Biology:Stoma
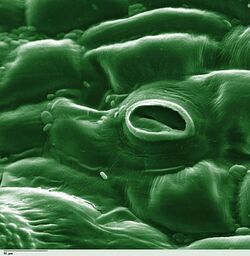
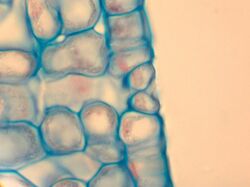

In botany, a stoma (pl.: stomata, from Greek στόμα, "mouth"), also called a stomate (pl.: stomates), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that regulate the size of the stomatal opening.
The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture.[1] Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere as part of a process called transpiration.
Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of the vast majority of land plants, with the exception of liverworts, as well as some mosses and hornworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. Dicotyledons usually have more stomata on the lower surface of the leaves than the upper surface. Monocotyledons such as onion, oat and maize may have about the same number of stomata on both leaf surfaces.[2]: 5 In plants with floating leaves, stomata may be found only on the upper epidermis and submerged leaves may lack stomata entirely. Most tree species have stomata only on the lower leaf surface.[3] Leaves with stomata on both the upper and lower leaf surfaces are called amphistomatous leaves; leaves with stomata only on the lower surface are hypostomatous, and leaves with stomata only on the upper surface are epistomatous or hyperstomatous.[3] Size varies across species, with end-to-end lengths ranging from 10 to 80 µm and width ranging from a few to 50 µm.[4]
Function
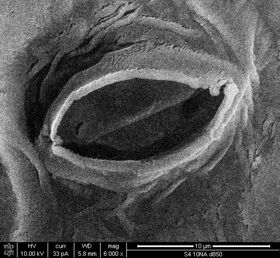
CO2 gain and water loss
Carbon dioxide, a key reactant in photosynthesis, is present in the atmosphere at a concentration of about 400 ppm. Most plants require the stomata to be open during daytime. The air spaces in the leaf are saturated with water vapour, which exits the leaf through the stomata in a process known as transpiration. Therefore, plants cannot gain carbon dioxide without simultaneously losing water vapour.[5]
Alternative approaches
Ordinarily, carbon dioxide is fixed to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) by the enzyme RuBisCO in mesophyll cells exposed directly to the air spaces inside the leaf. This exacerbates the transpiration problem for two reasons: first, RuBisCo has a relatively low affinity for carbon dioxide, and second, it fixes oxygen to RuBP, wasting energy and carbon in a process called photorespiration. For both of these reasons, RuBisCo needs high carbon dioxide concentrations, which means wide stomatal apertures and, as a consequence, high water loss.
Narrower stomatal apertures can be used in conjunction with an intermediary molecule with a high carbon dioxide affinity, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPcase). Retrieving the products of carbon fixation from PEPCase is an energy-intensive process, however. As a result, the PEPCase alternative is preferable only where water is limiting but light is plentiful, or where high temperatures increase the solubility of oxygen relative to that of carbon dioxide, magnifying RuBisCo's oxygenation problem.
C.A.M. plants
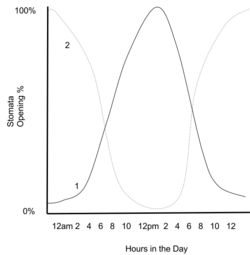
A group of mostly desert plants called "C.A.M." plants (crassulacean acid metabolism, after the family Crassulaceae, which includes the species in which the CAM process was first discovered) open their stomata at night (when water evaporates more slowly from leaves for a given degree of stomatal opening), use PEPcase to fix carbon dioxide and store the products in large vacuoles. The following day, they close their stomata and release the carbon dioxide fixed the previous night into the presence of RuBisCO. This saturates RuBisCO with carbon dioxide, allowing minimal photorespiration. This approach, however, is severely limited by the capacity to store fixed carbon in the vacuoles, so it is preferable only when water is severely limited.
