Medicine:Sciatica
Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back.[1] This pain may extend down the back, outside, or front of the leg.[2] Onset is often sudden following activities such as heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur.[3] The pain is often described as shooting.[1] Typically, symptoms occur on only one side of the body;[2] certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides.[2] Lower back pain is sometimes present.[2] Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot.[2]
About 90% of sciatica is due to a spinal disc herniation pressing on one of the lumbar or sacral nerve roots.[4] Spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, piriformis syndrome, pelvic tumors, and pregnancy are other possible causes of sciatica.[2] The straight-leg-raising test is often helpful in diagnosis.[2] The test is positive if, when the leg is raised while a person is lying on their back, pain shoots below the knee.[2] In most cases medical imaging is not needed.[5] However, imaging may be obtained if bowel or bladder function is affected, there is significant loss of feeling or weakness, symptoms are long standing, or there is a concern for tumor or infection.[5] Conditions that can present similarly are diseases of the hip and infections such as early shingles (prior to rash formation).[2]
Initial treatment typically involves pain medications.[5] However, evidence for effectiveness of pain medication, and of muscle relaxants, is lacking.[6] It is generally recommended that people continue with normal activity to the best of their abilities.[2] Often all that is required for resolution of sciatica is time; in about 90% of cases, symptoms resolve in less than six weeks.[5] If the pain is severe and lasts for more than six weeks, surgery may be an option.[5] While surgery often speeds pain improvement, its long term benefits are unclear.[2] Surgery may be required if complications occur, such as loss of normal bowel or bladder function.[5] Many treatments, including corticosteroids, gabapentin, pregabalin, acupuncture, heat or ice, and spinal manipulation, have only limited or poor evidence supporting their use.[2][7][8]
Depending on how it is defined, less than 1% to 40% of people have sciatica at some point in time.[4][9] Sciatica is most common between the ages of 40 and 59, and men are more frequently affected than women.[5][2] The condition has been known since ancient times.[2] The first known modern use of the word sciatica dates from 1451,[10] although Dioscorides (1st-century CE) mentions it in his Materia Medica.[11]
Definition
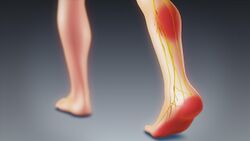
The term "sciatica" usually describes a symptom—pain along the sciatic nerve pathway—rather than a specific condition, illness, or disease.[4] Some use it to mean any pain starting in the lower back and going down the leg.[4] The pain is characteristically described as shooting or shock-like, quickly traveling along the course of the affected nerves.[12] Others use the term as a diagnosis (i.e. an indication of cause and effect) for nerve dysfunction caused by compression of one or more lumbar or sacral nerve roots from a spinal disc herniation.[4] Pain typically occurs in the distribution of a dermatome and goes below the knee to the foot.[4][6] It may be associated with neurological dysfunction, such as weakness and numbness.[4]
Causes
Risk factors
Modifiable risk factors for sciatica include smoking, obesity, occupation,[9] and physical sports where back muscles and heavy weights are involved. Non-modifiable risk factors include increasing age, being male, and having a personal history of low back pain.[9]
Spinal disc herniation
Spinal disc herniation pressing on one of the lumbar or sacral nerve roots is the most frequent cause of sciatica, being present in about 90% of cases.[4] This is particularly true in those under age 50.[13] Disc herniation most often occurs during heavy lifting.[14] Pain typically increases when bending forward or sitting, and reduces when lying down or walking.[13]
Spinal stenosis
Other compressive spinal causes include lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition in which the spinal canal, the space the spinal cord runs through, narrows and compresses the spinal cord, cauda equina, or sciatic nerve roots.[15] This narrowing can be caused by bone spurs, spondylolisthesis, inflammation, or a herniated disc, which decreases available space for the spinal cord, thus pinching and irritating nerves from the spinal cord that become the sciatic nerve.[15] This is the most frequent cause after age 50.[13] Sciatic pain due to spinal stenosis is most commonly brought on by standing, walking, or sitting for extended periods of time, and reduces when bending forward.[13][15] However, pain can arise with any position or activity in severe cases.[15] The pain is most commonly relieved by rest.[15]
Piriformis syndrome
Piriformis syndrome is a condition that, depending on the analysis, varies from a "very rare" cause to contributing up to 8% of low back or buttock pain.[16] In 17% of people, the sciatic nerve runs through the piriformis muscle rather than beneath it.[15] When the piriformis shortens or spasms due to trauma or overuse, it is posited that this causes compression of the sciatic nerve.[16] Piriformis syndrome has colloquially been referred to as "wallet sciatica" since a wallet carried in a rear hip pocket compresses the buttock muscles and sciatic nerve when the bearer sits down. Piriformis syndrome may be suspected as a cause of sciatica when the spinal nerve roots contributing to the sciatic nerve are normal and no herniation of a spinal disc is apparent.[17][18]
Deep gluteal syndrome
Deep gluteal syndrome is non-discogenic, extrapelvic sciatic nerve entrapment in the deep gluteal space.[19] Piriformis syndrome was once the traditional model of sciatic nerve entrapment in this anatomic region. The understanding of non-discogenic sciatic nerve entrapment has changed significantly with improved knowledge of posterior hip anatomy, nerve kinematics, and advances in endoscopic techniques to explore the sciatic nerve.[20][21] There are now many known causes of sciatic nerve entrapment, such as fibrous bands restricting nerve mobility, that are unrelated to the piriformis in the deep gluteal space. Deep gluteal syndrome was created as an improved classification for the many distinct causes of sciatic nerve entrapment in this anatomic region.[21] Piriformis syndrome is now considered one of many causes of deep gluteal syndrome.[20]
Endometriosis
Sciatic endometriosis, also called catamenial or cyclical sciatica, is a sciatica whose cause is endometriosis. Its incidence is unknown. Diagnosis is usually made by an MRI or CT-myelography.[22]
Pregnancy
Sciatica may also occur during pregnancy, especially during later stages, as a result of the weight of the fetus pressing on the sciatic nerve during sitting or during leg spasms.[15] While most cases do not directly harm the woman or the fetus, indirect harm may come from the numbing effect on the legs, which can cause loss of balance and falls. There is no standard treatment for pregnancy-induced sciatica.[23]
Other
Pain that does not improve when lying down suggests a nonmechanical cause, such as cancer, inflammation, or infection.[13] Sciatica can be caused by tumors impinging on the spinal cord or the nerve roots.[4] Severe back pain extending to the hips and feet, loss of bladder or bowel control, or muscle weakness may result from spinal tumors or cauda equina syndrome.[15] Trauma to the spine, such as from a car accident or hard fall onto the heel or buttocks, may also lead to sciatica.[15] A relationship has been proposed with a latent Cutibacterium acnes infection in the intervertebral discs, but the role it plays is not yet clear.[24][25]
Pathophysiology
The sciatic nerve comprises nerve roots L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3 in the spine.[26] These nerve roots merge in the pelvic cavity to form the sacral plexus and the sciatic nerve branches from that. Sciatica symptoms can occur when there is pathology anywhere along the course of these nerves.[27]
Intraspinal sciatica
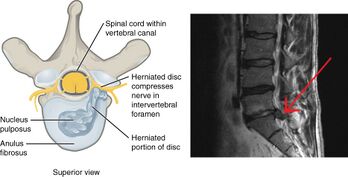
Intraspinal, or discogenic sciatica refers to sciatica whose pathology involves the spine. In 90% of sciatica cases, this can occur as a result of a spinal disc bulge or herniation.[14][28] Sciatica is generally caused by the compression of lumbar nerves L4 or L5 or sacral nerve S1.[29] Less commonly, sacral nerves S2 or S3 may cause sciatica.[29]
Intervertebral spinal discs consist of an outer anulus fibrosus and an inner nucleus pulposus.[14] The anulus fibrosus forms a rigid ring around the nucleus pulposus early in human development, and the gelatinous contents of the nucleus pulposus are thus contained within the disc.[14] Discs separate the spinal vertebrae, thereby increasing spinal stability and allowing nerve roots to properly exit through the spaces between the vertebrae from the spinal cord.[30] As an individual ages, the anulus fibrosus weakens and becomes less rigid, making it at greater risk for tear.[14] When there is a tear in the anulus fibrosus, the nucleus pulposus may extrude through the tear and press against spinal nerves within the spinal cord, cauda equina, or exiting nerve roots, causing inflammation, numbness, or excruciating pain.[31] Inflammation of spinal tissue can then spread to adjacent facet joints and cause facet syndrome, which is characterized by lower back pain and referred pain in the posterior thigh.[14]
Other causes of sciatica secondary to spinal nerve entrapment include the roughening, enlarging, or misalignment (spondylolisthesis) of vertebrae, or disc degeneration that reduces the diameter of the lateral foramen through which nerve roots exit the spine.[14] When sciatica is caused by compression of a dorsal nerve root, it is considered a lumbar radiculopathy or radiculitis when accompanied by an inflammatory response.[15]
Extraspinal sciatica

The sciatic nerve is highly mobile during hip and leg movements.[32][33] Any pathology which restricts normal movement of the sciatic nerve can put abnormal pressure, strain, or tension on the nerve in certain positions or during normal movements. For example, the presence of scar tissue around a nerve can cause traction neuropathy.[34]
