Chemistry:Omidenepag
From HandWiki
Short description: Medication
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eybelis, Omlonti |
| Other names | UR-7276, DE-117, Omidenepag isopropyl (JAN JP) |
| Routes of administration | Topical eye drops |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
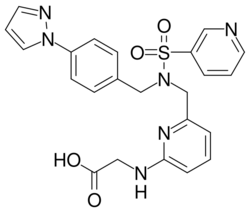
| Formula | C26H28N6O4S |
| Molar mass | 520.61 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Omidenepag, sold under the brand name Eybelis among others, is a medication used for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension.[1][3]
Omidenepag was approved for medical use in Japan in 2018,[3] and in the United States in September 2022.[2][4]
Medical uses
Omidenepag is indicated for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension.[1][3]
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects of omidenepag are conjunctival hyperemia and macular edema, including cystoid macular edema.[3]
Pharmacology
Omidenepag isopropyl is a prodrug that is converted by hydrolysis of its isopropyl ester to the active metabolite omidenepag.[5] Omidenepag is a selective prostaglandin E2 receptor agonist.[6][7]
History
Omidenepag was developed by Ube Industries and Santen Pharmaceutical.[3]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Omlonti- omidenepag isopropyl solution/ drops". 30 September 2022. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8e440b2c-fbe5-4c86-b7f3-3da00a5b2924.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 "Drug Approval Package: Omlonti". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 October 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2022/215092Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Omidenepag Isopropyl Ophthalmic Solution 0.002%: First Global Approval". Drugs 78 (18): 1925–1929. December 2018. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-1016-1. PMID 30465134.
- ↑ "Santen and UBE Received FDA Approval for Omlonti (Omidenepag Isopropyl Ophthalmic Solution) 0.002% for the Reduction of Elevated Intraocular Pressure in Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension" (Press release). Santen. 26 September 2022. Retrieved 1 October 2022 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ "Omidenepag isopropyl". DrugCentral. Division of Translational Informatics at University of New Mexico. https://drugcentral.org/drugcard/5312.
- ↑ "Pharmacologic Characterization of Omidenepag Isopropyl, a Novel Selective EP2 Receptor Agonist, as an Ocular Hypotensive Agent". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 59 (1): 145–153. January 2018. doi:10.1167/iovs.17-22745. PMID 29332128.
- ↑ "Omidenepag, a non-prostanoid EP2 receptor agonist, induces enlargement of the 3D organoid of 3T3-L1 cells". Scientific Reports 10 (1): 16018. September 2020. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72538-x. PMID 32994409. Bibcode: 2020NatSR..1016018I.
External links
- "Omidenepag". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/omidenepag.
- "Omidenepag isopropyl". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/omidenepag%20isopropyl.
- "Omidenepag". https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI%20Thesaurus&code=C170253.
- "Omidenepag isopropyl". https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C170254.
 |

