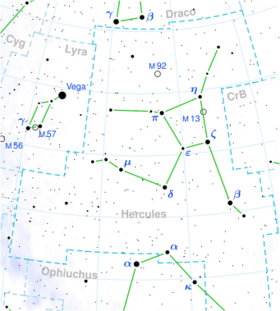
Astronomy:Pi Herculis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Hercules |
| Right ascension | 17h 15m 02.83424s[1] |
| Declination | +36° 48′ 32.9816″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.15[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K3 II[3][4] |
| U−B color index | +1.66[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.45[2] |
| Variable type | suspected[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −25.57±0.20[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −27.402[1] mas/yr Dec.: 2.925[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 8.8991 ± 0.1323[1] mas |
| Distance | 367 ± 5 ly (112 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.10+0.13 −0.12[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.77±0.2[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 64.02+0.89 −0.91[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,176±67[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.26±0.05[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,223±53[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.01±0.1[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 6.12[10] km/s |
| Age | 220±40[8] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Pi Herculis (π Her, π Herculis) is a third-magnitude star in the constellation Hercules. As one of the four stars in the Keystone asterism, specifically representing the northeastern corner, it is one of the constellation's more easily recognized. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.2,[11] which is visible to the naked eye and makes it one of its brighter members. The Gaia spacecraft mission estimated its distance at roughly 112 parsecs from Earth, or about 367 light years away.[1] The overall reduction in the star's visual magnitude due to extinction from the intervening cosmic dust is 0.11.[6]
Properties
Pi Herculis is a bright giant star with a stellar classification of K3 II.[3][4] P.C. Keenan and R. E. Pitts (1980) graded it as a spectral type K3 IIab[12] and it is sometimes listed with this alternate classification. The star is enormous compared to the Sun, having a mass that is 4.5 times solar and a radius approximately 60 times depending on which wavelength the star's angular diameter is measured at. Due to limb darkening, all giant and supergiant stars present unique challenges when measuring their photosphere. This orange-hued giant shines with 1,330 times the luminosity of the Sun.[13] It is a low-amplitude photometric variable star showing a typical change of roughly 0.0054 in magnitude over a 24-hour period.[14]
Radial velocity variations
Low-amplitude radial velocity variations with a period of 613 days in the bright giant have suggested the possible presence of a substellar companion. If this is really due to a low-mass object, such a companion would be as small as 0.027 solar masses (27 times the mass of Jupiter, probably a brown dwarf) and 3 astronomical units away from the bright primary. A substellar companion is only one of several hypotheses to explain the star's behaviour. Most likely the cause of the variation is weak pulsation of the star's atmosphere.[13]
With a luminosity more than 1,000 times that of the Sun, an orbit where a planet could be habitable would be located 37 AU away from Pi Herculis—in Solar System terms, halfway between Neptune's and Pluto's orbits. On the other hand, a putative companion would orbit in a scorching region and would be as hot as a planet would at 0.08 AU around a Sun-like star. In any case it's likely that it would soon be swallowed up by the expanding giant.[15]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986). "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)". Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data (SIMBAD). Bibcode: 1986EgUBV........0M.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Morgan, W. W.; Roman, Nancy G. (November 1950), "Revised Standards for Supergiants on the System of the Yerkes Spectral Atlas", Astrophysical Journal 112: 362–364, doi:10.1086/145351, Bibcode: 1950ApJ...112..362M
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Ivanov, Valentin D. et al. (April 2004), "A Medium-Resolution Near-Infrared Spectral Library of Late-Type Stars. I", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 151 (2): 387–397, doi:10.1086/381752, Bibcode: 2004ApJS..151..387I
- ↑ Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, GCVS 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Famaey, B. et al. (January 2005), "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters", Astronomy and Astrophysics 430: 165–186, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272, Bibcode: 2005A&A...430..165F
- ↑ Carney, Bruce W. et al. (March 2008), "Rotation and Macroturbulence in Metal-Poor Field Red Giant and Red Horizontal Branch Stars", The Astronomical Journal 135 (3): 892–906, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/3/892, Bibcode: 2008AJ....135..892C
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Baines, Ellyn K. et al. (2018), "Fundamental Parameters of 87 Stars from the Navy Precision Optical Interferometer", The Astronomical Journal 155 (1): 30, doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa9d8b, Bibcode: 2018AJ....155...30B.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Reffert, Sabine; Bergmann, Christoph; Quirrenbach, Andreas; Trifonov, Trifon; Künstler, Andreas (2015-02-01). "Precise radial velocities of giant stars. VII. Occurrence rate of giant extrasolar planets as a function of mass and metallicity". Astronomy and Astrophysics 574: A116. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322360. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2015A&A...574A.116R.
- ↑ Hekker, S.; Meléndez, J. (2007). "Precise radial velocities of giant stars. III. Spectroscopic stellar parameters". Astronomy and Astrophysics 475 (3): 1003–1009. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078233. Bibcode: 2007A&A...475.1003H.
- ↑ "* pi. Her". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=%2A+pi.+Her.
- ↑ Keenan, P. C.; Pitts, R. E. (April 1980), "Revised MK spectral types for G, K, and M stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 42: 541–563, doi:10.1086/190662, Bibcode: 1980ApJS...42..541K
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Kaler, James B., "Pi Herculis", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/piher.html, retrieved 2012-03-13
- ↑ Henry, Gregory W. et al. (September 2000), "Photometric Variability in a Sample of 187 G and K Giants", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 130 (1): 201–225, doi:10.1086/317346, Bibcode: 2000ApJS..130..201H
- ↑ Hatzes, Artie P.; Cochran, William D. (March 1999). "Long-period, low-amplitude radial velocity variations in the K giant star pi Herculis: rotation, substellar companion or non-radial pulsations?". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 304 (1): 109–118. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02288.x. Bibcode: 1999MNRAS.304..109H.
External links
See also
- Pi2 Ursae Majoris
- Beta Ophiuchi
Coordinates: ![]() 17h 15m 02.80s, +36° 48′ 33.0″
17h 15m 02.80s, +36° 48′ 33.0″
 |