Opening and closing

However, most plants do not have CAM and must therefore open and close their stomata during the daytime, in response to changing conditions, such as light intensity, humidity, and carbon dioxide concentration. When conditions are conducive to stomatal opening (e.g., high light intensity and high humidity), a proton pump drives protons (H+) from the guard cells. This means that the cells' electrical potential becomes increasingly negative. The negative potential opens potassium voltage-gated channels and so an uptake of potassium ions (K+) occurs. To maintain this internal negative voltage so that entry of potassium ions does not stop, negative ions balance the influx of potassium. In some cases, chloride ions enter, while in other plants the organic ion malate is produced in guard cells. This increase in solute concentration lowers the water potential inside the cell, which results in the diffusion of water into the cell through osmosis. This increases the cell's volume and turgor pressure. Then, because of rings of cellulose microfibrils that prevent the width of the guard cells from swelling, and thus only allow the extra turgor pressure to elongate the guard cells, whose ends are held firmly in place by surrounding epidermal cells, the two guard cells lengthen by bowing apart from one another, creating an open pore through which gas can diffuse.[6]
When the roots begin to sense a water shortage in the soil, abscisic acid (ABA) is released.[7] ABA binds to receptor proteins in the guard cells' plasma membrane and cytosol, which first raises the pH of the cytosol of the cells and cause the concentration of free Ca2+ to increase in the cytosol due to influx from outside the cell and release of Ca2+ from internal stores such as the endoplasmic reticulum and vacuoles.[8] This causes the chloride (Cl−) and organic ions to exit the cells. Second, this stops the uptake of any further K+ into the cells and, subsequently, the loss of K+. The loss of these solutes causes an increase in water potential, which results in the diffusion of water back out of the cell by osmosis. This makes the cell plasmolysed, which results in the closing of the stomatal pores.
Guard cells have more chloroplasts than the other epidermal cells from which guard cells are derived. Their function is controversial.[9][10]
Inferring stomatal behavior from gas exchange
The degree of stomatal resistance can be determined by measuring leaf gas exchange of a leaf. The transpiration rate is dependent on the diffusion resistance provided by the stomatal pores and also on the humidity gradient between the leaf's internal air spaces and the outside air. Stomatal resistance (or its inverse, stomatal conductance) can therefore be calculated from the transpiration rate and humidity gradient. This allows scientists to investigate how stomata respond to changes in environmental conditions, such as light intensity and concentrations of gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and ozone.[11] Evaporation (E) can be calculated as[12]
where ei and ea are the partial pressures of water in the leaf and in the ambient air respectively, P is atmospheric pressure, and r is stomatal resistance. The inverse of r is conductance to water vapor (g), so the equation can be rearranged to[12]
and solved for g:[12]
Photosynthetic CO2 assimilation (A) can be calculated from
where Ca and Ci are the atmospheric and sub-stomatal partial pressures of CO2 respectively[clarification needed]. The rate of evaporation from a leaf can be determined using a photosynthesis system. These scientific instruments measure the amount of water vapour leaving the leaf and the vapor pressure of the ambient air. Photosynthetic systems may calculate water use efficiency (A/E), g, intrinsic water use efficiency (A/g), and Ci. These scientific instruments are commonly used by plant physiologists to measure CO2 uptake and thus measure photosynthetic rate.[13][14]
Evolution
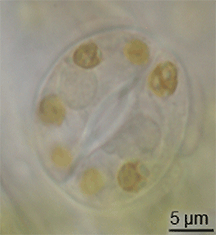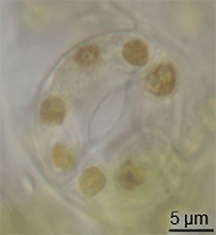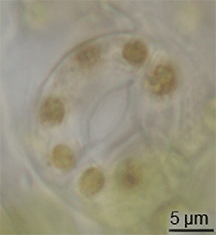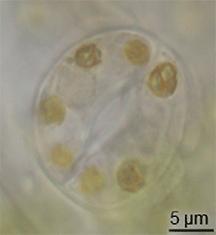
There is little evidence of the evolution of stomata in the fossil record, but they had appeared in land plants by the middle of the Silurian period.[15] They may have evolved by the modification of conceptacles from plants' alga-like ancestors.[16] However, the evolution of stomata must have happened at the same time as the waxy cuticle was evolving – these two traits together constituted a major advantage for early terrestrial plants.[citation needed]
Development
There are three major epidermal cell types which all ultimately derive from the outermost (L1) tissue layer of the shoot apical meristem, called protodermal cells: trichomes, pavement cells and guard cells, all of which are arranged in a non-random fashion.
An asymmetrical cell division occurs in protodermal cells resulting in one large cell that is fated to become a pavement cell and a smaller cell called a meristemoid that will eventually differentiate into the guard cells that surround a stoma. This meristemoid then divides asymmetrically one to three times before differentiating into a guard mother cell. The guard mother cell then makes one symmetrical division, which forms a pair of guard cells.[17] Cell division is inhibited in some cells so there is always at least one cell between stomata.[18]
Stomatal patterning is controlled by the interaction of many signal transduction components such as EPF (Epidermal Patterning Factor), ERL (ERecta Like) and YODA (a putative MAP kinase kinase kinase).[18] Mutations in any one of the genes which encode these factors may alter the development of stomata in the epidermis.[18] For example, a mutation in one gene causes more stomata that are clustered together, hence is called Too Many Mouths (TMM).[17] Whereas, disruption of the SPCH (SPeecCHless) gene prevents stomatal development all together.[18] Inhibition of stomatal production can occur by the activation of EPF1, which activates TMM/ERL, which together activate YODA. YODA inhibits SPCH, causing SPCH activity to decrease, preventing asymmetrical cell division that initiates stomata formation.[18][19] Stomatal development is also coordinated by the cellular peptide signal called stomagen, which signals the activation of the SPCH, resulting in increased number of stomata.[20]
Environmental and hormonal factors can affect stomatal development. Light increases stomatal development in plants; while, plants grown in the dark have a lower amount of stomata. Auxin represses stomatal development by affecting their development at the receptor level like the ERL and TMM receptors. However, a low concentration of auxin allows for equal division of a guard mother cell and increases the chance of producing guard cells.[21]
Most angiosperm trees have stomata only on their lower leaf surface. Poplars and willows have them on both surfaces. When leaves develop stomata on both leaf surfaces, the stomata on the lower surface tend to be larger and more numerous, but there can be a great degree of variation in size and frequency about species and genotypes. White ash and white birch leaves had fewer stomata but larger in size. On the other hand sugar maple and silver maple had small stomata that were more numerous.[22]
Types
Different classifications of stoma types exist. One that is widely used is based on the types that Julien Joseph Vesque introduced in 1889, was further developed by Metcalfe and Chalk,[23] and later complemented by other authors. It is based on the size, shape and arrangement of the subsidiary cells that surround the two guard cells.[24] They distinguish for dicots:
- actinocytic (meaning star-celled) stomata have guard cells that are surrounded by at least five radiating cells forming a star-like circle. This is a rare type that can for instance be found in the family Ebenaceae.
- anisocytic (meaning unequal celled) stomata have guard cells between two larger subsidiary cells and one distinctly smaller one. This type of stomata can be found in more than thirty dicot families, including Brassicaceae, Solanaceae, and Crassulaceae. It is sometimes called cruciferous type.
- anomocytic (meaning irregular celled) stomata have guard cells that are surrounded by cells that have the same size, shape and arrangement as the rest of the epidermis cells. This type of stomata can be found in more than hundred dicot families such as Apocynaceae, Boraginaceae, Chenopodiaceae, and Cucurbitaceae. It is sometimes called ranunculaceous type.
