Chemistry:Beclamide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
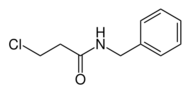
| Formula | C10H12ClNO |
| Molar mass | 197.66 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 94 °C (201 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Beclamide (marketed as Chloracon, Hibicon, Posedrine, Nydrane, Seclar, and other names) is a drug that possesses anticonvulsant activity.[1] It is no longer used.
Uses
It has been used as a sedative and as an anticonvulsant.
It was studied in the 1950s for its anticonvulsant properties, as a treatment for generalised tonic-clonic seizures. It was not effective for absence seizures.
Interest in the drug resumed in the 1990s for its psychiatric properties as an adjunct in the treatment of schizophrenia.[2]
Side effects
Side effects are uncommon but include stomach pain, nervousness, giddiness, skin rash and leukopenia. It is counter-indicated in breast feeding as it is passed in the milk.
Administration and pharmacology
Administration is oral, though it has an unpleasant taste. It is quickly absorbed and elimination is renal and complete within 48 hours. Beclamide is possibly metabolized to 3-chloropropanoic acid in vivo,[citation needed] which binds to the GHB receptor.
References
- ↑ "Metabolism of beclamide after a single oral dose in man: quantitative studies". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 47 (10): 876–8. October 1995. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1995.tb05757.x. PMID 8583359.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsants as adjuncts for the neuroleptic treatment of schizophrenic psychoses: a clinical study with beclamide". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 81 (2): 162–7. February 1990. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb06472.x. PMID 2183543.
- The Medical Treatment of Epilepsy by Stanley R Resor. Published by Marcel Dekker (1991). ISBN 0-8247-8549-5.
 |
