Carbol fuchsin
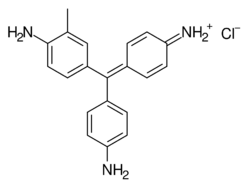
Carbol fuchsin, carbol-fuchsin, carbolfuchsin, or Castellani's paint (CAS ) is a mixture of phenol and basic fuchsin that is used in bacterial staining procedures. It is commonly used in the staining of mycobacteria because it has an affinity for the mycolic acids found in their cell membranes.
It is a component of Ziehl–Neelsen stain, a differential stain.[1][2] Carbol fuchsin is used as the primary stain dye to detect acid-fast bacteria because it is more soluble in the cells' wall lipids than in the acid alcohol. If the bacteria is acid-fast the bacteria will retain the initial red color of the dye because they are able to resist the destaining by acid alcohol (0.4–1% HCl in 70% EtOH).[3] Additionally, it can be used for the staining of bacterial spores.
Carbol-fuchsin is also used as a topical antiseptic and antifungal.
References
- ↑ "Comparison of two different strengths of carbol fuchsin in Ziehl-Neelsen staining for detecting acid-fast bacilli". J. Clin. Microbiol. 41 (7): 3459. July 2003. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.7.3459.2003. PMID 12843125.
- ↑ "Inefficiency of 0.3% carbol fuchsin in ziehl-neelsen staining for detecting acid-fast bacilli". J. Clin. Microbiol. 40 (8): 3041–3. August 2002. doi:10.1128/JCM.40.8.3041-3043.2002. PMID 12149374.
- ↑ Sokolovská, Ivana; Rozenberg, Raoul; Riez, Christophe et al. (2003-12-01). "Carbon Source-Induced Modifications in the Mycolic Acid Content and Cell Wall Permeability of Rhodococcus erythropolis E1" (in en). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 69 (12): 7019–7027. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.12.7019-7027.2003. ISSN 0099-2240. PMID 14660344. Bibcode: 2003ApEnM..69.7019S.
 |
