Astronomy:NGC 3054
From HandWiki
| NGC 3054 | |
|---|---|
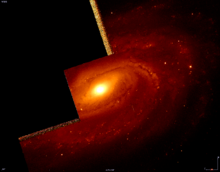 NGC 3054 (Hubble Space Telescope) | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Hydra |
| Right ascension | 09h 54m 28.605s[1] |
| Declination | −25° 42′ 12.37″[1] |
| Redshift | 2,425 km/s[2] |
| Distance | 130 Mly (40 Mpc)[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.6[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SAB(r)bc[3] |
| Apparent size (V) | 3′.8 × 2′.3[3] |
| Other designations | |
| ESO 499- G 18, NGC 3054, PGC 28571, UGCA 187, MCG -04-24-005[3] | |
NGC 3054 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Hydra. It was discovered by Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters in 1859. It is probably in the same galaxy group as NGC 2935.
Supernovae
Two supernovae have been observed in NGC 3054:
- SN 2006T (Type IIb, mag. 17.4) was discovered by L. A. G. "Berto" Monard on 30 January 2006.[4][5]
- SN 2022crv (Type Ib, mag. 18.0457) was discovered by the Distance Less Than 40 Mpc (DLT40) survey on 19 February 2022.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Skrutskie, Michael F.; Cutri, Roc M.; Stiening, Rae; Weinberg, Martin D.; Schneider, Stephen E.; Carpenter, John M.; Beichman, Charles A.; Capps, Richard W. et al. (1 February 2006). "The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)". The Astronomical Journal 131 (2): 1163–1183. doi:10.1086/498708. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2006AJ....131.1163S.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tully, R. Brent et al. (August 2016). "Cosmicflows-3". The Astronomical Journal 152 (2): 21. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/2/50. 50. Bibcode: 2016AJ....152...50T.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 3054. http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu/.
- ↑ Monard, L. A. G. (2006). "Supernova 2006T in NGC 3054". Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams (385): 1. Bibcode: 2006CBET..385....1M. http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iau/cbet/000300/CBET000385.txt.
- ↑ "SN 2006T". IAU. https://www.wis-tns.org/object/2006T.
- ↑ "SN 2022crv". IAU. https://www.wis-tns.org/object/2022crv.
External links
- SIMBAD: NGC 3054 -- Galaxy
- Some pretty pictures!
- NGC 3054 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
Coordinates: ![]() 09h 54m 28.6s, −25° 42′ 12″
09h 54m 28.6s, −25° 42′ 12″
 |