- diacytic (meaning cross-celled) stomata have guard cells surrounded by two subsidiary cells, that each encircle one end of the opening and contact each other opposite to the middle of the opening. This type of stomata can be found in more than ten dicot families such as Caryophyllaceae and Acanthaceae. It is sometimes called caryophyllaceous type.
- hemiparacytic stomata are bordered by just one subsidiary cell that differs from the surrounding epidermis cells, its length parallel to the stoma opening. This type occurs for instance in the Molluginaceae and Aizoaceae.
- paracytic (meaning parallel celled) stomata have one or more subsidiary cells parallel to the opening between the guard cells. These subsidiary cells may reach beyond the guard cells or not. This type of stomata can be found in more than hundred dicot families such as Rubiaceae, Convolvulaceae and Fabaceae. It is sometimes called rubiaceous type.
In monocots, several different types of stomata occur such as:
- gramineous or graminoid (meaning grass-like) stomata have two guard cells surrounded by two lens-shaped subsidiary cells. The guard cells are narrower in the middle and bulbous on each end. This middle section is strongly thickened. The axis of the subsidiary cells are parallel stoma opening. This type can be found in monocot families including Poaceae and Cyperaceae.[25]
- hexacytic (meaning six-celled) stomata have six subsidiary cells around both guard cells, one at either end of the opening of the stoma, one adjoining each guard cell, and one between that last subsidiary cell and the standard epidermis cells. This type can be found in some monocot families.
- tetracytic (meaning four-celled) stomata have four subsidiary cells, one on either end of the opening, and one next to each guard cell. This type occurs in many monocot families, but also can be found in some dicots, such as Tilia and several Asclepiadaceae.
In ferns, four different types are distinguished:
- hypocytic stomata have two guard cells in one layer with only ordinary epidermis cells, but with two subsidiary cells on the outer surface of the epidermis, arranged parallel to the guard cells, with a pore between them, overlying the stoma opening.
- pericytic stomata have two guard cells that are entirely encircled by one continuous subsidiary cell (like a donut).
- desmocytic stomata have two guard cells that are entirely encircled by one subsidiary cell that has not merged its ends (like a sausage).
- polocytic stomata have two guard cells that are largely encircled by one subsidiary cell, but also contact ordinary epidermis cells (like a U or horseshoe).
Stomatal crypts
Stomatal crypts are sunken areas of the leaf epidermis which form a chamber-like structure that contains one or more stomata and sometimes trichomes or accumulations of wax. Stomatal crypts can be an adaption to drought and dry climate conditions when the stomatal crypts are very pronounced. However, dry climates are not the only places where they can be found. The following plants are examples of species with stomatal crypts or antechambers: Nerium oleander, conifers, and Drimys winteri which is a species of plant found in the cloud forest.[26]
Stomata as pathogenic pathways
Stomata are obvious holes in the leaf by which, as was presumed for a while, pathogens can enter unchallenged. However, it has been recently shown that stomata do in fact sense the presence of some, if not all, pathogens. However, with the virulent bacteria applied to Arabidopsis plant leaves in the experiment, the bacteria released the chemical coronatine, which forced the stomata open again within a few hours.[27]
Stomata and climate change
Response of stomata to environmental factors
Photosynthesis, plant water transport (xylem) and gas exchange are regulated by stomatal function which is important in the functioning of plants.[28]
Stomata are responsive to light with blue light being almost 10 times as effective as red light in causing stomatal response. Research suggests this is because the light response of stomata to blue light is independent of other leaf components like chlorophyll. Guard cell protoplasts swell under blue light provided there is sufficient availability of potassium.[29] Multiple studies have found support that increasing potassium concentrations may increase stomatal opening in the mornings, before the photosynthesis process starts, but that later in the day sucrose plays a larger role in regulating stomatal opening.[30] Zeaxanthin in guard cells acts as a blue light photoreceptor which mediates the stomatal opening.[31] The effect of blue light on guard cells is reversed by green light, which isomerizes zeaxanthin.[31]
