Astronomy:S Boötis
From HandWiki
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| Right ascension | 14h 22m 52.9255s[2] |
| Declination | +53° 48′ 37.307″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.4 - 14.0[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3e-6e[3] |
| B−V color index | +1.3[4] |
| Variable type | Mira[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −17.00[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +7.283[2] mas/yr Dec.: −12.789[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.5746 ± 0.0407[2] mas |
| Distance | 5,700 ± 400 ly (1,700 ± 100 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.7[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 491[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 18,793[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.53[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,007[6] K |
| Age | 631[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
HIP 70291, SAO 29125, BD+54°1571, HD 126289[8] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
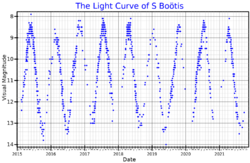
S Boötis is a Mira variable in the constellation Boötes. It ranges between magnitudes 7.8 and 13.8 over a period of approximately 270 days.[3] It is too faint to be seen with the naked eye, however when it is near maximum brightness it can be seen with binoculars.[9]
S Boötis was discovered at Bonn Observatory by Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander in 1860.[10][11][12]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 VSX (4 January 2010). "S Boötis". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=4305. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Fouesneau, M.; Andrae, R.; Dharmawardena, T.; Rybizki, J.; Bailer-Jones, C. A. L.; Demleitner, M. (2022). "Astrophysical parameters from Gaia DR2, 2MASS, and AllWISE". Astronomy and Astrophysics 662: A125. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141828. Bibcode: 2022A&A...662A.125F.
- ↑ Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics 657: A7. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202142146. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2022A&A...657A...7K.
- ↑ "S Bootis". SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=S+Boo&NbIdent=1&Radius=2&Radius.unit=arcmin&submit=submit+id. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ Macrobert, Alan. "The Stellar Magnitude System". American Astronomical Society. https://skyandtelescope.org/astronomy-resources/the-stellar-magnitude-system/.
- ↑ Cannon, Annie J. (1907). "Second catalogue of variable stars". Annals of Harvard College Observatory 55 (1): 1-94. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1907AnHar..55....1C. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ↑ Isles, J. E.; Saw, D. R. B. (February 1987). "Mira Stars, - I. R Ari, R Aur, X Aur, R Boo and S Boo". Journal of the British Astronomical Association 97 (2): 106-116. Bibcode: 1987JBAA...97..106I. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1987JBAA...97..106I. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ↑ "S Boo". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=4305.
 |