Earth:Paleobiota of the Hell Creek Formation
This is an overview of the fossil flora and fauna of the Maastrichtian-Danian Hell Creek Formation.
Invertebrates
insects
Insects from the groups Diptera, Zygoptera, and possibly Hemiphlebiidae have been unearthed in Hell Creek in amber.[1][2] Fossils found in the Hell Creek Formation and the Fort Union Formation of these insects went extinct during the K-T Event.[3][4][5]
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cephaloleichnites |
Cephaloleichnites strongi |
Possible hispine beetle herbivory on Zingiberopsis attenuta |
Molluscs
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plesielliptio |
P. postbiplicatus |
Freshwater Unionid river mussels |
||||
|
P. gibbosoides |
Freshwater Unionid river mussels |
|||||
|
P. whitfieldi |
Freshwater Unionid river mussels |
|||||
| Rhabdotophorus | R. aldrichi | Freshwater mussel of family Unionidae.[6] | ||||
| Pleurobema | P. cryptorhynchus | Freshwater mussel of family Unionidae.[6] | ||||
| Plethobasus | P. aesopiformis | Freshwater mussel of family Unionidae.[6] | ||||
| P. biesopoides | ||||||
| Quadrula | Q. cylindricoides | Freshwater mussel of family Unionidae.[6] | ||||
| Proparreysia | P. verrucosiformis | Freshwater mussel of family Unionidae.[6] | ||||
| P. holmesiana | ||||||
| P. barnumi | ||||||
| P. percorrugata | ||||||
| P. pyramidatoides | ||||||
| P. letsoni | ||||||
| P. retusoides | ||||||
| P. corbiculoides | ||||||
| P. paucinodosa | ||||||
| ?Obovaria | ?O. pyramidella | |||||
| Corbicula | C. cf. subelliptica | |||||
| C. sp | South Dakota | From a marine facies ("tongue"). Modern members of the genus live in fresh water | ||||
| Sphaerium | S. beckmani | "Pill clam". "Nut clam". "Fingernail clam". "Pea clam". Family Sphaeriidae. | ||||
| Pleiodon | Indeterminate | |||||
| Campeloma | C. sp | Freshwater snail | ||||
| Anomia | A. gryphorhyncha | Bivalve. Family Anomiidae. From a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Crassostrea | C. subtrigonalis | Oyster. Family Ostreidae. Collected from a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Granocardium | G. sp | Bivalve. Family Cardiidae (cockle). Collected from a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| ?Hiatella | ?H. sp | Bivalve. Present members of this genus are rock borers. Collected from a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Leptosolen | indeterminate | Bivalve. Family Cultellidae. Collected from a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Sphenodiscus | S. lenticularis | Ammonite. From a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Discoscaphites | D. rossi | Microconch of an ammonite. From a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. | ||||
| Scaphitidae | indeterminate | Ammonite. From a marine facies ("tongue") in South Dakota. Other attributes: specimen has hooks on its shell. |
Amphibians
| Amphibians reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
indeterminate[7] |
Middle to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
3 unassigned specimens[10] |
Anura indet. consists of material not currently assigned to any genus of frog.[7] |
||||
|
Indeterminate[12] |
|
||||||
|
Caudata (salamander)[7] |
indeterminate[7] |
Lower to uppermost Hell Creek Formation[9] |
149 unassigned specimens[10] |
Material of Caudata indet. is not currently assigned to any genus.[7] |
|||
|
Indeterminate[12] |
|
||||||
|
Middle to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
6 specimens[10] |
||||||
|
Lisserpeton[12] |
L. bairdi[12] |
|
|||||
|
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
22 specimens[10] |
Opisthotriton is classified as a Batrachosauroididae.[7] |
|||||
|
Paranecturus[15] |
P. garbanii[15] |
|
|||||
|
Proamphiuma[12] |
P. cretacica[12] |
|
|||||
|
P. copei[12] |
|
||||||
|
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
144 specimens[10] |
Scapherpeton is a scapherpetonid that is very common in the Hell Creek Formation.[7] |
|||||
|
S. pustulosa[12] |
|
A small frog |
|||||
Fish
Bony fish
| Bony fishes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
| Acipenser[7][16][17] | A. amnisinferos[17] | A sturgeon | |||||
| A. eruciferus[16] |
|
||||||
| A. praeparatorum[17] |
|
||||||
| A. cf. A. amnisinferos[17] |
|
||||||
|
cf. A. sp.[7] |
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
18 specimens are tentatively assigned to Acipenser sp.[10] |
Acipenser sp. is tentatively referred to the genus.[7] |
||||
| Anchiacipencer[19] | A. acanthaspis[19] |
|
A sturgeon, originally considered as indeterminate material[19] | ||||
| Belonostomus[7][16] | B. longirostris[7][16] | Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] | 28 specimens[10] | A long-snouted slender fish classified as an aspidorhynchid.[7] | |||
| Coriops[20] | C. amnicolus[20] |
|
|||||
|
Cyclurus[16] |
C. fragosus[16] |
A small amiid fish (ubiquitous). Previously known as Amia fragosa or Kindleia fragosa.[22] 2610 specimens have been assigned to Kindleia, making it an extremely common genus.[10] |
 |
||||
| "Lepisosteus"[7][16] | "L. occidentalis"[7][16] | Lower to uppermost Hell Creek Formation[9] | 938 specimens are assigned to Lepidosteus[10] | A lepidosteid that is very common in the Hell Creek Formation.[7] Nomen dubium.[23] | 
| ||
| Melvius[7] | M. thomasi[7] | Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] | 6 specimens are assigned to Melvius[10] | A large amiid fish.[7] | |||
| Phyllodus | P. paulkatoi | Fish with columnar teeth | |||||
| Palaeolabrus[16] | P. montanensis[16] |
|
|||||
| Paleopsephurus[16] | P. wilsoni[16] |
|
A paddlefish | ||||
| Paralbula[24] | P. casei[24] |
|
|||||
| Parapsephurus[25] | P. willybemisi[25] |
|
A paddlefish | 
| |||
| Platacodon[20] | P. nanus[20] |
|
Small teleost fish | ||||
| Protamia[16] | Indeterminate[16] |
|
|||||
| Pachyrhizodontoidei | Indeterminate | Fish | |||||
| Polyodontidae[26] | Indeterminate[26] |
|
Paddlefish | ||||
| Protoscaphirhynchus[16] | P. squamosus[16] |
|
A sturgeon | ||||
| Pugiopsephurus[25] | P. inundatus[25] |
|
A paddlefish | ||||
Cartilaginous fish
| Chondrichthyes reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
C. sp.[27] |
|
A member of Hemiscylliidae.[27] |
||||
|
G. nordquistae |
|
Isolated teeth |
||||
|
L. selachos[29] |
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
40 specimens[10] |
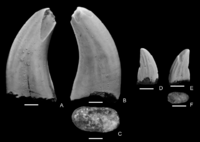
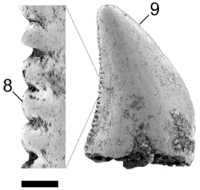
A genus of prehistoric sharks in the family Hybodontidae. It makes up 0.4% of the remains of the vertebrates of the Hell Creek Formation.[7] |
|||
|
M. pustulosus[27] |
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation.[9] |
1677 specimens[10] previously assigned to M. bipartitus.[27] |
Is an anacoracid batoid[7] rajiform related to guitarfishes.[27] Described on the basis of teeth formerly assigned to the species M. bipartitus.[27] The material assigned to Myledaphus bipartitus and makes up 16.5% of the vertebrate remains.[7] |
|||
|
Protoginglymostoma[27] |
P. estesi[27] |
|
A member of Ginglymostomatidae.[27] Formerly assigned to the genus Brachaelurus. |
|||
|
Restesia[27] |
R. americana[27] |
Middle Hell Creek Formation[9] |
5 specimens previously assigned to Squatirhina[10] |
A wobbegong-like shark.[27] Formerly assigned to Squatirhina. The remains consist of 0.05% of the vertebrates.[10] Also known from the Lance Formation.[27] |
||
|
Carcharhinidae indet.[28] |
Indeterminate |
|
An isolated tooth. |
|||
Dinosaurs
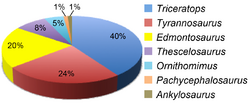
A paleo-population study is one of the most difficult of analyses to conduct in field paleontology. Here is the most recent estimate of the proportions of the eight most common dinosaurian families in the Hell Creek Formation, based on detailed field studies by White, Fastovsky and Sheehan.[31]
- Ceratopsidae 61%
- Hadrosauridae 23%
- Ornithomimidae 5%
- Tyrannosauridae 4%
- Hypsilophodontidae 3%
- Dromaeosauridae 2%
- Pachycephalosauridae 1%
- Troodontidae 1% (represented only by teeth)
Outcrops sampled by the Hell Creek Project were divided into three sections: lower, middle and upper slices. The top and bottom sections were the focus of the PLoS One report, and within each portion many remains of Triceratops, Edmontosaurus, and Tyrannosaurus were found. Triceratops was the most common in each section, but, surprisingly, Tyrannosaurus was just as common, if not slightly more common, than the hadrosaur Edmontosaurus. In the upper Hell Creek section, for example, the census included twenty two Triceratops, five Tyrannosaurus, and five Edmontosaurus.
The dinosaurs Thescelosaurus, Ornithomimus, Pachycephalosaurus and Ankylosaurus were also included in the breakdown, but were relatively rare. Other dinosaurs, such as Sphaerotholus, Denversaurus, Torosaurus, Struthiomimus, Acheroraptor, Dakotaraptor, Pectinodon, Richardoestesia, Paronychodon, Anzu, Leptorhynchos and Troodon (more likely Pectinodon), were reported as being rare and are not included in the breakdown.
The dinosaur collections made over the past decade during the Hell Creek Project yielded new information from an improved genus-level collecting schema and robust data set that revealed relative dinosaur abundances that were unexpected, and ontogenetic age classes previously considered rare. We recognize a much higher percentage of Tyrannosaurus than previous surveys. Tyrannosaurus equals Edmontosaurus in U3 and in L3 comprises a greater percentage of the large dinosaur fauna as the second-most abundant taxon after Triceratops, followed by Edmontosaurus. This is surprisingly consistent in (1) the two major lag deposits (MOR loc. HC-530 and HC-312) in the Apex sandstone and Jen-rex sand where individual bones were counted and (2) in two thirds of the formation reflected in L3 and U3 records of dinosaur skeletons only.
Triceratops is by far the most common dinosaur at 40% (n = 72), Tyrannosaurus is second at 24% (n = 44), Edmontosaurus is third at 20% (n = 36), followed by Thescelosaurus at 8% (n = 15), Ornithomimus at 5% (n = 9), and Pachycephalosaurus and Ankylosaurus both at 1% (n = 2) are relatively rare.
Fossil footprints of dinosaurs from the Hell Creek Formation are very rare. As of 2017, there is only one find of a possible Tyrannosaurus rex footprint, dating from 2007 and described a year later.[32] A trackway made by mid-sized theropod, possibly a small tyrannosaurid individual, was discovered in South Dakota in 1997, and in 2014 these footprints were named Wakinyantanka styxi.[33]
Ornithischians
Ankylosaurs
Indeterminate nodosaur remains have been unearthed in the Hell Creek Formation and other nearby areas.[34][35]
| Ankylosauria reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
A. magniventris[36] |
|
Upper | A partial skull, teeth, cervical vertebrae, dorsal vertebrae, caudal vertebrae, right scapulocoracoid, otic capsule, maxilla fragment, right jugal, left jugal and quadratojugal, sacral centra, additional fragments of the cervical half rings and a partial tail club handle. |
An ankylosaur. Also found in the Lance, Frenchman, Ferris and Scollard Formations. |
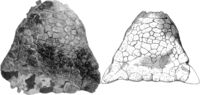 | |
|
D. schlessmani[36] |
Skull roof, pelvis and osteoderms. |
A nodosaurid ankylosaur whose remains have been found in the Lance and Laramie Formation.[34] |
||||
Pachycephalosaurs
An undescribed and unnamed pachycephalosaur is present in North Dakota.[38] Pachycephalosaur remains have been unearthed in Montana as in the case of Platytholus and the now invalid genus Stenotholus kohleri, which is now a junior synonym of Pachycephalosaurus.[39]
| Pachycephalosaurs reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
D. hogwartsia[40] |
|
|
A pachycephalosaur, possibly synonymous with Pachycephalosaurus. |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | ||
|
P. wyomingensis[36] |
A pachycephalosaur. Also found in the Lance Formation. |
|||||
| Platytholus[41] | P. clemensi[41] |
|
|
A partial skull[41] | A medium-sized pachycephalosaurine closely related to Acrotholus and Prenocephale | |
|
S. buchholtzae[36] |
|
"Skull material."[44] |
A pachycephalosaur whose remains have also been found in the Frenchman Formation. Genus also known from the Kirtland Formation, Dinosaur Park Formation and the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. |
|||
|
S. triregnum[43] |
|
|
A left squamosal.[43] |
A pachycephalosaur distinguished from S. buchholtzae by its more ornamented squamosal.[43] | ||
|
S. spinifer[36] |
|
A pachycephalosaur, possibly synonymous with Pachycephalosaurus. Also found in the Ferris Formation and the Lance Formation. |
||||
Ceratopsians
Indeterminate ceratopsid teeth and some identifiable bones from Triceratops can be extremely common.[45][46][47][48][49] 8.31% of all vertebrate remains from the Hell Creek Formation are unassigned ceratopsids.[10] In 2012, a new unidentified species of chasmosaur ceratopsian with noticeable differences from Triceratops was unearthed in South Dakota by a fossil hunter named John Carter.[50][51][52]
| Ceratopsians reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Synonyms | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
L. gracilis[36] |
|
A small primitive-looking ceratopsian. Fossils have also been found in the Lance Formation in Wyoming.[53] |
|||||
|
T. sacrisonorum[54] |
|
A controversial ceratopsian possibly synonymous with Triceratops[55] |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | ||||
|
Upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
A ceratopsian that was once proposed to be synonymous with Triceratops,[56] but is now regarded as a valid and distinct ceratopsian.[57] A rare ceratopsid.[9] Fossils have been in the Lance Formation, Javelina Formation, North Horn Formation, Laramie Formation, El Picacho Formation, Frenchman Formation and Scollard Formation. |
||||||
|
Lowermost to the middle Hell Creek Formation[59] |
Four specimens are assigned to Triceratops horridus from the Hell Creek Formation.[10] Isolated, shed ceratopsid teeth are incredibly common in the Hell Creek and Lance Formations, being by most collectors, with some being nothing more than worn down fragments up to superb teeth containing complete, preserved roots. Because the teeth of different ceratopsians are so similar to one another, its hard to differentiate between genera/species, but based on the abundance of identifiable bones belonging to Triceratops in Lancian-aged North American formations, especially the Hell Creek, isolated ceratopsid teeth from the lower and middle Hell Creek Formation have a high likelihood of originating from T. horridus. |
A ceratopsian.[7] Also found in the Evanston, Frenchman, Lance, Laramie, and Scollard Formations. |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | ||||
|
T. prorsus[36] |
|
Upper 1/3 of the Hell Creek Formation[59] |
Very common. Because the teeth of different ceratopsians are so similar to one another, its hard to differentiate between genera/species, but based on the abundance of identifiable bones belonging to Triceratops in Lancian-aged North American formations, especially the Hell Creek, isolated ceratopsid teeth from the upper 1/3 of the Hell Creek Formation have a high likelihood of originating from T. prorsus. | Also found in the Frenchman and Lance Formations. |
||||
Ornithopods and relatives
Indeterminate hadrosaurid remains are very common in the Hell Creek Formation.[7]
| Ornithopods and Thescelosaurs reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Synonyms | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
E. annectens |
Very common. |
A hadrosaur. Also found in the Denver, Frenchman, Lance, Laramie, and Scollard Formations.[63][64] Hatchlings have also been unearthed.[64] |
|||||
|
Thescelosaurus[37] |
|
||||||
|
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[9] |
50 specimens[10] |
A small thescelosaurine. Also found in the Frenchman, Lance, Laramie, and Scollard Formations.[68] Two species are known from Hell Creek; T. neglectus and T. garbanii.[69] |
|||||
Theropods
