Chemistry:JNJ-26489112
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
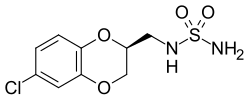 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H11ClN2O4S |
| Molar mass | 278.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
JNJ-26489112 is an anticonvulsant drug being developed by Johnson & Johnson for the treatment of epilepsy.[1][2][3] JNJ-26489112 was designed as a successor to topiramate.[4] It is expected to have fewer side effects than topiramate because it lacks activity against carbonic anhydrase.[4]
JNJ-26489112 was studied as a treatment for major depressive disorder.[5] This clinical trial was terminated in 2013 due to a "sponsor portfolio decision", and no new development of JNJ-26489112 has been reported.
Its mechanism of action is unknown.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Evaluation of JNJ-26489112, a Novel Antiepileptic Drug: A Placebo-Controlled, Exploratory Study". Clinical Therapeutics 35 (8): e70. August 2013. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.07.204. http://www.clinicaltherapeutics.com/article/S0149-2918(13)00587-0/fulltext.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00579384 for "A Study of the Effects of JNJ-26489112 on the Photic Induced Paroxysmal Electroencephalogram Response in Patients With Photosensitive Epilepsy" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ "Evaluation of JNJ-26489112 in patients with photosensitive epilepsy: a placebo-controlled, exploratory study". Epilepsy Research 108 (4): 709–16. May 2014. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.01.018. PMID 24560845.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Novel, broad-spectrum anticonvulsants containing a sulfamide group: pharmacological properties of (S)-N-[(6-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzo[1,4dioxin-2-yl)methyl]sulfamide (JNJ-26489112)"]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 56 (22): 9019–30. November 2013. doi:10.1021/jm400894u. PMID 24205976.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT01114698 for "A Safety and Efficacy Study of JNJ26489112 in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ "Do traditional anti-seizure drugs have a future? A review of potential anti-seizure drugs in clinical development". Pharmacological Research 104: 38–48. February 2016. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.12.011. PMID 26689774.
Further reading
- Toxicological study of JNJ-26489112: "Implications of retinal effects observed in chronic toxicity studies on the clinical development of a CNS-active drug candidate". Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 69 (2): 187–200. July 2014. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.03.005. PMID 24680767.
 |

