Astronomy:19521 Chaos
 19521 Chaos as imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2001 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Deep Ecliptic Survey |
| Discovery date | 19 November 1998 |
| Designations | |
| (19521) Chaos | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈkeɪ.ɒs/ |
| Named after | Chaos |
| 1998 WH24 | |
| Minor planet category | TNO (cubewano)[1][2] |
| Adjectives | Chaotian /keɪˈoʊʃən/[3] |
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 5902 days (16.16 yr) |
| Earliest precovery date | 17 October 1991 |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 50.636 astronomical unit|AU (7.5750 Tm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 40.957 AU (6.1271 Tm) |
| 45.796 AU (6.8510 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.10567 |
| Orbital period | 309.92 yr (113199 d) |
| Average Orbital speed | 4.3931 km/s |
| Mean anomaly | 337.2998° |
| Mean motion | 0° 0m 11.449s / day |
| Inclination | 12.0502° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 50.0239° |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | ≈ 23 December 2033[4] ±10 days |
| 58.4097° | |
| Jupiter MOID | 35.8 AU (5.36 Tm) |
| Neptune MOID | 12.5 AU (1.87 Tm)[5] |
| TJupiter | 5.884 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 612 km (est. at 0.05)[7] 600+140 −130 km [8] ~665 [9] |
| Geometric albedo | 0.050+0.030 −0.016 [8] |
| B–V=0.95±0.03 [9] V–R=0.63±0.03 [9] V–I=1.25±0.04 [9] | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 4.8 [6] 5.0 [7][9] |
19521 Chaos is a cubewano, a Kuiper-belt object not in resonance with any planet. Chaos was discovered in 1998 by the Deep Ecliptic Survey with Kitt Peak's 4 m telescope. Its albedo is 0.050+0.030
−0.016,[8] making it, with its absolute magnitude (H) of 4.8,[6] equivalent to a single spherical body 600+140
−130 km in diameter.[8]
On 20 November 2020, Chaos occulted a magnitude 16.8 star. Three observers detected the occultation, finding that the object is likely smaller than 600 km in diameter.[10] Another occultation was recorded on 14 January 2022; full results on size, shape, geometric albedo, and the spin-axis orientation have not been released[needs update].[11] A further occultation occurred on 28 September 2023, with a shadow crossing most of North America. This occultation was observed by over 30 observers;[12] preliminary analysis suggests that Chaos is a binary (possibly a contact binary).[13]
Name
It is named after the primeval state of existence in Greek mythology, from which the first gods appeared.
Planetary symbols are no longer much used in astronomy, so Chaos never received a symbol in the astronomical literature. There is no standard symbol for Chaos used by astrologers either. Michael Moorcock's Symbol of Chaos (![]() ) has been used.[14]
) has been used.[14]
Orbit
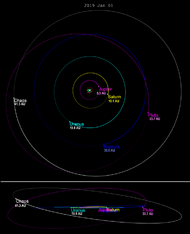
19521 Chaos has an orbital period of approximately 309 years. Its orbit is longer, but less eccentric than the orbit of Pluto. 19521 Chaos's orbit is inclined approximately 12° to the ecliptic. Its orbit never crosses the orbit of Neptune. Currently, the closest approach possible to Neptune (MOID) is 12.5 astronomical unit|AU (1.87 billion km).[5]

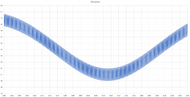
Chaos will come to perihelion at around December 2033,[4] coming as close as 40 AUs from Earth. Its brightest magnitude will be 20.8.
References
- ↑ "MPEC 2008-O05 : Distant Minor Planets (2008 AUG. 2.0 TT)". Minor Planet Center. 17 July 2008. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K08/K08O05.html.
- ↑ Buie, Marc W. (2004-11-09). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 19521". SwRI. http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~buie/kbo/astrom/19521.html.
- ↑ Thayer (1994). Gray World, Green Heart. Wiley. ISBN 9780471572732. https://archive.org/details/grayworldgreenhe00thay_0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 JPL Horizons Observer Location: @sun (Perihelion occurs when deldot changes from negative to positive. Uncertainty in time of perihelion is 3-sigma.)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "(19521) Chaos = 1998 WH24 orbit". IAU Minor Planet Center. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=Chaos.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "19521 Chaos (1998 WH24)". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=Chaos.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Brown, Michael E.. "How many dwarf planets are there in the outer solar system? (updates daily)". California Institute of Technology. http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dps.html.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Vilenius, E.; Kiss, C.; Mommert, M.; Müller, T.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Pal, A. et al. (2012). ""TNOs are cool": A survey of the trans-Neptunian region VI. Herschel / PACS observations and thermal modeling of 19 classical Kuiper belt objects". Astronomy and Astrophysics 541: A94. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118743. Bibcode: 2012A&A...541A..94V. https://archive.org/details/arxiv-1202.3657.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Doressoundiram, A.; Peixinho, N.; de Bergh, C.; Fornasier, S.; Thébault, Ph.; Barucci, M.A.; Veillet, C. (October 2002). "The color distribution in the Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt". The Astronomical Journal 124 (4): 2279–2296. doi:10.1086/342447. Bibcode: 2002AJ....124.2279D.
- ↑ Vara-Lubiano, Mónica; Morales, Nicolás; Rommel, Flavia; Ortiz, José Luis; Sicardy, Bruno; Santos-Sanz, Pablo (September 2021). "The multi-chord stellar occultation by (19521) Chaos on 2020 November 20". 15th Europlanet Science Congress 2021. Europlanet Society. doi:10.5194/epsc2021-626. EPSC2021-626. Bibcode: 2021EPSC...15..626V. https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EPSC2021/EPSC2021-626.html. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ↑ Ortiz, José Luis; Morales, Nicolás; Vara-Lubiano, Mónica; Kretlow, Mike; Sicardy, Bruno; Santos-Sanz, Pablo (September 2022). "The Trans-Neptunian Object (19521) Chaos as seen from stellar occultations and photometry observations". 16th Europlanet Science Congress 2022. Europlanet Society. doi:10.5194/epsc2022-520. EPSC2022-520. https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EPSC2022/EPSC2022-520.html. Retrieved 2 January 2023.
- ↑ Gault, Dave. "OccultWatcher Cloud". https://cloud.occultwatcher.net/event/1000-19521-87528-649970-U028826/1103807.
- ↑ Gómez-Limón Gallardo, José María; Leiva, R.; Ortiz, J. L.; Desmars, J.; Kilic, Y.; Vara-Lubiano, M.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Kretlow, M. et al. (2023). "Chaos: Stellar Occultations Reveal a Binary Tno?". Seventh Edition of the Spanish Meeting of Planetary Sciences and Exploration of the Solar System (7Th Cpess. Bibcode: 2023pses.conf80462G. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2023pses.conf80462G/abstract.
- ↑ Miller, Kirk (26 October 2021). "Unicode request for dwarf-planet symbols". https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2021/21224-dwarf-planet-syms.pdf.
External links
- "Original Minor Planet Electronic Circular (1998-X08) for 19521 Chaos". http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/mpec/J98/J98X08.html.
- "Revised Minor Planet Electronic Circular (1999-V03) 19521 Chaos". http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/mpec/J99/J99V03.html.
- 19521 Chaos at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 19521 Chaos at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |


