Astronomy:SN 1000+0216
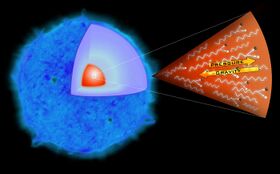 The pair instability process that triggered the explosion in SN 1000+0216 | |
| Spectral class | SLNS-R or SLNS-II ? |
|---|---|
| Date | Supernova Legacy Survey |
| Constellation | Sextans |
| Right ascension | 10h 00m 05.8720s[1] |
| Declination | +02° 16′ 23.621″[1] |
| Epoch | J2000.0 |
| Distance | z=3.8993 ± 0.0074 |
| Progenitor | initially a 140–250 M☉ star |
SN 1000+0216 was an extremely remote superluminous supernova (SLSN), which occurred in between June and November 2006 in the constellation Sextans. Its peak far-ultraviolet absolute magnitude reached −21.5, which exceeded the total absolute magnitude of its host galaxy. The distance (redshift) to this supernova z=3.8993 ± 0.0074 makes it the most distant supernova observed as of 2012. The luminosity of SN 1000+0216 evolved slowly over several years as it was still detectable in November 2008. Both the high luminosity and slow decay indicate that the supernova's progenitor was a very massive star. The supernova explosion itself was likely either a pair-instability supernova or a pulsational pair-instability supernova similar to the SN 2007bi event. It also had some similarities to the low redshift SN 2006gy supernova. Overall classification of SN 1000+0216 remains uncertain.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "[CSG2012 SN J1000+0216"]. SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=%5BCSG2012%5D+SN+J1000%2B0216.
- ↑ Cooke, J.; Sullivan, M.; Gal-Yam, A.; Barton, E. J.; Carlberg, R. G.; Ryan-Weber, E. V.; Horst, C.; Omori, Y. et al. (2012). "Superluminous supernovae at redshifts of 2.05 and 3.90". Nature 491 (7423): 228–231. doi:10.1038/nature11521. PMID 23123848. Bibcode: 2012Natur.491..228C.
External links
- Light curves on the Open Supernova Catalog
- 12 Billion-Year Old Supernova Discovered by Astronomers
- Elemental origins glimpsed in 12 billion year old supernova
 |