Theropod tracks have been found in South Dakota.[37] A trackway from South Dakota, named Wakinyantanka, was made by a mid-sized theropod with three slender toes, possibly a small tyrannosaurid.[33] A second footprint that may have been made by a specimen of Tyrannosaurus was first reported in 2007 by British paleontologist Phil Manning, from the Hell Creek Formation of Montana.[70] This second track measures 72 centimeters (28 in) long, shorter than the track described by Lockley and Hunt. Whether or not the track was made by Tyrannosaurus is unclear, though Tyrannosaurus is the only large theropod known to have existed in the Hell Creek Formation, though in past albertosaurine remains have described here but its most likely that they are the remains of Tyrannosaurus rex.[71][72] Theropod remains are very common in Hell Creek, some of which belong to indeterminate species on maniraptorans.[73]
Alvarezsaurs
| Alvarezsaurs reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Synonyms | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| "Ornithomimus" | "O." minutus | ||||||
|
T. prairiensis[36] |
|
upper Hell Creek Formation. |
An alvarezsaur known from a partial post-cranial skeleton.[74] |
||||
Tyrannosaurids
| Tyrannosaurids reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Synonyms | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation. |
A tyrannosaur, known from several specimens including a juvenile nicknamed "Jane".[75] Also found in the Denver, Frenchman, Hill Creek South, Javelina, Lance, Ferris, Livingston, McRae, North Horn, Scollard, Willow Creek Formation, and also found in Lomas Coloradas Formations. Isolated teeth in the Hell Creek are common enough to be dug commercially by collectors, but rare enough that they are often sold for very high prices with fragmentary teeth usually beginning at least in the hundreds of USD, and complete teeth in the thousands of USD. |
|||||
|
|
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation. |
A few specimens are known |
Invalid genus, now recognised as juvenile T. rex. |
|||
Ornithomimosaurs
Ornithomimid remains are not uncommon in the Hell Creek Formation.[7] Fifteen specimens from the Hell Creek Formation are undetermined ornithomimids[10]
| Ornithomimids reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
"Orcomimus" |
unnamed |
|
One partial skeleton. |
An ornithomimid. Numem nudum |
|||
|
S. sedens[77] |
|
|
A large ornithomimid similar to Gallimimus in size. Also found in the Lance Formation.[77] |
||||
|
O. velox[77] |
|
Fragmentary specimens |
An ornithomimid which was also found in the Denver Formation. |
||||
Oviraptorosaurs
Oviraptorosaur fossils have been found at the Hell Creek Formation for many years, most notably from isolated elements until the discovery of Anzu. In the past, oviraptorosaur fossils found were thought to have belonged to Caenagnathus, Chirostenotes, and Elmisaurus.[36][78][79][80][81] In 2016, an undescribed large-bodied caenagnathid was unearthed in Montana.[82]
| Oviraptorosaurs reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
A. wyliei[78] |
Lower to upper Hell Creek Formation[10] |
12 well-preserved specimens[9] |
One of the largest known oviraptorosaurs, and the largest known from North America. Material previously assigned to Caenagnathidae indet. is now placed in the genus Anzu.[78] |
||||
|
Indeterminate |
|
Similar to Citipes and Elmisaurus. |
|||||
| Eoneophron | E. infernalis |
|
A partial right hindlimb[83] | Closely related to Citipes and Elmisaurus.[83] | 
| ||
Eumaniraptorans
Historically, numerous teeth have been attributed to various dromaeosaurid and troodontid taxa with known body fossils from only older formations, including Saurornithoides, Zapsalis, Dromaeosaurus, Saurornitholestes, and Troodon. However, in a 2013 study, Evans et al. concluded that there is little evidence for more than a single dromaeosaurid taxon, Acheroraptor, in the Hell Creek-Lance assemblages, which would render these taxa invalid for this formation. This was disproved in a 2015 study, DePalma et al., when they described the new genus Dakotaraptor, a large species of dromaeosaur.[84] Fossilized teeth of various troodontids and coelurosaurs are common throughout the Hell Creek Formation; the best known examples include Paronychodon, Pectinodon and Richardoestesia, respectively. Teeth belonging to possible intermediate species of Dromaeosaurus[85] and Saurornitholestes[86] have been unearthed at the Hell Creek Formation and the nearby Lance Formation.
| Eumaniraptorans reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
A. temertyorum [84] |
Lower? to upper Hell Creek Formation[7] |
A velociraptorine dromaeosaurid. Teeth previously referred to various Campanian dromaeosaurids Saurornitholestes and Dromaeosaurus, frequently found throughout the formation, probably belong to this one species. Evans et al. conclude that there is little evidence for the former two taxa being present in the Hell Creek-Lance assemblages.[84] |
|||||
|
Middle Hell Creek Formation[9] |
|
|||||
|
cf. A. archibaldi[87] |
|
Uppermost Hell Creek Formation[87] |
|
An avisaurid tentatively referred to A. archibaldi based on its size.[87] |
|||
|
A. sp.[88] |
|
|
|||||
|
B. baileyi[89] |
|
|
A primitive hesperornithiform.[89] |
||||
|
D. steini [90] |
|
Upper Hell Creek Formation[90] |
A dromaeosaurid. Second-largest dromaeosaurid known.[84] |
||||
|
P. caperatus [91] |
|
|
A troodontid theropod who is known from fossil teeth. Fossils have also been found in the Lance Formation in Wyoming. |
||||
|
|
|
|||||
| Potamornis[89] |
P. skutchi [93] |
|
|
A hesperornithiform also found in the Lance Formation.[93] |
|||
|
|
A coelurosaur that is known from teeth and from two species Richardoestesia gilmorei and Richardestesia isosceles, which have also been unearthed in the Lance Formation in Wyoming. |
|||||
| "Styginetta"[96] | "S. lofgreni." |
|
A Presbyornithid, it is notable for being one of the few birds known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. | ||||
|
"Unnamed enantiornithine B"[87] |
Unnamed |
|
|
An unnamed enantiornithean.[87] |
|||
|
"Unnamed hesperornithiform A"[87] |
Unnamed |
|
|
A primitive hesperornithiform.[89] The Hell Creek specimen was referred to the same unnamed taxon as RSM P 2315.1 from the Canadian Frenchman Formation.[87] RSM P 2315.1 was later made the holotype of Brodavis americanus.[89] May be a synonym of Potamornis.[87] |
|||
|
"Unnamed ornithurine B"[87] |
Unnamed[97] |
|
|
An ornithurine possibly similar to Cimolopteryx[87][97] |
|||
|
"Unnamed ornithurine C"[87] |
Unnamed |
An ornithurine, also present in the Lance Formation and Fort Union Formation, one of the few individual bird species known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction[87] |
|||||
|
"Unnamed ornithurine D"[87] |
Unnamed |
|
|
An ichthyornithean also present in the Frenchman Formation[87] |
|||
Pterosaurs
Indeterminate azhdarchid remains, most likely belong to Quetzalcoatlus or an unidentified genus, have been found in Hell Creek as well as the Javelina Formation and the Ojo Alamo Formation.[99][100] Indeterminate pteranodontid remains have also been found here as well.[101][102]
| Pterosaurs of the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Species | State | Stratigraphic location | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
Azhdarchidae spp. |
Indeterminate |
|
Records of pterosaur remains from the Hell Creek Formation are two indeterminate specimens, which have been recorded from North Dakota but not described (Johnson et al., 2000; Pearson et al., 2002). A single azhdarchid neck bone may belong to the genus Quetzalcoatlus, though they are not diagnostic to the generic level.[99] |
 | |||
|
Indeterminate |
|
||||||
Crocodylomorphs
| Crocodylomorphs reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
|
Extinct genus of crocodylians that lived from the Late Cretaceous to the Eocene in North America. |
|||||
|
|
Extinct genus of alligatoroid. |
|||||
|
|
Extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian which existed during the Late Cretaceous and early Paleocene. |
|||||
Turtles
| Turtles reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
Indeterminate[105] |
|
Extinct genus of aquatic turtles belonging to the family Adocidae. |
|||||
|
A. infernalis[107] |
|
A turtle belonging to the family Trionychidae. Its fossils from the Hell Creek Formation were formerly assigned to the late Campanian species Axestemys splendidus.[108][107] |
|||||
|
C. victa[105] |
|
A relative of Dermatemydidae. |
|||||
|
P. brinkman |
|
A relative of Baenidae. |
|||||
|
E. cretacea |
|
A relative of chelydrids.[109] |
|||||
|
Eubaena[105] |
E. cephalica[105] |
|
Baenid turtle |
||||
|
G. sonsalla |
|
||||||
|
P. cohen |
|
A relative of extinct family of cryptodiran turtles. |
|||||
|
C. putorius |
|
A relative of Baenidae. |
|||||
|
G. lancensis |
|
Trionychidae related to the softshell turtle. |
|||||
|
H. clark[109] |
|
A kinosternoid related to the Central American river turtle.[109] |
|||||
| Hutchemys[110] | H. walkerorum[110] |
|
A shell[110] | A Plastomeninae related to the softshell turtle.[110] | |||
|
Plastomenus |
P. sp |
||||||
|
B. sinuosa |
Largest dermatemydid land tortoise. |
||||||
|
Indeterminate[105] |
|
A genus of softshell turtles belonging to the family Trionychidae. |
|||||
|
Aspideretoides |
A. foveatus |
||||||
|
Helopanoplia |
H. distincta |
||||||
|
Judithemys |
J. backmani |
Thin-shelled macrobaenid turtle. |
|||||
|
P. antiqua |
Baenid turtle. |
||||||
|
Stygiochelys |
S. estesi |
Baenid turtle. |
|||||
|
N. eximius |
Largest baenid turtle in Hell Creek Formation. |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |||||
|
Saxochelys[111] |
S. gilberti |
|
|
A member of the family Baenidae. |
|||
|
Thescelus |
T. insiliens |
Baenid turtle. |
|||||
|
Indeterminate |
Chelydrids-like turtle. |
||||||
Squamata
Indeterminate mosasaur remains have been unearthed in North Dakota; they may belong to a mosasaur measuring 11 m (36 ft) in length.[112][113]Template:Paleobiota-key-compact
| Squamates reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
A platynotan lizard of uncertain phylogenetic placement, also known from the Lance Formation.[114] |
||||||
|
An alethinophidian snake of uncertain phylogenetic placement.[114] |
||||||
|
A polyglyphanodontian lizard of uncertain phylogenetic placement. Also known from the Lance Formation.[114] |
||||||
|
Peneteius[114] |
P. aquilonius[114] |
|
A chamopsiid polyglyphanodontian lizard.[114] |
||||
|
Haptosphenus |
H. placodon |
||||||
|
Leptochamops |
L. denticulatus |
||||||
|
C. segnis |
|||||||
|
Contogenys |
C. sloani |
||||||
|
Exostinus |
E. lancensis |
||||||
|
Proxestops |
P. jepseni |
||||||
|
Parasaniwa |
P. wyomingensis |
Necrosaurid lizard. |
|||||
|
P. bogerti |
|||||||
|
P. canadensis |
A large Monstersauria lizard, closely related to today's varanid lizards. It was the largest lizard in the Hell Creek formation. |
||||||
|
Indeterminate |
Snake. Earliest-known boid. |
||||||
Choristoderans
| Choristoderans reported from the Hell Creek Formation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
|
C. laramiensis[104] |
|
A champsosaur. |
|||||
Mammals
Multituberculates
| Multituberculates reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
C. minor[116] |
|
A multituberculate of uncertain phylogenetic placement. |
||||
|
C. nitidus |
|
A cimolodontid multituberculate. |
||||
|
C. cf. nitidus[116] |
|
A cimolodontid multituberculate. |
||||
|
C. sp.[116] |
|
A cimolodontid multituberculate. |
||||
|
C. gracilis |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
E. browni[116] |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. conquistus |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. robustus |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. cf. robustus |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. sp. |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
?M. sp.[116] |
|
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. formosa |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. cf. formosa |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. hensleighi |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. cf. hensleighi |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. thompsoni |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M. cf. thompsoni |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
M sp.[116] |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
?M sp.[116] |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
?N. burgessi[116] |
|
A neoplagiaulacid multituberculate. |
||||
|
P. priscus[116] |
|
A multituberculate of uncertain phylogenetic placement. |
||||
|
P. nelsoni[117] |
A cimolomyid multituberculate. |
|||||
|
S. kuszmauli |
|
It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. |
||||
Metatherians
| Metatherians reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
A. florencae |
|
A pediomyid. |
||||
|
A. hatcheri[118] |
|
A pediomyid. |
||||
|
A. marshi |
|
An alphadontid. genus of small, primitive mammal that was a member of the Metatheria, a group of mammals that includes modern-day marsupials. |
||||
|
A. cf. marshi |
|
An alphadontid. |
||||
|
A. wilsoni |
|
An alphadontid. |
||||
|
A. cf. wilsoni |
|
An alphadontid. |
||||
|
A. sp.[116] |
|
An alphadontid. |
||||
|
D. padanicus |
|
A stagodontid. |
||||
|
D. vorax |
|
A stagodontid. genus of Stagodontidae marsupials from the Late Cretaceous of North America. |
||||
|
D. cf. vorax |
|
A stagodontid. |
||||
|
D. sp. |
|
A stagodontid. |
||||
|
cf. D. sp.[116] |
|
A stagodontid. |
||||
|
Glasbius[116] |
G. twitchelli |
|
A glasbiid. |
|||
|
G. cf. twitchelli[116] |
|
A glasbiid. |
||||
|
Leptalestes[118] |
L. cooki |
|
A pediomyid. |
|||
|
L. krejcii[118] |
|
A pediomyid. |
||||
|
N. improvida[117] |
||||||
|
Nortedelphys |
|
|||||
|
Pediomys[116] |
P. elegans[116] |
|
A pediomyid. |
|||
|
P. foxi |
|
An alphadontid. |
||||
|
P. lulli[116] |
|
An alphadontid. | ||||
|
Turgidodon[116] |
T. rhaister[116] |
|
An alphadontid. |
|||
Eutherians
| Eutherians reported from the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
|
A. magnus |
|
a possible creodont, formerly a species of Cimolestes[121] |
||||
|
Alostera[116] |
A. saskatchewanensis[116] |
|
A eutherian of uncertain phylogenetic placement. |
|||
|
Ambilestes |
A. cerberoides |
|
A eutherian of uncertain classification, formally a species of Cimolestes |
|||
|
Batodon[116] |
B. tenuis[116] |
|
A cimolestid eutherian. |
|||
|
C. incisus |
|
A cimolestid eutherian. | ||||
|
C. stirtoni[116] |
|
A cimolestid eutherian. |
||||
|
G. hypoconus |
|
A gypsonictopsid eutherian. |
||||
|
G. illuminatus |
|
A gypsonictopsid eutherian. |
||||
|
G. cf. illuminatus |
|
A gypsonictopsid eutherian. |
||||
|
G. sp.[116] |
|
A gypsonictopsid eutherian. |
||||
|
cf. Paranyctoides[116] |
cf. Paranyctoides sp.[116] |
|
A nyctitheriid eutherian. |
|||
|
P. coombsi[118] |
|
A stem-placental. |
||||
|
P. ceratops |
|
A genus with four species believed to be either stem-placentals or stem-primates. |
||||
|
Scollardius |
S. propalaeoryctes |
|
A eutherian of uncertain classification, formally a species of Cimolestes |
|||
Flora
The Hell Creek Formation was a low floodplain at the time before the sea retreated, and in the wet ground of the dense woodland, the diversity of angiosperms and conifers were present. An endless diversity of herbaceous flowering plants, ferns and moss grew in the forest understory. On the exposed point bars of large river systems, there were shrubs and vines. The evidence of the forested environment is overwhelmingly supported by petrified wood, rooted gley paleosols,[122] and ubiquitous tree leaves. The presence of the simple and lobed leaves, combined with an extremely high dicot diversity, extinct cycadeoid Nilssoniocladus, Ginkgo, many types of monocots, and several types of conifers is different from any modern plant community. There are numerous types of leaves, seeds, flowers and other structures from Angiosperms, or flowering plants. The Hell Creek Formation of this layer contains over 300 tablets, of which angiosperms are by far the most diverse and dominant flora of the entire population, about 90 percent, followed by about 5% of conifers, 4% of ferns, and others. Compared to today Hell Creek's flora which is prairie, then Hell Creek's flora was hardwood forest mixed with deciduous and evergreen forest. In sharp contrast to the Great Plains today, the presence of many thermophilous taxa such as palm trees and gingers meant the climate was warmer and wetter then.

