Astronomy:Kappa Boötis
| Observation data {{#ifeq:J2000|J2000.0 (ICRS)|Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS)| Epoch J2000 [[Astronomy:Equinox (celestial coordinates)|Equinox J2000}} | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| κ1 Boötis | |
| Right ascension | 14h 13m 27.824s[1] |
| Declination | +51° 47′ 16.62″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +6.69[2] |
| κ2 Boötis | |
| Right ascension | 14h 13m 29.009s[3] |
| Declination | +51° 47′ 23.88″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +4.50 to +4.58[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| κ1 Boötis | |
| Spectral type | F2V[5] |
| κ2 Boötis | |
| Spectral type | A8IV[6] |
| U−B color index | 0.14 |
| B−V color index | 0.2 |
| R−I color index | 0.12 |
| Variable type | Delta Scuti variable[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| κ1 Boötis | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −22.09[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 44.094[1] mas/yr Dec.: −39.325[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 20.3067 ± 0.2221[1] mas |
| Distance | 161 ± 2 ly (49.2 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +3.34 |
| κ2 Boötis | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −15.60[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 44.094[3] mas/yr Dec.: −39.325[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 21.1980 ± 0.4118[3] mas |
| Distance | 154 ± 3 ly (47.2 ± 0.9 pc) |
| Details | |
| κ1 Boötis | |
| Mass | 1.40[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.43[1] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 3.801[1] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.32[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,699[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.09[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 38[10] km/s |
| Age | 900[9] Myr |
| κ2 Boötis | |
| Mass | 2.12[11] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.78[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 28[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.66[5] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,760[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.29[12] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 128[8] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| κ1 Boötis: HD 124674, HIP 69481, SAO 29045 | |
| κ2 Boötis: HD 124675, HIP 69483, SAO 29046 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| κ1 | |
| κ2 | |
Kappa Boötis (κ Boo, κ Boötis) is a double star in the constellation Boötes. It has the traditional name Asellus Tertius /əˈsɛləs ˈtɜːrʃiəs/ (Latin for "third donkey colt")[13][14] and the Flamsteed designation 17 Boötis. The components are separated by an angular distance of 13.5 arcsec,[14] viewable in a small telescope. Kappa Boötis is approximately 155 light years from Earth.
Nomenclature
κ2 Boötis, the brighter star of the pair, is also designated HD 124675, while κ1 Boötis is HD 124674. The two stars share the Bright Star Catalogue designation HR 5328, but they have separate entries in the Hipparcos catalogue: HIP 69483 and HIP 69481 respectively.
Properties
κ1 Boötis is a spectroscopic binary star system. The visible primary is an F2 main sequence star, while the secondary is half the mass and much fainter.[16]
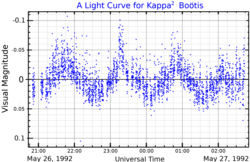
κ2 Boötis is classified as a Delta Scuti type variable star with a period of 1.08 hours[6] Its brightness varies from magnitude +4.50 to +4.58.[4] It is a slightly evolved A8 subgiant.
A 17th-magnitude star nearly two arc-minutes away has been identified as a member of the multiple system with an estimated orbital period of 177,000 years. It is itself a close binary with two similar low-mass stars in a 234-year orbit.[17]
Etymology
This star, along with the other Aselli (θ Boo and ι Boo) and λ Boo, were Aulād al Dhiʼbah (أولاد الضّباع - awlād al-ḍibā‘), "the Whelps of the Hyenas".[18]
In Chinese, 天槍 (Tiān Qiāng), meaning Celestial Spear, refers to an asterism consisting of κ (actually κ2) Boötis, ι Boötis and θ Boötis.[19] Consequently, the Chinese name for κ Boötis itself is 天槍一 (Tiān Qiāng yī, English: the First Star of Celestial Spear.)[20]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". VizieR On-line Data Catalog. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/gcvs. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Gray, R. O.; Napier, M. G.; Winkler, L. I. (2001). "The Physical Basis of Luminosity Classification in the Late A-, F-, and Early G-Type Stars. I. Precise Spectral Types for 372 Stars". The Astronomical Journal 121 (4): 2148. doi:10.1086/319956. Bibcode: 2001AJ....121.2148G.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Balona, L. A.; Dziembowski, W. A. (October 1999). "Excitation and visibility of high-degree modes in stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 309 (1): 221–232. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02821.x. Bibcode: 1999MNRAS.309..221B.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/s1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Zorec, J.; Royer, F.; Asplund, Martin; Cassisi, Santi; Ramirez, Ivan; Melendez, Jorge; Bensby, Thomas; Feltzing, Sofia (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Casagrande, L.; Schönrich, R.; Asplund, M.; Cassisi, S.; Ramírez, I.; Meléndez, J.; Bensby, T.; Feltzing, S. (2011). "New constraints on the chemical evolution of the solar neighbourhood and Galactic disc(s). Improved astrophysical parameters for the Geneva-Copenhagen Survey". Astronomy and Astrophysics 530: A138. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201016276. Bibcode: 2011A&A...530A.138C.
- ↑ Royer, F.; Grenier, S.; Baylac, M. -O.; Gómez, A. E.; Zorec, J. (2002). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars in the northern hemisphere. II. Measurement of v sin I". Astronomy and Astrophysics 393 (3): 897–911. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020943. Bibcode: 2002A&A...393..897R.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Liakos, Alexios; Niarchos, Panagiotis (2017). "Catalogue and properties of δ Scuti stars in binaries". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 465 (1): 1181. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2756. Bibcode: 2017MNRAS.465.1181L.
- ↑ Gáspár, András; Rieke, George H.; Ballering, Nicholas (2016). "The Correlation between Metallicity and Debris Disk Mass". The Astrophysical Journal 826 (2): 171. doi:10.3847/0004-637x/826/2/171. Bibcode: 2016ApJ...826..171G.
- ↑ Star Name - R.H.Allen p.105
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Kaler, Jim. "Asellus Tertius". http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/asellust.html.
- ↑ Frandsen, S.; Jones, A.; Kjeldsen, H.; Viskum, M.; Hjorth, J.; Andersen, N. H.; Thomsen, B. (September 1995). "CCD photometry of the δ-Scuti star κ2 Bootis". Astronomy and Astrophysics 301: 123. Bibcode: 1995A&A...301..123F. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1995A&A...301..123F. Retrieved 3 September 2022.
- ↑ Halbwachs, J. -L; Arenou, F.; Pourbaix, D.; Famaey, B.; Guillout, P.; Lebreton, Y.; Salomon, J. -B.; Tal-Or, L. et al. (2014). "Masses of the components of SB2 binaries observed with Gaia - I. Selection of the sample and mass ratios of 20 new SB2s discovered with Sophie". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 445 (3): 2371. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1838. Bibcode: 2014MNRAS.445.2371H.
- ↑ Tokovinin, Andrei (2018-03-01). "The Updated Multiple Star Catalog". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 235 (1): 6. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/aaa1a5. ISSN 0067-0049. Bibcode: 2018ApJS..235....6T.
- ↑ Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York: Dover Publications Inc. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-486-21079-7. https://archive.org/details/starnamestheirlo00alle/page/105. Retrieved 2010-12-12.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN:978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (in Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 , Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
External links
 |