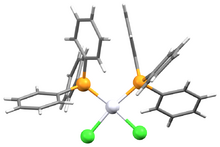
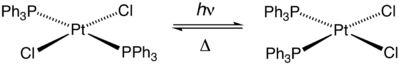Chemistry:Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
cis-dichlorbis(triphenylphosphine)platinum(II)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H30Cl2P2Pt | |
| Molar mass | 790.57 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
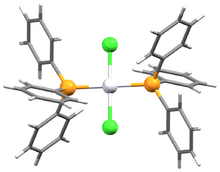
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
trans-dichlorbis(triphenylphosphine)platinum(II)
| |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| C36H30Cl2P2Pt | |
| Molar mass | 790.57 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride is a metal phosphine complex with the formula PtCl2[P(C6H5)3]2. Cis- and trans isomers are known. The cis isomer is a white crystalline powder, while the trans isomer is yellow.[3] Both isomers are square planar about the central platinum atom. The cis isomer is used primarily as a reagent for the synthesis of other platinum compounds.
Preparation
The cis isomer is the prepared by heating solutions of platinum(II) chlorides with triphenylphosphine. For example, starting from potassium tetrachloroplatinate:
- K2PtCl4 + 2 PPh3 → cis-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + 2 KCl
The trans isomer is the prepared by treating potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II) (Zeise's salt) with triphenylphosphine:[3]
- KPt(C2H4)Cl3 + 2 PPh3 → trans-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + KCl + C2H4
With heating or in the presence of excess PPh3, the trans isomer converts to the cis complex. The latter complex is the thermodynamic product due to triphenylphosphine being a strong trans effect ligand.
In cis-bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride, the average Pt-P has a bond distance of 2.261 Å and the average Pt-Cl has a bond distance of 2.346 Å.[2] In trans-bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride, the Pt-P distance is 2.316 Å and the Pt-Cl distance is 2.300 Å.[1]
The complex also undergoes photoisomerization.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 M. H. Johansson; S. Otto (2000). "trans-Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine-P)platinum(II)". Acta Crystallogr. C 56: e12–e15. doi:10.1107/S010827019901608X.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 H.-K. Fun; S. Chantrapromma; Y.-C. Liu; Z.-F. Chen; H. Liang (2006). "cis-Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine-κP)platinum(II)". Acta Crystallogr. E 62 (6): m1252–m1254. doi:10.1107/S1600536806016540.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hsu, C. Y.; Leshner, B. T.; Orchin, M. (1979). "Trans Phosphine Complexes of Platinum(II) Chloride". Inorganic Syntheses. 19. 114–116. doi:10.1002/9780470132500.ch25. ISBN 9780470132500.
 |