The plants of the Hell Creek Formation generally represent angiosperm-dominated riparian forests of variable diversity, depending on stratigraphic position and sedimentary environment. There appears to be floral transitions visible on a stratigraphic range from the lower to the upper Hell Creek Formation. For this reason, Kirk Johnson and Leo Hickey divided it into five zones and described them as HCIa, HCIb, HCIIa, HCIIb, and HCIII as a reflection of floral change through time.[123] For example, the HCIa zone is dominated by "Dryophyllum" subfalcatum, Leepierceia preartocarpoides, "Vitis" stantonii, and "Celastrus" taurenensis, and is located 55 to 105 meters below the K-Pg boundary layer. Although the HCIb zone is a very thin layer, about 5 meters of rock, it bears unusually high diversity of herbaceous and shrubby plants, including Urticaceae, Ranunculaceae, Rosaceae, and Cannabaceae.[124][125]

There is evidence of transitional floras in the middle of the Hell Creek Formation as shown by HCII and HCIII zones. The HCII flora represents a transitional period where taxa from the lower Hell Creek are replaced by the HCIII flora. The diversity of the HCIII zone is very high, and its composition is more uniform than that of HCII, many of which were rare or absent from the zones below, and some others that used to be common below became rarer in the HCIII zone. These forms include Elatides longifolia, "Dryophyllum" tennessensis, Liriodendrites bradacii, and many members of the Laurales including Bisonia niemii, "Ficus" planicostata, and Marmarthia trivialis, while "Celastrus" taurenensis, Leepierceia preartocarpoides, and many cupressaceous conifers became rarer. This phenomenon suggests that the global temperature was warming during the last 300,000-500,000 years of the Cretaceous period.[124][125][126][127]
Johnson claims that there are no grasses, oaks, maples, beeches, figs, or willows in the Hell Creek Formation. There is no evidence of fern prairie either.[128] However, there was an extremely high angiosperm diversity — common plane trees, "Dryophyllum" subfalcatum, Leepierceia preartocarpoides, and palm trees — along with extinct cycadeoid Nilssoniocladus, Ginkgo, araucariaceous, podocarpaceous, and cupressaceous conifers. This represents the mixed deciduous and evergreen broad-leaved forest as the Hell Creek landscape. The nature of these forests is uncertain because Johnson found that the majority of the angiosperm and conifer genera are now extinct. He also believes that, very roughly 80% of the terrestrial plant taxa died out in what is now Great Plains at the K-Pg boundary. On other hand, there is a great increase in the abundance of fossil fern spores in the two centimeters of rock that directly overlies the impact fallout layer (the famous K-Pg boundary layer). This increase in fern spore abundance is commonly referred as "the fern spike" (meaning that if the abundance of spores as a function of stratigraphic position were plotted out, the graph would show a spike just above the impact fallout layer).
Many of the modern plant affinities in the Hell Creek Formation (e.g., those with the prefix "aff." or with quotes around the genus name) may not in reality belong to these genera; instead they could be entirely different plants that resemble modern genera. Therefore, there is some question regarding whether the modern Ficus or Juglans, as two examples, actually lived in the Late Cretaceous.
Compared to the rich Hell Creek Formation fossil plant localities of the Dakotas, relatively few plant specimens have been collected from Montana. A few taxa were collected at Brownie Butte Montana by Shoemaker, but most plants were collected from North Dakota (Slope County) and from South Dakota. Among the localities, the Mud Buttes, located in Bowman County, North Dakota, is probably the richest megaflora assemblage known and the most diverse leaf quarry from the Hell Creek Formation.[125] "TYPE" after the binomial means that it is represented by a type specimen found in the Yale-Peabody Museum collections. "YPM" is the prefix for the Yale-Peabody Museum specimen number; "DMNH" is for the Denver Museum of Nature & Science; "USNM" is for Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History; and so on. The majority of Hell Creek megafloral specimens are collected at the Denver Museum of Nature & Science.
Overview (from Johnson, 2002): 302 plant morphotypes based on leaf only, including:
- 1 bryophyte (mosses and liverworts)
- 11 ferns
- 1 sphenopsid
- 10 conifers
- 1 ginkgo (uncommon)
- 278 angiosperms (roughly 92% of all taxa found)
-
Ferns from Hell Creek
-
Cycads are found in Hell Creek
-
Ginkgo (uncommon) are found in Hell Creek
-
Various angiosperms from Hell Creek
-
Monkey-puzzle leaves are found in Hell Creek
-
Fossil palm trees indicate a hotter paleoclimate
-
Redwood seed cones are known from Hell Creek
-
Laurus are found in Hell Creek
-
Cercidiphyllum are found in Hell Creek
-
Magnolia is commonly found in Hell Creek
- Plants of the Hell Creek Formation
- various ferns and cycads.
- Equisetum (Equisetaceae)
- Platyspiroxylon (Cupressaceae)
- Podocarpoxylon (Podocarpaceae)
- Elatocladus (Taxodiaceae)
- Sequoiaxylon (Taxodiaceae)
- Taxodioxylon (Taxodiaceae)
- Araucaria (Araucariaceae)
- †Cheirolepidiaceae
- Artocarpus (Moraceae)
- Rose family (Rosaceae)
- Trochodendriodes (Cercidiphyllaceae)
- Penosphyllum (Sterculiaceae)
- Laurel family (Lauraceae)
- Magnolia (Magnoliaceae)
- Palms (Arecaceae)
- Platanites, sycamore or plane tree (Platanaceae)
| Flora of the Hell Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Alnipollenites |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
Aquilapollenites |
"Aquilapollenites" attenuatus |
Fossil pollen | ||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" collaris |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" conatus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" delicatus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" marmarthensis |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" quadricretaeus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" quadrilobus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" reductus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" senonicus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" turbidus |
Fossil pollen | |||||
|
"Aquilapollenites" striatus |
Fossil pollen |
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | ||||
|
Balmeisporites |
Balmeisporites sp. |
Fossil pollen | ||||
|
Ilexpollenites |
Ilexpollenites compactus |
Fossil pollen | ||||
|
Interpollis |
Interpollis cf. I. supplingensis |
Fossil pollen | ||||
|
Tricolpites |
Tricolpites interangulus |
Fossil pollen | ||||
|
"A." lessigiana |
Abundant at Brownie Butte, Montana. |
|||||
|
A?. robusta |
Abundant at Brownie Butte, Montana. |
|||||
| Araliaephyllum |
A. polevoi |
A lobed leaf. Closely relating to Bisonia. Fairly common. | ||||
| Araucaria? |
indeterminate |
Casts of Monkey-puzzle leaves are found in Hell Creek. |
||||
| Averrhoites | cf. A. affinis | An uncommon taxon with compound leaves. | 
| |||
| Bisonia |
B. niemii |
Incertae sedis. Johnson, 1996. A broad leaf, probably in the Laurales. A common taxon. Type specimen was found near a Tyrannosaurus skeleton in South Dakota. |