A well known muscular cause of extraspinal sciatica is piriformis syndrome. The piriformis muscle is directly adjacent to the course of the sciatic nerve as it traverses through the intrapelvic space. Pathologies of the piriformis muscle such as injury (e.g. swelling and scarring), inflammation (release of cytokines affecting the local cellular environment), or space occupying lesions (e.g. tumor, cyst, hypertrophy) can affect the sciatic nerve.[27] Anatomic variations in nerve branching can also predispose the sciatic nerve to further compression by the piriformis muscle, such as if the sciatic nerve pierces the piriformis muscle.[35]
The sciatic nerve can also be entrapped outside of the pelvic space and this is called deep gluteal syndrome.[19] Surgical research has identified new causes of entrapment such as fibrovascular scar bands, vascular abnormalities, heterotropic ossification, gluteal muscles, hamstring muscles, and the gemelli-obturator internus complex.[20] In almost half of the endoscopic surgery cases, fibrovascular scar bands were found to be the cause of entrapment, impeding the movement of the sciatic nerve.[36][37]
Diagnosis
Sciatica is typically diagnosed by physical examination, and the history of the symptoms.[4]
Physical tests
Generally, if a person reports the typical radiating pain in one leg, as well as one or more neurological indications of nerve root tension or neurological deficit, sciatica can be diagnosed.[6]
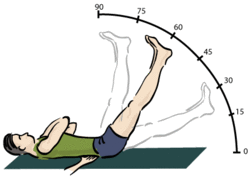
The most frequently used diagnostic test is the straight leg raise to produce Lasègue's sign, which is considered positive if pain in the distribution of the sciatic nerve is reproduced with passive flexion of the straight leg between 30 and 70 degrees.[38] While this test is positive in about 90% of people with sciatica, approximately 75% of people with a positive test do not have sciatica.[4] Straight leg raising of the leg unaffected by sciatica may produce sciatica in the leg on the affected side; this is known as the Fajersztajn sign.[15] The presence of the Fajersztajn sign is a more specific finding for a herniated disc than Lasègue's sign.[15] Maneuvers that increase intraspinal pressure, such as coughing, flexion of the neck, and bilateral compression of the jugular veins, may transiently worsen sciatica pain.[15]
Medical imaging
Imaging modalities such as computerised tomography or magnetic resonance imaging can help with the diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation.[39] Both are equally effective at diagnosing lumbar disk herniation, but computerized tomography has a higher radiation dose.[6] Radiography is not recommended because disks cannot be visualized by X-rays.[6] The utility of MR neurography in the diagnosis of piriformis syndrome is controversial.[16]
Discography could be considered to determine a specific disc's role in an individual's pain.[14] Discography involves the insertion of a needle into a disc to determine the pressure of disc space.[14] Radiocontrast is then injected into the disc space to assess for visual changes that may indicate an anatomic abnormality of the disc.[14] The reproduction of an individual's pain during discography is also diagnostic.[14]
Differential diagnosis
Cancer should be suspected if there is previous history of it, unexplained weight loss, or unremitting pain.[13] Spinal epidural abscess is more common among those who have diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency, or who have had spinal surgery, injection or catheter; it typically causes fever, leukocytosis and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.[13] If cancer or spinal epidural abscess is suspected, urgent magnetic resonance imaging is recommended for confirmation.[13] Proximal diabetic neuropathy typically affects middle aged and older people with well-controlled type-2 diabetes mellitus; onset is sudden, causing pain, usually in multiple dermatomes, quickly followed by weakness. Diagnosis typically involves electromyography and lumbar puncture.[13] Shingles is more common among the elderly and immunocompromised; typically, pain is followed by the appearance of a rash with small blisters along a single dermatome.[13][40] Acute Lyme radiculopathy may follow a history of outdoor activities during warmer months in likely tick habitats in the previous 1–12 weeks.[41] In the U.S., Lyme is most common in New England and Mid-Atlantic states and parts of Wisconsin and Minnesota, but it is expanding to other areas.[42][43] The first manifestation is usually an expanding rash possibly accompanied by flu-like symptoms.[44] Lyme can also cause a milder, chronic radiculopathy an average of 8 months after the acute illness.[13]
Management
Sciatica can be managed with a number of different treatments[45] with the goal of restoring a person's normal functional status and quality of life.[14] When the cause of sciatica is lumbar disc herniation (90% of cases),[4] most cases resolve spontaneously over weeks to months.[46] Initially treatment in the first 6–8 weeks should be conservative.[4] More than 75% of sciatica cases are managed without surgery.[14] Smokers with sciatica are strongly urged to quit in order to promote healing.[14] Treatment of the underlying cause of nerve compression is needed in cases of epidural abscess, epidural tumors, and cauda equina syndrome.[14]