Stomatal density and aperture (length of stomata) varies under a number of environmental factors such as atmospheric CO2 concentration, light intensity, air temperature and photoperiod (daytime duration). [32][33]
Decreasing stomatal density is one way plants have responded to the increase in concentration of atmospheric CO2 ([CO2]atm).[34] Although changes in [CO2]atm response is the least understood mechanistically, this stomatal response has begun to plateau where it is soon expected to impact transpiration and photosynthesis processes in plants.[28][35]
Drought inhibits stomatal opening, but research on soybeans suggests moderate drought does not have a significant effect on stomatal closure of its leaves. There are different mechanisms of stomatal closure. Low humidity stresses guard cells causing turgor loss, termed hydropassive closure. Hydroactive closure is contrasted as the whole leaf affected by drought stress, believed to be most likely triggered by abscisic acid.[36]
Future adaptations during climate change
It is expected for [CO2]atm to reach 500–1000 ppm by 2100.[28] 96% of the past 400,000 years experienced below 280 ppm CO2 levels. From this figure, it is highly probable that genotypes of today’s plants diverged from their pre-industrial relative.[28]
The gene HIC (high carbon dioxide) encodes a negative regulator for the development of stomata in plants.[37] Research into the HIC gene using Arabidopsis thaliana found no increase of stomatal development in the dominant allele, but in the ‘wild type’ recessive allele showed a large increase, both in response to rising CO2 levels in the atmosphere.[37] These studies imply the plants response to changing CO2 levels is largely controlled by genetics.
Agricultural implications
The CO2 fertiliser effect has been greatly overestimated during Free-Air Carbon dioxide Enrichment (FACE) experiments where results show increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere enhances photosynthesis, reduce transpiration, and increase water use efficiency (WUE).[34] Increased biomass is one of the effects with simulations from experiments predicting a 5–20% increase in crop yields at 550 ppm of CO2.[38] Rates of leaf photosynthesis were shown to increase by 30–50% in C3 plants, and 10–25% in C4 under doubled CO2 levels.[38] The existence of a feedback mechanism results a phenotypic plasticity in response to [CO2]atm that may have been an adaptive trait in the evolution of plant respiration and function.[28][33]
Predicting how stomata perform during adaptation is useful for understanding the productivity of plant systems for both natural and agricultural systems.[32] Plant breeders and farmers are beginning to work together using evolutionary and participatory plant breeding to find the best suited species such as heat and drought resistant crop varieties that could naturally evolve to the change in the face of food security challenges.[34]
References
- ↑ Esau, K. (1977). Anatomy of Seed Plants. Wiley and Sons. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-471-24520-9. https://archive.org/details/anatomyofseedpla00esau.
- ↑ Weyers, J. D. B.; Meidner, H. (1990). Methods in stomatal research. Longman Group UK Ltd.. ISBN 978-0582034839.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Willmer, Colin; Fricker, Mark (1996) (in en). Stomata. Springer. pp. 16. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-0579-8. ISBN 978-94-010-4256-7.
- ↑ Fricker, M.; Willmer, C. (2012). Stomata. Springer Netherlands. p. 18. ISBN 978-94-011-0579-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=9sjoCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA18. Retrieved 15 June 2016.
- ↑ Debbie Swarthout and C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Stomata. Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and the Environment, Washington DC
- ↑ N. S. CHRISTODOULAKIS; J. MENTI; B. GALATIS (January 2002). "Structure and Development of Stomata on the Primary Root of Ceratonia siliqua L.". Annals of Botany 89 (1): 23–29. doi:10.1093/aob/mcf002. PMID 12096815.
- ↑ C. L. Trejo; W. J. Davies; LdMP. Ruiz (1993). "Sensitivity of Stomata to Abscisic Acid (An Effect of the Mesophyll)". Plant Physiology 102 (2): 497–502. doi:10.1104/pp.102.2.497. PMID 12231838.