| |||
| Browniea | B. serrata | In the Nyssaceae, closely relating to extant Camptotheca. Less common. | ||||
| Cannabaceae? |
indeterminate |
Incertae sedis. It's not likely in the Cannabaceae. [129] | ||||
| Carpites | C. ulmiformis | Though this fossil fruit is abundant in the Early Paleocene, it's also found in Hell Creek. It may belong to Apiaceae. [130] | ||||
|
"C." taurenensis |
Incertae sedis. It's common in the lowermost to the middle Hell Creek Formation, but less common in the upper 1/3 Hell Creek Formation. [131] |
|||||
|
"C." lineafolia |
Included in Ficus affinis by L. Hickey. Belongs in Rhamnaceae (modern buckthorns and Ceanothus). Some other specimens referred to Cinnamomum sezanensis(?) sp.), a real cinnamon bush. Its affinity is questionable. |
|||||
| Cissites | cf. C. acerifolia | This morphotype was first described from the Cenomanian Dakota Group.[124] | ||||
|
C. insignis |
This form represents of the group of Cenomanian leaves from Dakota Formation. [124] |
|||||
|
C. lobata |
A lobed leaf with half-naked basal lateral veins. Common in the upper 1/3 of the Hell Creek Formation. | |||||
|
C. puilasokensis |
A palmately lobed leaf with 5 primary veins. Common in the upper 1/3 of the Hell Creek Formation. | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | ||||
|
Cobbania |
C. corrugata |
A prehistoric species of water lettuce, previously assigned to the genus Pistia. |
||||
| C. hickeyi | Another Cobbania species from pond sediments known as "Licking Leaves."[132] | |||||
| Cornophyllum | C. newberryi | The majority of leaves are entire-margined but some may develop a few teeth.[124] | ||||
| Cupressinocladus |
C. interruptus |
Casts of conifer leaves are found in Hell Creek. Uncommon | ||||
| "Cypercites" | "C." sp | A reed-type plant. | 
| |||
| Dammarites | D. sp | A cone seed. It's likely to belong to Elatides longifolia. | ||||
| Ditaxocladus |
D. catenulata |
A cupressaceous conifer closely related to Cupressinocladus. Common. | Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |||
| "Dryophyllum" |
"D." subfalcatum |
This taxon is extremely common throughout the Hell Creek Formation, but is rare in Paleocene sediments. It is believed to be in Sabiaceae, closely relating to living genus Meliosma. [124][133] |

| |||
|
aff. "Dryophyllum" subfalcatum |
see above. |
|||||
|
"D." tenneseensis |
This taxon is similar to "D." subfalcatum but with extremely high L/W ratio and craspedodromous venation. [124] | |||||
| Elatides |
E. longifolia |
Araucaria-like or Cunninghamia-like conifer. Less common in the lower 2/3 but more common in the upper 1/3 of the Hell Creek Formation.[125] | 
| |||
| Erlingdorfia |
E. montana |
Johnson, 1996. In the Platanaceae (related to today's Sycamore). A very common taxon. |

| |||
| Equisetum | E. sp | Contrary to common belief, it's actually rare in Hell Creek. | 
| |||
|
"Ficus" |
"F." planicostata |
Despite the genus name, it's in Lauraceae. | ||||
|
Grewiopsis |
G. saportana |
Another generic Platanaceae. |

| |||
|
The only ginkgo in the Hell Creek Formation; uncommon |

| |||||
| Glyptostrobus | Uncommon conifer. | |||||
|
H. hydrocotyloidea |
Incertae sedis. May be related to lotus. An uncommon taxon. | |||||
|
aff. Humulus sp. |
May be related to the extant genus Humulus. | 
| ||||
|
Hydropteris |
H. pinnata |
Floating aquatic fern |

| |||
| Limnobiophyllum |
L. scutatum |
Floating aquatic monocot, closely related to Pistia. | 
| |||
|
L. bradacii |
Johnson, 1996. In the Magnoliidae: a common taxon. |

| ||||
|
"L." laramiense |
Unlobed leaf. May be related to today's tulip tree (yellow poplar). An uncommon taxon. | 
| ||||
|
L. sp |
Four-lobed leaf. May be related to today's tulip tree (yellow poplar). An uncommon taxon. |
|||||
|
Leepierceia |
L. preartocarpoides |
Incertae sedis but possibly in Proteales. Johnson, 1996. |

| |||
| Laurophyllum |
L. wardiana |
Large leaves. Closely related to "Dryophyllum" subfalcatum. | ||||
| "Magnolia" |
M. pulchra |
This species was thought to occur only in southern Wyoming flora, but Leo Hickey claims it is found further north in Montana and the Dakotas. |
||||
|
M. pealii |
Only known liverwort in Hell Creek. | |||||
| Marmarthia |
M. johnsonii |
A new Marmarthia species described in Peppe et. al. 2007. [134] | ||||
|
M. pearsonii |
Johnson, 1996. In the Lauraceae: a very common taxon. |
|||||
|
M. trivialis |
Johnson, 1996. In the Lauraceae: a very common taxon. |
|||||
|
M. occidentalis |
Casts of Dawn Redwood seed cones are known from the Hell Creek. |
|||||
|
"Myrica" |
"Myrica" torreyi |
Incertae sedis. Not actually a bayberry. | ||||
|
N. sp |
One of the most common aquatic plants in Hell Creek. | 
| ||||
| Nelumbium |
N. montanum |
An aquatic angiosperm, closely related to lotus. Uncommon. | ||||
|
N. yukonensis |
The only Hell Creek Formation cycadeoid. A simple leaf. Common. |

| ||||
| N. comtula | Unlike N. yukonensis, its leaves are pinnatisect pinnules. Common. | |||||
| Nordenskioldia |
N. borealis |
A fossil fruit that is likely to belong to Zizyphoides flabella. [135] |
||||
|
Paranymphaea |
P. hastata |
Despite the name, it's not related to extant genus Nymphaea. | ||||
| Palaeoaster |
P. inquirenda |
A poppy with quite similar seed pods and seeds to that of the extant poppy genus Romneya, though it's dubious. |

| |||
|
Penosphyllum |
P. cordatum |
May be related to Sterculiaceae. A common taxon. | ||||
|
Platanites |
P. marginata |
Johnson, 1996. In the Platanaceae. A common taxon. |

| |||
|
P. raynoldsii |
An uncommon taxon. | |||||
| Polypodiaceae? |
indeterminate |

| ||||
|
P. verrucosa |
A fossil fruit that may belong to Rutaceae.[136] | |||||
|
Rhamnica |
R. cleburnii |

| ||||
|
S. sp |
Coryphoid palm tree. Very common. |

| ||||
|
S. sp |
Floating aquatic plant. | 
| ||||
|
Spinifructus |
S. antiquus |
A fruit seed that may belong to the palm family (Arecaceae), closely related to the genus Astrocaryum.[137] |

| |||
|
T. olrikii |
Related to today's bald cypress. |

| ||||
|
Trapago |
T. angulata |
A water caltrop look-alike. |

| |||
|
Trochodendroides |
T. arctica |
A fossil fruit that may belong to Trochodendroides nebrascensis'. | ||||
| T. ellipticum | A katsura look-alike. An uncommon taxon. | |||||
| T. genetrix | A katsura look-alike. A common taxon. | |||||
|
T. nebrascensis |
A very common taxon. | 
| ||||
|
"Vitis" |
"V." stantonii |
Possibly a member of the Platanaceae rather than Vitaceae[125][138] |

| |||
|
"Z." fibrillosus |
A common taxon. | |||||
|
Zingiberopsis |
Z. attenuata |
Related to today's ginger plant. Its closest living relative is the Asian genus Alpinia. Some Hell Creek Formation specimens show damage from hispine beetles ("leaf beetles" (Wilf et al., 2000)). |
||||
| Z. magnifolia | Another Zinigberopsis species, previously assigned to Canna? magnifolia. | |||||
|
Zizyphoides |
Z. flabella |
An uncommon taxon. | ||||
See also
- List of fossil sites (with link directory)
- Lists of dinosaur-bearing stratigraphic units
- Paleobiota of the Morrison Formation
- Tremp Formation, Spain
- Tremp Formation, Spain
- Lefipán Formation, Argentina
- Lopez de Bertodano Formation, Antarctica
References
- ↑ DePalma, Robert; Cichocki, Frederich; Dierick, Manuel; Feeney, Robert (2010). "Preliminary Notes on the First Recorded Amber Insects from the Hell Creek Formation". The Journal of Paleontological Sciences 10: 1–7. https://aaps-journal.org/pdf/JPS-C-10-0001.pdf. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ↑ Nel, André; DePalma, Robert A.; Engel, Michael S. (2010). "A possible hemiphlebiid damselfly in Late Cretaceous amber from South Dakota (Odonata: Zygoptera)". Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science 113 (3/4): 231–234. doi:10.1660/062.113.0312.
- ↑ Messer, A'ndrea Eluse. "Leaf-mining insects destroyed with the dinosaurs, others quickly appeared". Pennsylvania State University. https://news.psu.edu/story/321434/2014/07/24/research/leaf-mining-insects-destroyed-dinosaurs-others-quickly-appeared.
- ↑ "North Dakota site shows wreckage from same object that killed the dinosaurs". University of Washington. https://www.washington.edu/news/2019/03/29/north-dakota-site-shows-wreckage-from-same-object-that-killed-the-dinosaurs/.
- ↑ Peterson, Douglas. "The Day the Dinosaurs Died". The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2019/04/08/the-day-the-dinosaurs-died.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Graf, Dan; Cummings, Kevin. "The Mussel Project". The University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point. http://mussel-project.uwsp.edu/fmuotwaolcb/.
- ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 7.15 7.16 7.17 7.18 7.19 7.20 7.21 7.22 7.23 7.24 7.25 7.26 7.27 7.28 7.29 7.30 7.31 7.32 7.33 7.34 7.35 7.36 7.37 7.38 7.39 7.40 7.41 7.42 7.43 7.44 7.45 7.46 7.47 7.48 Pearson et al. (2002) p. 154
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 8.18 8.19 8.20 8.21 8.22 8.23 8.24 8.25 8.26 8.27 8.28 8.29 8.30 8.31 8.32 8.33 8.34 8.35 Pearson et al. (2002) pp. 145–167
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 Pearson et al. (2002) p. 155
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 10.15 10.16 10.17 10.18 Pearson et al. (2002) pp. 156
- ↑ Listed as "cf. Barbourula sp." in "Class Amphibia," Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4.
- ↑ 12.00 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 12.08 12.09 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 12.14 12.15 "Class Amphibia," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 13.7 13.8 "Class Amphibia," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ Listed as "Eopelobates? sp." in "Class Amphibia," Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 David G. Demar Jr. (2013). "A new fossil salamander (Caudata, Proteidae) from the Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Hell Creek Formation, Montana, U.S.A". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 33 (3): 588–598. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.734887. Bibcode: 2013JVPal..33..588D.
- ↑ 16.00 16.01 16.02 16.03 16.04 16.05 16.06 16.07 16.08 16.09 16.10 16.11 16.12 16.13 16.14 16.15 "Class Osteichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 3.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 Hilton, Eric J.; Grande, Lance (2022-10-03). "Late Cretaceous sturgeons (Acipenseridae) from North America, with two new species from the Tanis site in the Hell Creek Formation of North Dakota". Journal of Paleontology 97 (1): 189–217. doi:10.1017/jpa.2022.81.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 18.7 "Class Osteichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 3. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 Sato, Hiroki; Murray, Alison M.; Vernygora, Oksana; Currie, Philip J. (4 July 2018). "A rare, articulated sturgeon (Chondrostei: Acipenseriformes) from the Upper Cretaceous of Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta, Canada". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 38 (4): (1)-(15). doi:10.1080/02724634.2018.1488137.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 "Class Osteichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 "Class Osteichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ Grande, Lance; Bemis, William E. (10 April 1998). "A Comprehensive Phylogenetic Study of Amiid Fishes (Amiidae) Based on Comparative Skeletal Anatomy. an Empirical Search for Interconnected Patterns of Natural History". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 18 (sup1): 1–696. doi:10.1080/02724634.1998.10011114. Bibcode: 1998JVPal..18S...1G.
- ↑ Grande, Lance (2010). "An Empirical Synthetic Pattern Study of Gars (lepisosteiformes) and Closely Related Species, Based Mostly on Skeletal Anatomy. the Resurrection of Holostei". Copeia 2010 (2A): iii–871.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Listed as "cf. Paralbula casei" in "Class Osteichthyes," Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 4.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 Hilton, Eric J.; During, Melanie A.D.; Grande, Lance; Ahlberg, Per E. (May 2023). "New paddlefishes (Acipenseriformes, Polyodontidae) from the Late Cretaceous Tanis Site of the Hell Creek Formation in North Dakota, USA". Journal of Paleontology 97 (3): 675–692. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.19. Bibcode: 2023JPal...97..675H.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Grande, Lance; Bemis, William E. (1991). "Osteology and Phylogenetic Relationships of Fossil and Recent Paddlefishes (Polyodontidae) with Comments on the Interrelationships of Acipenseriformes". Memoir (Society of Vertebrate Paleontology) 1: ii–121. doi:10.2307/3889328.
- ↑ 27.00 27.01 27.02 27.03 27.04 27.05 27.06 27.07 27.08 27.09 27.10 27.11 27.12 27.13 27.14 27.15 27.16 27.17 27.18 Todd D. Cook; Michael G. Newbrey; Donald B. Brinkman; James I. Kirkland (2014). "Euselachians from the freshwater deposits of the Hell Creek Formation of Montana". Through the End of the Cretaceous in the Type Locality of the Hell Creek Formation in Montana and Adjacent Areas. Geological Society of America Special Papers. 503. pp. 229–246. doi:10.1130/2014.2503(08). ISBN 978-0-8137-2503-1.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Terry A. Gates; Eric Gorscak; Peter J. Makovicky (2019). "New sharks and other chondrichthyans from the latest Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) of North America". Journal of Paleontology 93 (3): 512–530. doi:10.1017/jpa.2018.92. Bibcode: 2019JPal...93..512G.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Class Chondrichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 3.
- ↑ "Class Chondrichthyes," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 3. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ White, Paul; Fastovsky, David; Sheehan, Peter (1998). "Taphonomy and suggested structure of the dinosaurian assemblage of the Hell Creek Formation (Maastrichtian), eastern Montana and western North Dakota". PALAIOS 13 (1): 41. doi:10.2307/3515280. Bibcode: 1998Palai..13...41W. https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1080&context=cels_past_depts_facpubs.
- ↑ Manning, P. L.; Ott, C.; Falkingham, P. L. (2008). "The first tyrannosaurid track from the Hell Creek Formation (Late Cretaceous), Montana, U.S.A". PALAIOS 23 (10): 645–647. doi:10.2110/palo.2008.p08-030r. Bibcode: 2008Palai..23..645M.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Lockley, M.; Triebold, M.; Janke, P. R. (2014). "Dinosaur Tracks from the Hell Creek Formation (Upper Cretaceous, Maastrichtian), South Dakota". Fossil Footprints of Western North America: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 62: 459–468. https://econtent.unm.edu/digital/collection/bulletins/id/7309.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Carpenter, Kenneth; Breithaupt, Brent (2 September 1986). "Latest Cretaceous occurrence of nodosaurid ankylosaurs (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) in Western North America and the gradual extinction of the dinosaurs". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 6 (3): 251–257. doi:10.1080/02724634.1986.10011619. Bibcode: 1986JVPal...6..251C.
- ↑ Carpenter, K. (November 2002). "Late Cretaceous dinosaurs from the Denver Basin, Colorado". Rocky Mountain Geology 37 (2): 237–254. doi:10.2113/11. Bibcode: 2002RMGeo..37..237C. http://doc.rero.ch/record/14415/files/PAL_E1598.pdf.
- ↑ 36.00 36.01 36.02 36.03 36.04 36.05 36.06 36.07 36.08 36.09 36.10 36.11 36.12 36.13 36.14 36.15 36.16 36.17 36.18 36.19 36.20 36.21 36.22 36.23 36.24 36.25 36.26 36.27 36.28 36.29 36.30 36.31 36.32 36.33 36.34 36.35 36.36 36.37 36.38 36.39 36.40 36.41 36.42 "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; Montana)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 584.
- ↑ 37.00 37.01 37.02 37.03 37.04 37.05 37.06 37.07 37.08 37.09 37.10 "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; South Dakota)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 586.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 38.3 "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; North Dakota)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 585.
- ↑ Giffin, Emily B.; Gabriel, Diane L.; Johnson, Rolf E. (22 January 1988). "A New Pachycephalosaurid Hell Creek Formation of Montana". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 7 (4): 398–407. doi:10.1080/02724634.1988.10011672.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 40.3 Bakker et al. (2006)
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 41.3 41.4 Horner, John R.; Goodwin, Mark B.; Evans, David C. (28 October 2022). "A new pachycephalosaurid from the Hell Creek Formation, Garfield County, Montana, U.S.A.". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 42 (4). doi:10.1080/02724634.2023.2190369. Bibcode: 2022JVPal..42E0369H.
- ↑ Williamson, Thomas E.; Carr, Thomas D. (2003). "A new genus of derived pachycephalosaurian from western North America". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 22 (4): 779–801. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0779:ANGODP2.0.CO;2].
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 43.3 43.4 43.5 Woodruff, D. Cary; Schott, Ryan K.; Evans, David C. (November 2023). "Two new species of small-bodied pachycephalosaurine (Dinosauria, Marginocephalia) from the uppermost Cretaceous of North America suggest hidden diversity in well-sampled formations". Papers in Palaeontology 9 (6). doi:10.1002/spp2.1535.
- ↑ "Table 21.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 465.
- ↑ Carpenter, Kenneth (2006). Horns and Beaks: Ceratopsian and Ornithopod Dinosaurs. Indiana University Press. Project MUSE book 49401. ISBN 978-0-253-02795-5.[page needed]
- ↑ Ryan, Michael J.; Chinnery-Allgeier, Brenda J.; Eberth, David A. (2010). New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs: The Royal Tyrrell Museum Ceratopsian Symposium. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-35358-0.
- ↑ Scannella, John B.; Fowler, Denver W. (2014). "A stratigraphic survey of Triceratops localities in the Hell Creek Formation, northeastern Montana (2006–2010)". Through the End of the Cretaceous in the Type Locality of the Hell Creek Formation in Montana and Adjacent Areas. doi:10.1130/2014.2503(12).
- ↑ Scannella, B.; Fowler, W.; Goodwin, B.; Horner, R. (2014). Evolutionary Trends in Triceratops from the Hell Creek Formation, Montana (Project). doi:10.7934/p1099.
- ↑ Scannella, John (10 November 2020). "A chasmosaurine ceratopsid premaxilla from the basal sandstone of the Hell Creek Formation, Montana". Vertebrate Anatomy Morphology Palaeontology 8: 154–169. doi:10.18435/vamp29366.
- ↑ Biles, Jan. "Rare dinosaur skull being prepared for exhibition". Topeka Capital-Journal. http://cjonline.com/news-local/2015-09-07/rare-dinosaur-skull-being-prepared-exhibition.
- ↑ "Super-sized Ceratopsian Skull Might be New Species". 29 August 2015. https://blog.everythingdinosaur.co.uk/blog/_archives/2015/08/29/super-sized-ceratopsian-skull-might-be-new-species.html.
- ↑ O' Connell, Max (27 August 2015). "Dinosaur skull found in Buffalo likely a new species". http://rapidcityjournal.com/news/local/dinosaur-skull-found-in-buffalo-likely-a-new-species/article_b33d3375-b74c-5941-aa0b-281ad59b430a.html.
- ↑ Ostrom, John H. (May 1978). "Leptoceratops gracilis from the 'Lance' Formation of Wyoming". Journal of Paleontology 52 (3): 697–704.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 Christopher J. Ott and Peter L. Larson, 2010, "A New, Small Ceratopsian Dinosaur from the Latest Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation, Northwest South Dakota, United States: A Preliminary Description", In: Ryan, M.J., Chinnery-Allgeier, B.J., and Eberth, D.A. (eds.) New Perspectives on Horned Dinosaurs: The Royal Tyrrell Museum Ceratopsian Symposium, Bloomington, Indiana University Press, 656 pp.
- ↑ Nicholas R. Longrich (2011). "Titanoceratops ouranous, a giant horned dinosaur from the Late Campanian of New Mexico". Cretaceous Research 32 (3): 264–276. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2010.12.007. Bibcode: 2011CrRes..32..264L.
- ↑ Scannella, J.; Horner, J.R. (2010). "Torosaurus Marsh, 1891, is Triceratops Marsh, 1889 (Ceratopsidae: Chasmosaurinae): synonymy through ontogeny". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 30 (4): 1157–1168. doi:10.1080/02724634.2010.483632. Bibcode: 2010JVPal..30.1157S.
- ↑ Mallon, Jordan C; Holmes, Robert B; Bamforth, Emily L; Schumann, Dirk (7 May 2022). "The record of Torosaurus (Ornithischia: Ceratopsidae) in Canada and its taxonomic implications". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 195 (1): 157–171. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab120.
- ↑ Forster, Catherine A. (March 1993). "Taxomomic validity of the ceratopsid dinosaur Ugrosaurus olsoni (Cobabe and Fastovsky)". Journal of Paleontology 67 (2): 316–318. doi:10.1017/S0022336000032273. Bibcode: 1993JPal...67..316F.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 Scannella, John B.; Fowler, Denver W.; Goodwin, Mark B.; Horner, John R. (15 July 2014). "Evolutionary trends in Triceratops from the Hell Creek Formation, Montana". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111 (28): 10245–10250. doi:10.1073/pnas.1313334111. PMID 24982159. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..11110245S.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 Campione, N.E.; Evans, D.C. (2011). "Cranial Growth and Variation in Edmontosaurs (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae): Implications for Latest Cretaceous Megaherbivore Diversity in North America". PLOS ONE 6 (9): e25186. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025186. PMID 21969872. Bibcode: 2011PLoSO...625186C.
