retrieved 2009-05-01, p. 44.. Accessed 2009-05-01.
- ↑ Stillwell, John (1989). Mathematics and its history. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 38–39. ISBN 978-1-4899-0007-4. https://archive.org/details/mathematicsitshi0000stil.
- ↑ Stillwell, John (1989). Mathematics and its history. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 104. ISBN 978-1-4899-0007-4. https://archive.org/details/mathematicsitshi0000stil.
- ↑ Stillwell, John (1989). Mathematics and its history. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 106. ISBN 978-1-4899-0007-4. https://archive.org/details/mathematicsitshi0000stil.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Buckley, Benjamin Lee (2012). The continuity debate : Dedekind, Cantor, du Bois-Reymond and Peirce on continuity and infinitesimals. p. 31-35. ISBN 9780983700487.
- ↑ Pourciau, B. (2001), "Newton and the Notion of Limit", Historia Mathematica 28 (1): 18–30, doi:10.1006/hmat.2000.2301
- ↑ Nakane, Michiyo. Did Weierstrass's differential calculus have a limit-avoiding character? His definition of a limit in ε−δ style. BSHM Bull. 29 (2014), no. 1, 51–59.
- ↑ Tao, Terence (2008). Structure and randomness : pages from year one of a mathematical blog. Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society. pp. 95–110. ISBN 978-0-8218-4695-7.
- ↑ Spivak, Michael (2008). Calculus (4th ed.). Houston, Tex.: Publish or Perish. p. 90. ISBN 978-0914098911. https://archive.org/details/calculus4thediti00mich.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Spivak, Michael (2008). Calculus (4th ed.). Houston, Tex.: Publish or Perish. p. 96. ISBN 978-0914098911. https://archive.org/details/calculus4thediti00mich.
- ↑ "Epsilon-Delta Definition of a Limit | Brilliant Math & Science Wiki" (in en-us). https://brilliant.org/wiki/epsilon-delta-definition-of-a-limit/.
- ↑ "1.2: Epsilon-Delta Definition of a Limit" (in en). 2017-04-21. https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Calculus/Book%3A_Calculus_(Apex)/01%3A_Limits/1.02%3A_Epsilon-Delta_Definition_of_a_Limit.
- ↑ Rudin, Walter (1976). Principles of Mathematical Analysis. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. p. 30. ISBN 978-0070542358. https://archive.org/details/principlesofmath00rudi.
- ↑ Rudin, Walter (1976). Principles of Mathematical Analysis. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. p. 83. ISBN 978-0070542358. https://archive.org/details/principlesofmath00rudi.
- ↑ Rudin, Walter (1976). Principles of Mathematical Analysis. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. p. 84. ISBN 978-0070542358. https://archive.org/details/principlesofmath00rudi.
- ↑ Spivak, Michael (2008). Calculus (4th ed.). Houston, Tex.: Publish or Perish. p. 97. ISBN 978-0914098911. https://archive.org/details/calculus4thediti00mich.
- ↑ Stewart, James (2016), Calculus (8 ed.), Cengage
- ↑ Spivak, Michael (2008). Calculus (4th ed.). Houston, Tex.: Publish or Perish. p. 95. ISBN 978-0914098911. https://archive.org/details/calculus4thediti00mich.
- ↑ Keisler, H. Jerome (2008), "Quantifiers in limits", Andrzej Mostowski and foundational studies, IOS, Amsterdam, pp. 151–170, http://www.math.wisc.edu/~keisler/limquant7.pdf
- ↑ Hrbacek, K. (2007), "Stratified Analysis?", in Van Den Berg, I.; Neves, V., The Strength of Nonstandard Analysis, Springer
- ↑ Błaszczyk, Piotr; Katz, Mikhail; Sherry, David (2012), "Ten misconceptions from the history of analysis and their debunking", Foundations of Science 18: 43–74, doi:10.1007/s10699-012-9285-8, Bibcode: 2012arXiv1202.4153B
- ↑ Hrbacek, K. (2009). "Relative set theory: Internal view". Journal of Logic and Analysis 1. http://logicandanalysis.org/index.php/jla/article/view/25/17.
Further reading
- Grabiner, Judith V. (1982). The Origins of Cauchy's Rigorous Calculus. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-14374-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=XuFcx-laQmIC.
- Schubring, Gert (2005). Conflicts Between Generalization, Rigor, and Intuition: Number Concepts Underlying the Development of Analysis in 17th–19th Century France and Germany (illustrated ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-22836-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=rMWe3okqPOcC.
