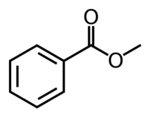
Chemistry:Methyl benzoate
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl benzoate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl benzenecarboxylate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.0837 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −12.5 °C (9.5 °F; 260.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 199.6 °C (391.3 °F; 472.8 K) | ||
| −81.95×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5164 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | ScienceLab MSDS | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 82 °C (180 °F; 355 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methyl benzoate is an organic compound. It is an ester with the chemical formula C6H5CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Methyl benzoate has a pleasant smell, strongly reminiscent of the fruit of the feijoa tree, and it is used in perfumery. It also finds use as a solvent and as a pesticide used to attract insects such as orchid bees.
Synthesis and reactions
Methyl benzoate is formed by the condensation of methanol and benzoic acid, in presence of a strong acid.[1][2]
Methyl benzoate reacts at both the ring and the ester, depending on the substrate. Electrophiles attack the ring, illustrated by acid-catalysed nitration with nitric acid to give methyl 3-nitrobenzoate. Nucleophiles attack the carbonyl center, illustrated by hydrolysis with addition of aqueous NaOH to give methanol and sodium benzoate.
Occurrence
Methyl benzoate can be isolated from the freshwater fern Salvinia molesta.[3] It is one of many compounds that is attractive to males of various species of orchid bees, which apparently gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones; it is commonly used as bait to attract and collect these bees for study.[4]
Cocaine hydrochloride hydrolyzes in moist air to give methyl benzoate;[5] drug-sniffing dogs are thus trained to detect the smell of methyl benzoate.[6]
Uses
Non electric Heat cost allocators. See: DIN EN 835.
References
- ↑ Maki, Takao; Takeda, Kazuo. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_555..
- ↑ John McMurry (2008). Organic Chemistry (7th ed.). Thompson - Brooks/Cole. p. 623. ISBN 978-1-4390-4972-3.
- ↑ Choudhary, MI; Naheed, N; Abbaskhan, A; Musharraf, SG; Siddiqui, H; Atta-Ur-Rahman (2008). "Phenolic and other constituents of fresh water fern Salvinia molesta". Phytochemistry 69 (4): 1018–23. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.028. PMID 18177906.
- ↑ Schiestl, F.P.; Roubik, D.W. (2003). "Odor Compound Detection in Male Euglossine Bees". Journal of Chemical Ecology 29 (1): 253–257. doi:10.1023/A:1021932131526. PMID 12647866.
- ↑ Dejarme, Lindy E.; Gooding, Rachel E.; Lawhon, Sara J.; Ray, Prasenjit; Kuhlman, Michael R. (1997). "Formation of methyl benzoate from cocaine hydrochloride under different temperatures and humidities". in Works, George; Rudin, Leonid I; Hicks, John et al.. Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE Proceedings. 2937. pp. 19. doi:10.1117/12.266783.
- ↑ Waggoner, L. Paul; Johnston, James M.; Williams, Marc; Jackson, Jan; Jones, Meredith H.; Boussom, Teresa; Petrousky, James A. (1997). "Canine olfactory sensitivity to cocaine hydrochloride and methyl benzoate". in Works, George; Rudin, Leonid I; Hicks, John et al.. Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE Proceedings. 2937. pp. 216. doi:10.1117/12.266775.
 |