Physical activity
Physical activity is often recommended for the conservative management of sciatica for persons who are physically able.[2] Bed rest is not recommended.[47] Although structured exercises provide small, short-term benefit for leg pain, in the long term no difference is seen between exercise or simply staying active.[48] The evidence for physical therapy in sciatica is unclear though such programs appear safe.[2] Physical therapy is commonly used.[2] Nerve mobilization techniques for sciatic nerve are supported by tentative evidence.[49]
Medication
There is no one medication regimen used to treat sciatica.[45] Evidence supporting the use of opioids and muscle relaxants is poor.[50] Low-quality evidence indicates that NSAIDs do not appear to improve immediate pain, and all NSAIDs appear to be nearly equivalent in their ability to relieve sciatica.[50][51][52] Nevertheless, NSAIDs are commonly recommended as a first-line treatment for sciatica.[45] In those with sciatica due to piriformis syndrome, botulinum toxin injections may improve pain and function.[53] While there is little evidence supporting the use of epidural or systemic steroids,[54][55] systemic steroids may be offered to individuals with confirmed disc herniation if there is a contraindication to NSAID use.[45] Low-quality evidence supports the use of gabapentin for acute pain relief in those with chronic sciatica.[50] Anticonvulsants and biologics have not been shown to improve acute or chronic sciatica.[45] Antidepressants have demonstrated some efficacy in treating chronic sciatica, and may be offered to individuals who are not amenable to NSAIDs or who have failed NSAID therapy.[45]
Surgery
If sciatica is caused by a herniated disc, the disc's partial or complete removal, known as a discectomy, has tentative evidence of benefit in the short term.[56] A modest reduction in pain is seen after 26 weeks, but not after one year (about 52 weeks).[47] If the cause is spondylolisthesis or spinal stenosis, surgery appears to provide pain relief for up to two years.[56]
For non-discogenic sciatica, the surgical treatment is typically a nerve decompression. A decompression seeks to remove tissue around the nerve that may be compressing it or restricting movement of the nerve.[57][58][59]
Alternative medicine
Low to moderate-quality evidence suggests that spinal manipulation is an effective treatment for acute sciatica.[2][60] For chronic sciatica, the evidence supporting spinal manipulation as treatment is poor.[60] Spinal manipulation has been found generally safe for the treatment of disc-related pain; however, case reports have found an association with cauda equina syndrome,[61] and it is contraindicated when there are progressive neurological deficits.[62]
Prognosis
About 39% to 50% of people with sciatica still have symptoms after one to four years.[63] In one study, around 20% were unable to work at their one-year followup, and 10% had surgery for the condition.[63]
Epidemiology
Depending on how it is defined, less than 1% to 40% of people have sciatica at some point in time.[9][4] Sciatica is most common between the ages of 40 and 59, and men are more frequently affected than women.[5][2]
See also
- Failed back syndrome
- Low back pain
- Lumbar spinal stenosis
- Nerve compression syndrome
- Neuropathic pain
- Paresthesia
- Piriformis syndrome
- Sciatic nerve
- Spinal disk herniation
- Spondylolisthesis
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Sciatica". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0024494/.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 Ropper, AH; Zafonte, RD (26 March 2015). "Sciatica.". The New England Journal of Medicine 372 (13): 1240–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1410151. PMID 25806916.
- ↑ T.J. Fowler; J.W. Scadding (28 November 2003). Clinical Neurology, 3Ed. CRC. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-340-80798-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=k56tZUQ8RfkC&pg=PA59.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 Valat, JP; Genevay, S; Marty, M; Rozenberg, S; Koes, B (April 2010). "Sciatica.". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology 24 (2): 241–52. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2009.11.005. PMID 20227645.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 "Slipped disk: Overview". October 9, 2014. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0072656/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 "Diagnosis and treatment of sciatica". The BMJ 334 (7607): 1313. 2007. doi:10.1136/bmj.39223.428495.BE. PMID 17585160.
- ↑ Markova, Tsvetio (2007). "Treatment of Acute Sciatica". Am Fam Physician 75 (1): 99–100. PMID 17225710. http://www.aafp.org/afp/2007/0101/p99.html.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". CMAJ 190 (26): E786–E793. July 2018. doi:10.1503/cmaj.171333. PMID 29970367.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "Risk factors for first time incidence sciatica: a systematic review". Physiother Res Int 19 (2): 65–78. June 2014. doi:10.1002/pri.1572. PMID 24327326.