- ↑ Manning, Phillip L.; Morris, Peter M.; McMahon, Adam; Jones, Emrys; Gize, Andy; Macquaker, Joe H. S.; Wolff, George; Thompson, Anu et al. (7 October 2009). "Mineralized Soft-Tissue Structure and Chemistry in a Mummified Hadrosaur from the Hell Creek Formation, North Dakota (USA)". Proceedings: Biological Sciences 276 (1672): 3429–3437. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0812. PMID 19570788.
- ↑ Vajda, Vivi; Lyson, Tyler R.; Bercovici, Antonie; Doman, Jessman H.; Pearson, Dean A. (November 2013). "A snapshot into the terrestrial ecosystem of an exceptionally well-preserved dinosaur (Hadrosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous of North Dakota, USA". Cretaceous Research 46: 114–122. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2013.08.010. Bibcode: 2013CrRes..46..114V. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:nrm:diva-1409.
- ↑ Rohrer, W. L.; Konizeski, R. (May 1960). "On the Occurrence of Edmontosaurus in the Hell Creek Formation of Montana". 34 34 (3): 464–466.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Wosik, Mateusz; Goodwin, Mark B.; Evans, David C. (2 November 2017). "A nestling-sized skeleton of Edmontosaurus (Ornithischia, Hadrosauridae) from the Hell Creek Formation of northeastern Montana, U.S.A., with an analysis of ontogenetic limb allometry". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 37 (6): e1398168. doi:10.1080/02724634.2017.1398168. Bibcode: 2017JVPal..37E8168W. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/5899300.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Listed as "?Thescelosaurus garbanii" in "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; Montana)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 584.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 Boyd, Clint A.; Brown, Caleb Marshal; Scheetz, Rodney D.; Clarke, Julia A. (12 September 2009). "Taxonomic Revision of the Basal Neornithischian Taxa Thescelosaurus and Bugenasaura". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 29 (3): 758–770. doi:10.1671/039.029.0328. Bibcode: 2009JVPal..29..758B.
- ↑ Noted as being present, although misspelled as "Thescelosaurus garbani, in " "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; South Dakota)." Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 586.
- ↑ Boyd, Brown, et al. (2009)
- ↑ Galton, Peter M. (September 1974). "Notes on Thescelosaurus, a Conservative Ornithopod Dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of North America, with Comments on Ornithopod Classification". Journal of Paleontology 48 (5): 1048–1067.
- ↑ Manning, Phillip L.; Ott, Christopher; Falkingham, Peter L. (September–October 2008). "A Probable Tyrannosaurid Track from the Hell Creek Formation (Upper Cretaceous), Montana, United States". PALAIOS 23 (9/10): 645–647. doi:10.2110/palo.2008.p08-030r. Bibcode: 2008Palai..23..645M.
- ↑ Dalman, S.G.; Lucas, S.G.. "A new large Tyrannosaurid Alamotyrannus brinkmani, n. gen., n. sp. (Theropoda: Tyrannosauridae), from the Upper Cretaceous Ojo Alamo Formation (Naashoibito Member), San Juan Basin, New Mexico". New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin.
- ↑ Molnar, R.E. (January 1980). "An Albertosaur from the Hell Creek Formation of Montana". Journal of Paleontology 54 (1): 102–108.
- ↑ Molnar, R. E. (January 1978). "A New Theropod Dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of Central Montana". Journal of Paleontology 52 (1): 73–82.
- ↑ Hutchinson and Chiappe, 1998. The first known alvarezsaurid (Theropoda: Aves) from North America. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 18(3), 447–450.
- ↑ Horner, John R.; Goodwin, Mark B.; Myhrvold, Nathan (9 February 2011). "Dinosaur Census Reveals Abundant Tyrannosaurus and Rare Ontogenetic Stages in the Upper Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation (Maastrichtian), Montana, USA". PLOS ONE 6 (2): e16574. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016574. Bibcode: 2011PLoSO...616574H.
- ↑ Triebold, 1997. The Sandy Site: Small Dinosaurs from the Hell Creek Formation of South Dakota. in Wolberg, Stump and Rosenberg (eds). Dinofest International: Proceedings of a Symposium sponsored by Arizona
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 77.2 Longrich (2008), pages 983–996.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 78.2 78.3 78.4 78.5 Lamanna, M. C.; Sues, H. D.; Schachner, E. R.; Lyson, T. R. (2014). "A New Large-Bodied Oviraptorosaurian Theropod Dinosaur from the Latest Cretaceous of Western North America". PLOS ONE 9 (3): e92022. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092022. PMID 24647078. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...992022L.
- ↑ Stein, Walter W. (2019). "TAKING COUNT: A Census of Dinosaur Fossils Recovered From the Hell Creek and Lance Formations (Maastrichtian).". The Journal of Paleontological Sciences 8: 1–42. https://www.aaps-journal.org/pdf/JPS.C.2019.01a.pdf.
- ↑ Schachner, Emma; Larson, Tyler; Hanks, Harold. A preliminary report of a new specimen of Chirostenotes (Oviraptorosauria: Theropoda) from the Hell Creek Formation of North Dakota (Report). in "Abstracts of Papers". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26: 1–152. 2006. doi:10.1080/02724634.2006.10010069. Bibcode: 2006JVPal..26S...1..
- ↑ Russel, Dale A.; Manabe, Makoto (2002). "Synopsis of the Hell Creek (uppermost Cretaceous) dinosaur assemblage.". Geological Society of America Special Papers 361: 169–176. ISBN 9780813723617. https://books.google.com/books?id=cHvcIeh2f84C&dq=Hell+Creek+Chirostenotes&pg=PA169. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- ↑ Benner, Elizabeth K. C.; Cullen, T. M.; Evans, D. C. (May 18–21, 2016). "MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF A NEW LARGE-BODIED 10 CAENAGNATHID SPECIMEN (THEROPODA: OVIRAPTOROSAURIA) FROM THE HELL CREEK FORMATION (MONTANA)". Canadian Society of Vertebrate Paleontology: 17–18. https://cansvp.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/csvp-2016-abstract-book-compressed.pdf. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 Atkins-Weltman, K. L.; Simon, D. J.; Woodward, H. N.; Funston, G. F.; Snively, E. (2024). "A new oviraptorosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the end-Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of North America". PLOS ONE 19 (1): e0294901. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0294901. PMID 38266012.
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 84.2 84.3 84.4 84.5 84.6 84.7 84.8 Evans, D. C.; Larson, D. W.; Currie, P. J. (2013). "A new dromaeosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) with Asian affinities from the latest Cretaceous of North America". Naturwissenschaften 100 (11): 1041–9. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1107-5. PMID 24248432. Bibcode: 2013NW....100.1041E.
- ↑ Russel, Dale A.; Manabe, Makoto (2002). "Synopsis of the Hell Creek (uppermost Cretaceous) dinosaur assemblage.". Geological Society of America Special Papers 361: 169–176. ISBN 9780813723617. https://books.google.com/books?id=cHvcIeh2f84C&dq=Hell+Creek+Dromaeosaurus&pg=PA169. Retrieved 23 October 2020.
- ↑ Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous; North America; North Dakota). Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 585
- ↑ 87.00 87.01 87.02 87.03 87.04 87.05 87.06 87.07 87.08 87.09 87.10 87.11 87.12 87.13 87.14 87.15 87.16 87.17 87.18 87.19 87.20 87.21 87.22 87.23 87.24 87.25 Longrich, N.R.; Tokaryk, T.; Field, D.J. (2011). "Mass extinction of birds at the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108 (37): 15253–15257. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110395108. PMID 21914849. Bibcode: 2011PNAS..10815253L.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 88.2 Stidham, 1999. North American avisaurids (Aves: Enantiornithes): New data on morphology and phylogeny. VII International Symposium on Mesozoic Terrestrial Ecosystems, abstracts.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 89.3 89.4 89.5 89.6 89.7 Larry D. Martin; Evgeny N. Kurochkin; Tim T. Tokaryk (2012). "A new evolutionary lineage of diving birds from the Late Cretaceous of North America and Asia". Palaeoworld 21: 59–63. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2012.02.005.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 90.2 90.3 90.4 90.5 90.6 90.7 Bakker, Robert T.; Larson, Peter L.; Martin, Larry D.; Burnham, David A.; DePalma, Robert A. (30 October 2015). "The first giant raptor (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Hell Creek Formation". Paleontological Contributions 14: 1–16. doi:10.17161/paleo.1808.18764.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 91.2 91.3 Olshevsky, G., 1991, A Revision of the Parainfraclass Archosauria Cope, 1869, Excluding the Advanced Crocodylia. Mesozoic Meanderings 2 pp 196
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 Carpenter, K. (1982). "Baby dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Lance and Hell Creek formations and a description of a new species of theropod". Contributions to Geology, University of Wyoming 20 (2): 123–134. http://doc.rero.ch/record/232469/files/PAL_E4465.pdf.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 93.2 Elzanowski, A.; Paul, G.S.; Stidham, T.A. (2001). "An avian quadrate from the Late Cretaceous Lance Formation of Wyoming". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 20 (4): 712–719. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2000)020[0712:aaqftl2.0.co;2].
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Estes, Richard (1964). Fossil vertebrates from the late Cretaceous Lance formation, eastern Wyoming. University of California Press. OCLC 3753287.[page needed]
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 Larson, Derek W.; Currie, Philip J. (23 January 2013). "Multivariate Analyses of Small Theropod Dinosaur Teeth and Implications for Paleoecological Turnover through Time". PLOS ONE 8 (1): e54329. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054329. PMID 23372708. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...854329L.
- ↑ Stidham, Thomas Allen (2001). The origin and ecological diversification of modern birds: Evidence from the extinct wading ducks, Presbyornithidae (Neornithes: Anseriformes) (Thesis). OCLC 892837810. ProQuest 304684225.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 "Class Aves," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 7.
- ↑ "Class Aves," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 7. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 99.2 Henderson, Michael; Peterson, Joseph (30 March 2006). "An Azhdarchid Pterosaur Cervical Vertebra from the Hell Creek Formation (Maastrichtian) of Southeastern Montana". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26 (1): 192–195. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[192:AAPCVF2.0.CO;2]. http://doc.rero.ch/record/15687/files/PAL_E2073.pdf.
- ↑ Averianov, Alexander (11 August 2014). "Review of taxonomy, geographic distribution, and paleoenvironments of Azhdarchidae (Pterosauria)". ZooKeys (432): 1–107. doi:10.3897/zookeys.432.7913. PMID 25152671. Bibcode: 2014ZooK..432....1A.
- ↑ Longrich, Nicholas; Martill, David; Andres, Brian (13 March 2018). "Late Maastrichtian pterosaurs from North Africa and mass extinction of Pterosauria at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary". PLOS Biology 16 (3): e2001663. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.2001663. PMID 29534059.
- ↑ Longrich, Nicholas; Martill, David; Andres, Brian (11 April 2018). "Correction: Late Maastrichtian pterosaurs from North Africa and mass extinction of Pterosauria at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary". PLOS Biology 16 (4): e1002627. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002627. PMID 29641516.
- ↑ "New Hell Creek Pterosaur Species". http://trieboldpaleontology.com/hellcreekpterosaur.html.
- ↑ 104.0 104.1 104.2 104.3 104.4 104.5 104.6 104.7 R. Matsumoto; S. E. Evans (2010). "Choristoderes and the freshwater assemblages of Laurasia". Journal of Iberian Geology 36 (2): 253–274. doi:10.5209/rev_jige.2010.v36.n2.11. Bibcode: 2010JIbG...36..253M. http://revistas.ucm.es/index.php/JIGE/article/view/33860.
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 105.2 105.3 105.4 105.5 105.6 105.7 "Order Testudinata," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 5.
- ↑ 106.0 106.1 106.2 106.3 "Order Testudinata," in Estes and Berberian, (1970). Page 5. All taxa listed occur in Montana, see page 1.
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 107.2 Walter G. Joyce; Donald B. Brinkman; Tyler R. Lyson (2019). "A new species of trionychid turtle, Axestemys infernalis sp. nov., from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Hell Creek and Lance formations of the Northern Great Plains, USA". Palaeontologia Electronica 22 (3): Article number 22.3.72. doi:10.26879/949.
- ↑ Arbour, Victoria M.; Zanno, Lindsay E.; Larson, Derek W.; Evans, David C.; Sues, Hans-Dieter (9 February 2016). "The furculae of the dromaeosaurid dinosaur Dakotaraptor steini are trionychid turtle entoplastra". PeerJ 4: e1691. doi:10.7717/peerj.1691. PMID 26893972.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 109.2 109.3 109.4 Georgia E. Knauss; Walter G. Joyce; Tyler R. Lyson; Dean Pearson (2011). "A new kinosternoid from the Late Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation of North Dakota and Montana and the origin of the Dermatemys mawii lineage". Paläontologische Zeitschrift 85 (2): 124–142. doi:10.1007/s12542-010-0081-x. Bibcode: 2011PalZ...85..125K.
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 110.2 110.3 110.4 "Cretaceous-Period Softshell Turtle Lived alongside Giant Dinosaurs | Sci-News.com" (in en-US). 14 March 2022. http://www.sci-news.com/paleontology/hutchemys-walkerorum-10616.html.
- ↑ Tyler R. Lyson; Jacob L. Sayler; Walter G. Joyce (2019). "A new baenid turtle, Saxochelys gilberti, gen. et sp. nov., from the uppermost Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Hell Creek Formation: sexual dimorphism and spatial niche partitioning within the most speciose group of Late Cretaceous turtles". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 39 (4): e1662428. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1662428. Bibcode: 2019JVPal..39E2428L. https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/A_new_baenid_turtle_i_Saxochelys_gilberti_i_gen_et_sp_nov_from_the_uppermost_Cretaceous_Maastrichtian_Hell_Creek_Formation_sexual_dimorphism_and_spatial_niche_partitioning_within_the_most_speciose_group_of_Late_Cretaceous_turtles/9944129.
- ↑ "Fossils may capture the day the dinosaurs died. Here's what you should know." (in en). 2019-03-31. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/fossils-found-from-day-dinosaurs-died-chicxulub-tanis-cretaceous-extinction.
