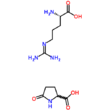
Chemistry:L-Arginine L-pyroglutamate
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid;
(2S)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (1:1)
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C11H21N5O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 303.319 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white powder | ||
| Density | solid | ||
| Melting point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) | ||
| soluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 201.2 °C (394.2 °F; 474.3 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
l-Arginine l-pyroglutamate, also known as pirglutargine and arginine pidolate, is the l-arginine salt of pyroglutamic acid. Arginine pyroglutamate is a delivery form of arginine.
Physical and chemical properties
l-Arginine l-pyroglutamate is a crystalline solid powder with a sour taste. It is soluble in cold water.
Hazards
The compound is hazardous if ingested or inhaled in concentrated form. It is slightly hazardous in case of skin and eye contact.[1]
References
 |