Chemistry:Enduracididine
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
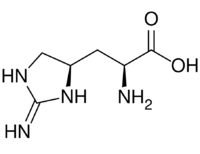
| IUPAC name
3-[(4R)-2-Imino-4-imidazolidinyl]-L-alanine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 172.188 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Enduracididine is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid that is a cyclic analogue of arginine.[1] It is not genetically encoded into peptide sequences, but rather is generated as a posttranslational modification.
Biological roles
Enduracididine occurs rarely in nature, appearing principally in peptide antibiotics such as the antibacterial compounds enramycin and teixobactin.[2]
References
- ↑ Atkinson, DJ; Naysmith, BJ; Furkert, DP; Brimble, MA (7 November 2016). "Enduracididine, a rare amino acid component of peptide antibiotics: Natural products and synthesis.". Beilstein J Org Chem 12: 2325-2342. doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.226. PMID 28144300.
- ↑ Ling, LL; Schneider, T; Peoples, AJ; Spoering, AL; Engels, I; Conlon, BP; Mueller, A; Schäberle, TF et al. (22 January 2015). "A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance.". Nature 517 (7535): 455–9. doi:10.1038/nature14098. PMID 25561178.
 |