Astronomy:g Herculis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Hercules |
| Right ascension | 16h 28m 38.54859s[2] |
| Declination | +41° 52′ 54.0406″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.3 - 6.3[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[4] |
| Spectral type | M6− III[5] |
| B−V color index | 1.289±0.024[6] |
| Variable type | SRb[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 1.49±0.38[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +30.16[2] mas/yr Dec.: −5.14[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.21 ± 0.18[2] mas |
| Distance | 354 ± 7 ly (109 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.41[7] |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 843.7±21.1 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.37±0.11 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,451,918.2±43.9 HJD |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 246±21° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 2.3±0.3 km/s |
| Details | |
| g Her A | |
| Mass | 1.65±0.30[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 69.71+27.39 −13.20[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,455[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.20[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,400[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.01[11] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
g Herculis is a binary star[13] system in the northern constellation of Hercules. It has the Flamsteed designation 30 Herculis, while g Herculis is the Bayer designation. This system is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued point of light. Based upon a measured parallax of 9.2 mas, it is located around 354 light years away from the Sun. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 1.5 km/s.[6]
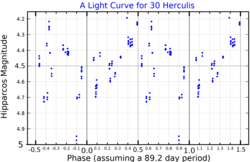
This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 2.310 years and an eccentricity of 0.37.[4] The visible component is an aging red giant on the asymptotic giant branch[4] with a stellar classification of M6− III.[5] According to Samus et al. (2017), it is a semiregular variable of subtype SRb, which ranges between visual magnitudes 4.3 and 6.3 over 89.2 days.[3][14] It displays cyclical periods of 62.3, 89.5, and 888.9 days.[4] The star is surrounded by a circumstellar dust shell that seems primarily composed of oxides of iron, magnesium, and aluminium, rather than silicates.[15]
References
- ↑ Light Curve, ESA, https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/hipparcos/java-tools/light-curve, retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Hinkle, Kenneth H. et al. (February 2002), "Velocity Observations of Multiple-Mode Asymptotic Giant Branch Variable Stars", The Astronomical Journal 123 (2): 1002–1012, doi:10.1086/338314, Bibcode: 2002AJ....123.1002H
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Keenan, P.; McNeil, R. (October 1989), "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 71: 245–266, doi:10.1086/191373, Bibcode: 1989ApJS...71..245K.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Schiavon, Ricardo P. (July 2007), "Population Synthesis in the Blue. IV. Accurate Model Predictions for Lick Indices and UBV Colors in Single Stellar Populations", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 171 (1): 146–205, doi:10.1086/511753, Bibcode: 2007ApJS..171..146S.
- ↑ Halabi, Ghina M.; Eid, Mounib El (August 2015), "Exploring masses and CNO surface abundances of red giant stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 451 (3): 2957–2967, doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1141, Bibcode: 2015MNRAS.451.2957H.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Charbonnel, C.; Lagarde, N.; Jasniewicz, G.; North, P. L.; Shetrone, M.; Krugler Hollek, J.; Smith, V. V.; Smiljanic, R. et al. (2020), "Lithium in red giant stars: Constraining non-standard mixing with large surveys in the Gaia era", Astronomy and Astrophysics 633: A34, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201936360, Bibcode: 2020A&A...633A..34C.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Ramírez, Solange V. et al. (2000), "Stellar Iron Abundances at the Galactic Center", The Astrophysical Journal 537 (1): 205–220, doi:10.1086/309022, Bibcode: 2000ApJ...537..205R.
- ↑ "g Her". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=g+Her.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ Otero, Sebastian Alberto (June 28, 2011), "g Herculis", AAVSO Website (American Association of Variable Star Observers), http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=15898, retrieved 20 July 2014
- ↑ Posch, Th. et al. (October 2002), "On the origin of the 19.5 μ m feature. Identifying circumstellar Mg-Fe-oxides", Astronomy and Astrophysics 393: L7–L10, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021127, Bibcode: 2002A&A...393L...7P.
 |