- ↑ Petra Dietrich; Dale Sanders; Rainer Hedrich (October 2001). "The role of ion channels in light-dependent stomatal opening". Journal of Experimental Botany 52 (363): 1959–1967. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.363.1959. PMID 11559731.
- ↑ "Guard Cell Photosynthesis". http://6e.plantphys.net/essay10.01.html.
- ↑ Eduardo Zeiger; Lawrence D. Talbott; Silvia Frechilla; Alaka Srivastava; Jianxin Zhu (March 2002). "The Guard Cell Chloroplast: A Perspective for the Twenty-First Century". New Phytologist 153 (3 Special Issue: Stomata): 415–424. doi:10.1046/j.0028-646X.2001.NPH328.doc.x. PMID 33863211.
- ↑ Hopkin, Michael (2007-07-26). "Carbon sinks threatened by increasing ozone". Nature 448 (7152): 396–397. doi:10.1038/448396b. PMID 17653153. Bibcode: 2007Natur.448..396H.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "Calculating Important Parameters in Leaf Gas Exchange". Plant Physiology Online. Sinauer. http://4e.plantphys.net/article.php?ch=9&id=134.
- ↑ Waichi Agata; Yoshinobu Kawamitsu; Susumu Hakoyama; Yasuo Shima (January 1986). "A system for measuring leaf gas exchange based on regulating vapour pressure difference". Photosynthesis Research 9 (3): 345–357. doi:10.1007/BF00029799. ISSN 1573-5079. PMID 24442366.
- ↑ Portable Gas Exchange Fluorescence System GFS-3000. Handbook of Operation, March 20, 2013, http://www.walz.com/downloads/manuals/gfs-3000/gfs-3000_Manual_8a.pdf
- ↑ D. Edwards, H. Kerp; Hass, H. (1998). "Stomata in early land plants: an anatomical and ecophysiological approach". Journal of Experimental Botany 49 (Special Issue): 255–278. doi:10.1093/jxb/49.Special_Issue.255.
- ↑ Krassilov, Valentin A. (2004). "Macroevolutionary events and the origin of higher taxa". in Wasser, Solomon P.. Evolutionary theory and processes : modern horizons : papers in honour of Eviatar Nevo. Dordrecht: Kluwer Acad. Publ.. pp. 265–289. ISBN 978-1-4020-1693-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=tJeZC885-OcC&pg=PA265.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Bergmann, Dominique C.; Lukowitz, Wolfgang; Somerville, Chris R.; Lukowitz, W; Somerville, CR (4 July 2004). "Stomatal Development and Pattern Controlled by a MAPKK Kinase". Science 304 (5676): 1494–1497. doi:10.1126/science.1096014. PMID 15178800. Bibcode: 2004Sci...304.1494B. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/ful/304/5676/1494/DC1.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 Pillitteri, Lynn Jo; Dong, Juan (2013-06-06). "Stomatal Development in Arabidopsis". The Arabidopsis Book / American Society of Plant Biologists 11: e0162. doi:10.1199/tab.0162. ISSN 1543-8120. PMID 23864836.
- ↑ Casson, Stuart A; Hetherington, Alistair M (2010-02-01). "Environmental regulation of stomatal development". Current Opinion in Plant Biology 13 (1): 90–95. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2009.08.005. PMID 19781980.
- ↑ Sugano, Shigeo S.; Shimada, Tomoo; Imai, Yu; Okawa, Katsuya; Tamai, Atsushi; Mori, Masashi; Hara-Nishimura, Ikuko (2010-01-14). "Stomagen positively regulates stomatal density in Arabidopsis" (in en). Nature 463 (7278): 241–244. doi:10.1038/nature08682. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 20010603. Bibcode: 2010Natur.463..241S.
- ↑ Balcerowicz, M.; Ranjan, A.; Rupprecht, L.; Fiene, G.; Hoecker, U. (2014). "Auxin represses stomatal development in dark-grown seedling via Aux/IAA proteins". Development 141 (16): 3165–3176. doi:10.1242/dev.109181. PMID 25063454.