- ↑ Van Vranken, Nathan E.; Boyd, Clint A. (21 August 2021). "The first in situ collection of a mosasaurine from the marine Breien Member of the Hell Creek Formation in south-central North Dakota, USA". PaleoBios 38 (1). doi:10.5070/P938054460.
- ↑ 114.00 114.01 114.02 114.03 114.04 114.05 114.06 114.07 114.08 114.09 114.10 114.11 114.12 114.13 114.14 114.15 Nicholas R. Longrich; Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar; Jacques A. Gauthier (2012). "Mass extinction of lizards and snakes at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109 (52): 21396–21401. doi:10.1073/pnas.1211526110. PMID 23236177. Bibcode: 2012PNAS..10921396L.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 115.2 115.3 115.4 115.5 Nicholas R. Longrich; Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar; Jacques A. Gauthier (2013). "Correction for "Mass extinction of lizards and snakes at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary," by Nicholas R. Longrich, Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar, and Jacques A. Gauthier, which appeared in issue 52, December 26, 2012, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (109:21396–21401; first published December 10, 2012; 10.1073/pnas.1211526110)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110 (16): 6608. doi:10.1073/pnas.1303907110. Bibcode: 2013PNAS..110Q6608..
- ↑ 116.00 116.01 116.02 116.03 116.04 116.05 116.06 116.07 116.08 116.09 116.10 116.11 116.12 116.13 116.14 116.15 116.16 116.17 116.18 116.19 116.20 116.21 116.22 116.23 116.24 116.25 116.26 116.27 116.28 116.29 116.30 116.31 116.32 116.33 116.34 116.35 116.36 116.37 116.38 116.39 116.40 116.41 116.42 116.43 116.44 116.45 116.46 116.47 116.48 116.49 116.50 116.51 116.52 116.53 116.54 116.55 116.56 116.57 116.58 116.59 116.60 116.61 116.62 116.63 116.64 116.65 116.66 116.67 116.68 116.69 116.70 116.71 116.72 116.73 116.74 116.75 116.76 116.77 116.78 116.79 116.80 116.81 116.82 116.83 116.84 116.85 116.86 116.87 116.88 116.89 116.90 Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, Richard L. Cifelli, and Zhe-Xi Luo, Mammals from the Age of Dinosaurs: Origins, Evolution, and Structure, Columbia University Press, New York, 2004 ISBN 0-231-11918-6, p. 98-99
- ↑ 117.0 117.1 117.2 117.3 117.4 Gregory P. Wilson (2013). "Mammals across the K/Pg boundary in northeastern Montana, U.S.A.: dental morphology and body-size patterns reveal extinction selectivity and immigrant-fueled ecospace filling". Paleobiology 39 (3): 429–469. doi:10.1666/12041. Bibcode: 2013Pbio...39..429W.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 118.2 118.3 118.4 118.5 118.6 J. David Archibald; Yue Zhang; Tony Harper; Richard L. Cifelli (2011). "Protungulatum, confirmed Cretaceous occurrence of an otherwise Paleocene eutherian (placental?) mammal". Journal of Mammalian Evolution 18 (3): 153–161. doi:10.1007/s10914-011-9162-1.
- ↑ Davis, B. M. (2007). "A revision of 'pediomyid' marsupials from the Late Cretaceous of North America". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 2 (52). https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.agro-article-dd7126e7-9923-4ef2-870f-f8f654995651.
- ↑ Thomas E. Williamson; Stephen L. Brusatte; Thomas D. Carr; Anne Weil; Barbara R. Standhardt (2012). "The phylogeny and evolution of Cretaceous–Palaeogene metatherians: cladistic analysis and description of new early Palaeocene specimens from the Nacimiento Formation, New Mexico". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 10 (4): 625–651. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.631592. Bibcode: 2012JSPal..10..625W.
- ↑ Fox, Richard C. (December 2015). "A revision of the Late Cretaceous–Paleocene eutherian mammal Cimolestes Marsh, 1889". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 52 (12): 1137–1149. doi:10.1139/cjes-2015-0113. Bibcode: 2015CaJES..52.1137F.
- ↑ Fastovsky, David E.; McSWEENEY, Kevin (1987). "Paleosols spanning the Cretaceous-Paleogene transition, eastern Montana and western North Dakota". Geological Society of America Bulletin 99 (1): 66. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1987)99<66:PSTCTE>2.0.CO;2. Bibcode: 1987GSAB...99...66F.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk R.; Hickey, Leo J. (1990). "Megafloral change across the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary in the northern Great Plains and Rocky Mountains, U.S.A.". Global Catastrophes in Earth History; an Interdisciplinary Conference on Impacts, Volcanism, and Mass Mortality. Geological Society of America Special Papers. 247. pp. 433–444. doi:10.1130/SPE247-p433. ISBN 0-8137-2247-0.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 124.2 124.3 124.4 124.5 124.6 124.7 Johnson, Kirk Richard (1989). A high-resolution megafloral biostratigraphy spanning the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in the northern Great Plains (Thesis).[page needed]
- ↑ 125.0 125.1 125.2 125.3 125.4 Johnson, Kirk R. (2002). "Megaflora of the Hell Creek and lower Fort Union Formations in the western Dakotas: Vegetational response to climate change, the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary event, and rapid marine transgression". The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary Boundary in the Northern Great Plains: An Integrated Continental Record of the End of the Cretaceous. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2361-2.329. ISBN 9780813723617.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk R.; Nichols, Douglas J.; Attrep, Moses; Orth, Charles J. (August 1989). "High-resolution leaf-fossil record spanning the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary". Nature 340 (6236): 708–711. doi:10.1038/340708a0. Bibcode: 1989Natur.340..708J.
- ↑ Barnet, James S.K.; Littler, Kate; Kroon, Dick; Leng, Melanie J.; Westerhold, Thomas; Röhl, Ursula; Zachos, James C. (1 February 2018). "A new high-resolution chronology for the late Maastrichtian warming event: Establishing robust temporal links with the onset of Deccan volcanism". Geology 46 (2): 147–150. doi:10.1130/G39771.1. Bibcode: 2018Geo....46..147B.
- ↑ Retallack, Gregory J. (November 1994). "A pedotype approach to latest Cretaceous and earliest Tertiary paleosols in eastern Montana". Geological Society of America Bulletin 106 (11): 1377–1397. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1994)106<1377:APATLC>2.3.CO;2. Bibcode: 1994GSAB..106.1377R.
- ↑ "Cruisin' the fossil freeway : an epoch tale of a scientist and an artist on the ultimate 5,000-mile paleo road trip | WorldCat.org" (in en). https://search.worldcat.org/title/125404857.
- ↑ Manchester, Steven R.; O'Leary, Elizabeth L. (2010). "Phylogenetic Distribution and Identification of Fin-winged Fruits". Botanical Review 76 (1): 1–82. doi:10.1007/s12229-010-9041-0. Bibcode: 2010BotRv..76....1M.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk R. (2002). "Megaflora of the Hell Creek and lower Fort Union Formations in the western Dakotas: Vegetational response to climate change, the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary event, and rapid marine transgression". The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in the northern Great Plains: An Integrated continental record of the end of the Cretaceous. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2361-2.329. ISBN 978-0-8137-2361-7.
- ↑ Stockey, Ruth A.; Rothwell, Gar W.; Johnson, Kirk R. (October 2016). "Evaluating Relationships among Floating Aquatic Monocots: A New Species of Cobbania (Araceae) from the Upper Maastrichtian of South Dakota" (in en). International Journal of Plant Sciences 177 (8): 706–725. doi:10.1086/688285.
- ↑ Peppe, Daniel J.; Hickey, Leo J. (October 2014). "Fort Union Formation Fossil Leaves (Paleocene, Williston Basin, North Dakota, USA) Indicate Evolutionary Relationships Between Paleocene and Eocene Plant Species". Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History 55 (2): 171–189. doi:10.3374/014.055.0209.
- ↑ Peppe, Daniel J.; Erickson, J. Mark; Hickey, Leo J. (May 2007). "Fossil leaf species from the Fox Hills Formation (Upper Cretaceous: North Dakota, USA) and their paleogeographic significance". Journal of Paleontology 81 (3): 550–567. doi:10.1666/05067.1. Bibcode: 2007JPal...81..550P.
- ↑ Crane, Peter R.; Manchester, Steven R.; Dilcher, David L. (October 1991). "Reproductive and Vegetative Structure of Nordenskioldia (Trochodendraceae), A Vesselless Dicotyledon from the Early Tertiary of the Northern Hemisphere". American Journal of Botany 78 (10): 1311–1334. doi:10.1002/j.1537-2197.1991.tb12599.x.
- ↑ Manchester, Steven R.; Kodrul, Tatyana M. (June 2014). "Morphology, affinities and phytogeographic history of Porosia Hickey in the Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America and Asia". Acta Palaeobotanica 54 (1): 77–99. doi:10.2478/acpa-2014-0002.
- ↑ McIver, Elisabeth E (February 2002). "The paleoenvironment of Tyrannosaurus rex from southwestern Saskatchewan, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 39 (2): 207–221. doi:10.1139/e01-073. Bibcode: 2002CaJES..39..207M.
- ↑ Arens, Nan Crystal; Allen, Sarah E. (1 January 2014). "A florule from the base of the Hell Creek Formation in the type area of eastern Montana: Implications for vegetation and climate". Through the End of the Cretaceous in the Type Locality of the Hell Creek Formation in Montana and Adjacent Areas. doi:10.1130/2014.2503(06). ISBN 9780813725031.
Bibliography
- General
- Lua error in Module:Cite_LSA at line 99: attempt to concatenate local 'year' (a nil value).
- Preston, Douglas. 2019. The Day the Dinosaurs Died, 1. The New Yorker. Accessed 2019-04-01.
- U.S. National, Park Service. 1966. National Natural Landmarks - National Natural Landmarks (U.S. National Park Service), 1. www.nps.gov. Accessed 2019-03-22.
- Geology
- DePalma, Smit J, Burnham DA, Kuiper K, Manning PL, Oleinik A, Larson P, Maurrasse FJ, Vellekoop J, Richards MA, Gurche L and Walter Alvarez W, R.A. 2019. A seismically induced onshore surge deposit at the K-Pg boundary, North Dakota. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 116. 8190–8199. Accessed 2020-03-30. doi:10.1073/pnas.1817407116 PMID 30936306 PMC 6486721 Bibcode: 2019PNAS..116.8190D
- Evans, D.C.; D.W. Larson, and P.J. Currie. 2013. A new dromaeosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) with Asian affinities from the latest Cretaceous of North America. Naturwissenschaften 100. 1041–1049. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1107-5 Bibcode: 2013NW....100.1041E PMID 24248432
- Husson, D.; B. Galbrun; J. Laskar; L.A. Hinnov; N. Thibault; S. Gardin, and R.E. Locklair. 2011. Astronomical calibration of the Maastrichtian (late Cretaceous). Earth and Planetary Science Letters 305. 328–340. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.03.008 Bibcode: 2011E&PSL.305..328H
- LeCain, Rebecca. 2010. Magnetostratigraphy of the Hell Creek and lower Fort Union formations in northeast Montana, 1. Master's Theses and Capstones. Accessed 2020-03-30.
- Johnson, K.R.; D.J. Nichols, and J.H. Hartman. 2002. Hell Creek Formation: A 2001 synthesis. The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary Boundary in the northern Great Plains. Geological Society of America Special Paper 361. 503–510.
- Paleontology
- DePalma, Robert. 2010. Preliminary Notes on the First Recorded Amber Insects from the Hell Creek Formation. The Journal of Paleontological Sciences x. x. Accessed 2019-02-21.
- Boyd, Clint A.; Caleb M. Brown; Rodney D. Scheetz, and Julia A. Clarke. 2009. Taxonomic revision of the basal neornithischian taxa Thescelosaurus and Bugenasaura. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 29. 758–770. doi:10.1671/039.029.0328
- Longrich, N. 2008. A new, large ornithomimid from the Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada: Implications for the study of dissociated dinosaur remains. Palaeontology 54. 983–996. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00791.x
- Manning, P.L.; C. Ott, and P.L. Falkingham. 2008. The first tyrannosaurid track from the Hell Creek Formation (Late Cretaceous), Montana, U.S.A. PALAIOS 23. 645–647. doi:10.2110/palo.2008.p08-030r Bibcode: 2008Palai..23..645M
- Bakker, R.T.; R.M. Sullivan; V. Porter; P. Larson, and S.J. Saulsbury. 2006. Dracorex hogwartsia, n. gen., n. sp., a spiked, flat-headed pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation of South Dakota in Lucas, S. G. and Sullivan, R. M., eds., Late Cretaceous vertebrates from the Western Interior. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 35. 331–354. Accessed 1907-10-31.
- Henderson, M.D., and J.E. Peterson. 2006. [192:AAPCVF2.0.CO;2 An azhdarchid pterosaur cervical vertebra from the Hell Creek Formation (Maastrichtian) of southeastern Montana]. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26. 192–195.
- Weishampel, David B.; Peter Dodson, and Halszka Osmólska (eds.). 2004. The Dinosauria, 2nd edition, 1–880. Berkeley: University of California Press. Accessed 2019-02-21. ISBN 0-520-24209-2
- Pearson, D.A.; T. Schaefer; K.R. Johnson; D.J. Nichols, and J.P. Hunter. 2002. The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in the northern Great Plains: An integrated continental record of the end of the Cretaceous. Vertebrate Biostratigraphy of the Hell Creek Formation in Southwestern North Dakota and Northwestern South Dakota, Geological Society of America Special Paper 361. 145–167. Accessed 2019-03-22. ISBN 9780813723617
- Varricchio, D.J. 2001. Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Theropoda) dinosaurs from Montana, 42–57. D. H. Tanke and K. Carpenter (eds.), Mesozoic Vertebrate Life. Indiana University Press, Indianapolis, Indiana.
- Currie, P.J., and K. Padian. 1997. The Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs, 1–901. Academic Press. Accessed 2020-03-30. ISBN 978-0-122-26810-6
- Eberth, D.A. (1997). Edmonton Group. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 199–204. ISBN 978-0-122-26810-6. https://archive.org/details/encyclopediadino00curr_075.
- Lofgren, D.F. (1997). Hell Creek Formation. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 302–303. ISBN 978-0-122-26810-6. https://archive.org/details/encyclopediadino00curr_075.
- Breithaupt, B.H (1997). Lance Formation. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 394–395. ISBN 978-0-122-26810-6. https://archive.org/details/encyclopediadino00curr_075.
- Christophel, D.C.. 1976. Fossil floras from the Smoky Tower locality, Alberta, Canada. Palaeontographica, Abt. B 157. x.
- Chandrasekharam, A.. 1974. Megafossil flora from the Genesee locality, Alberta, Canada. Palaeontographica, Abt. A 174. x.
- Estes, R., and P. Berberian. 1970. Paleoecology of a late Cretaceous vertebrate community from Montana. Breviora 343. 1.
External links
- Cretaceous Hell Creek Faunal Facies provides a faunal list
- Phillip Bigelow, "Hell Creek life: Fossil Flora & Fauna, a Paleoecosystem"
- Paleobiology Database: MPM locality 3850 (Hell Creek Formation): Maastrichtian, Montana
 |