Chemistry:Methylcyclopropane
From HandWiki
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylcyclopropane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | C105498 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 56.108 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas[1] | ||
| Density | 0.6912 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | −177.3 °C (−287.1 °F; 95.8 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 0.7 °C (33.3 °F; 273.8 K)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
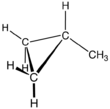
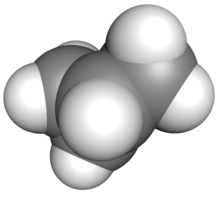
Methylcyclopropane is an organic compound with the structural formula C3H5CH3. This colorless gas is the monomethyl derivative of cyclopropane.
Reactions
Methylcyclopropane, like many other cyclopropanes, undergoes ring-opening reactions. Bond cleavage in certain reactions is also reported in conjunction with the use of methylenecyclopropane groups as protective groups for amines.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lide, David. R, ed (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (89th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-6679-1. https://archive.org/details/crchandbookofche00davi.
 |