- ↑ Pallardy, Stephen (1983). "Physiology of Woody Plants". Journal of Applied Ecology 20 (1): 14. doi:10.2307/2403413. Bibcode: 1983JApEc..20..352J.
- ↑ Metcalfe, C.R.; Chalk, L. (1950). Anatomy of Dicotyledons. 1: Leaves, Stem, and Wood in relation to Taxonomy, with notes on economic Uses.
- ↑ van Cotthem, W.R.F. (1970). "A Classification of Stomatal Types". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 63 (3): 235–246. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.1970.tb02321.x.
- ↑ Nunes, Tiago D. G.; Zhang, Dan; Raissig, Michael T. (February 2020). "Form, development and function of grass stomata". The Plant Journal 101 (4): 780–799. doi:10.1111/tpj.14552. PMID 31571301.
- ↑ Roth-Nebelsick, A.; Hassiotou, F.; Veneklaas, E. J (2009). "Stomatal crypts have small effects on transpiration: A numerical model analysis.". Plant Physiology 151 (4): 2018–2027. doi:10.1104/pp.109.146969. PMID 19864375.
- ↑ Maeli Melotto; William Underwood; Jessica Koczan; Kinya Nomura; Sheng Yang He (September 2006). "Plant Stomata Function in Innate Immunity against Bacterial Invasion". Cell 126 (5): 969–980. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.054. PMID 16959575.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 28.4 Rico, C; Pittermann, J; Polley, HW; Aspinwall, MJ; Fay, PA (2013). "The effect of subambient to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on vascular function in Helianthus annuus: implications for plant response to climate change". New Phytologist 199 (4): 956–965. doi:10.1111/nph.12339. PMID 23731256.
- ↑ McDonald, Maurice S. (2003). Photobiology of Higher Plants. Wiley. p. 293. ISBN 978-0-470-85523-2.
- ↑ Principles of Plant Nutrition. Springer. 2001. p. 205. doi:10.1007/978-94-010-1009-2. ISBN 978-94-010-1009-2.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Kochhar, S. L.; Gujral, Sukhbir Kaur (2020). "Transpiration". Plant Physiology: Theory and Applications (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 75–99. doi:10.1017/9781108486392.006. ISBN 978-1-108-48639-2.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Buckley, TN; Mott, KA (2013). "Modelling stomatal conductance in response to environmental factors". Plant, Cell and Environment 36 (9): 1691–1699. doi:10.1111/pce.12140. PMID 23730938.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Rogiers, SY; Hardie, WJ; Smith, JP (2011). "Stomatal density of grapevine leaves (Vitis Vinifera L.) responds to soil temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide". Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research 17 (2): 147–152. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0238.2011.00124.x.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Ceccarelli, S; Grando, S; Maatougui, M; Michael, M; Slash, M; Haghparast, R; Rahmanian, M; Taheri, A et al. (2010). "Plant breeding and climate changes". The Journal of Agricultural Science 148 (6): 627–637. doi:10.1017/s0021859610000651.
- ↑ Serna, L; Fenoll, C (2000). "Coping with human CO2 emissions". Nature 408 (6813): 656–657. doi:10.1038/35047202. PMID 11130053.
- ↑ Principles of Plant Nutrition. Springer. 2001. p. 223. doi:10.1007/978-94-010-1009-2. ISBN 978-94-010-1009-2.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 Gray, J; Holroyd, G; van der Lee, F; Bahrami, A; Sijmons, P; Woodward, F; Schuch, W; Hetherington, A (2000). "The HIC signalling pathway links CO2 perception to stomatal development". Nature 408 (6813): 713–716. doi:10.1038/35047071. PMID 11130071. Bibcode: 2000Natur.408..713G.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Tubiello, FN; Soussana, J-F; Howden, SM (2007). "Crop and pasture response to climate change". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104 (50): 19686–19690. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701728104. PMID 18077401. Bibcode: 2007PNAS..10419686T.
External links
 |