- ↑ Simpson, John (2009). Oxford English dictionary (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-956383-8.
- ↑ Dioscorides, Materia Medica (2-184, s.v. Sinepi), p. 311
- ↑ Bhat, Sriram (2013). SRB's Manual of Surgery. p. 364. ISBN 9789350259443.
- ↑ 13.00 13.01 13.02 13.03 13.04 13.05 13.06 13.07 13.08 13.09 13.10 "Lumbosacral radiculopathy". Neurologic Clinics 25 (2): 387–405. May 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2007.01.008. PMID 17445735. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/27a9/f13596f9bc2fdb873eb83302d14aaa176381.pdf.
- ↑ 14.00 14.01 14.02 14.03 14.04 14.05 14.06 14.07 14.08 14.09 14.10 14.11 14.12 14.13 14.14 Butterworth IV, John F. (2013). Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. David C. Mackey, John D. Wasnick (5th. ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. Chapter 47. Chronic Pain Management. ISBN 978-0-07-162703-0. OCLC 829055521. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookID=564.
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 Ropper, Allan H.; Samuels, Martin A.; Klein, Joshua P. (2014). "Chapter 11. Pain in the Back, Neck, and Extremities". Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology (Tenth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education Medical. ISBN 978-0-07-179479-4. OCLC 857402060. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=690.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 "The diagnosis and management of Piriformis Syndrome: myths and facts". Can J Neurol Sci 39 (5): 577–83. September 2012. doi:10.1017/s0317167100015298. PMID 22931697.
- ↑ "Piriformis syndrome, diagnosis and treatment". Muscle Nerve 40 (1): 10–18. July 2009. doi:10.1002/mus.21318. PMID 19466717.
- ↑ "Magnetic resonance neurography in extraspinal sciatica". Arch. Neurol. 63 (10): 1469–72. October 2006. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.10.1469. PMID 17030664.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Deep gluteal syndrome is defined as a non-discogenic sciatic nerve disorder with entrapment in the deep gluteal space: a systematic review". Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28 (10): 3354–3364. October 2020. doi:10.1007/s00167-020-05966-x. PMID 32246173.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Deep gluteal syndrome". J Hip Preserv Surg 2 (2): 99–107. July 2015. doi:10.1093/jhps/hnv029. PMID 27011826.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Deep gluteal syndrome: anatomy, imaging, and management of sciatic nerve entrapments in the subgluteal space". Skeletal Radiol 44 (7): 919–34. July 2015. doi:10.1007/s00256-015-2124-6. PMID 25739706.
- ↑ Gandhi, Jason; Wilson, Anthony L; Liang, Raymond; Weissbart, Steven J; Khan, Sardar Ali (2020-11-11). "Sciatic endometriosis: A narrative review of an unusual neurogynecologic condition". Journal of Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain Disorders (SAGE Publications) 13 (1): 3–9. doi:10.1177/2284026520970813. ISSN 2284-0265.
- ↑ Sciatic Nerve Pain During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment. American Pregnancy Association. Published September 20, 2017. Accessed November 12, 2018.
- ↑ "Can bacterial infection by low virulent organisms be a plausible cause for symptomatic disc degeneration? A systematic review". Spine 40 (10): E587–92. May 2015. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000832. PMID 25955094.
- ↑ "Overview: the role of Propionibacterium acnes in nonpyogenic intervertebral discs.". Int Orthop 40 (6): 1291–8. 2016. doi:10.1007/s00264-016-3115-5. PMID 26820744.
- ↑ Giuffre BA, Black AC, Jeanmonod R. Anatomy, Sciatic Nerve. [Updated 2023 May 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (Florida): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 January. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482431/.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Davis D, Maini K, Vasudevan A. Sciatica. [Updated 2022 May 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (Florida): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 January. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507908/.
- ↑ "Extra-spinal sciatica and sciatica mimics: a scoping review". Korean J Pain 33 (4): 305–317. October 2020. doi:10.3344/kjp.2020.33.4.305. PMID 32989195.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Parks, Edward (2017). Practical Office Orthopedics. [New York, N.Y.]: McGraw-Hill. pp. Chapter 6: Low Back Pain. ISBN 978-1-259-64287-6. OCLC 986993775.
- ↑ Halpern, Casey H. (2015). Schwartz's Principles of Surgery. Grady, M. Sean (Tenth ed.). [New York]: McGraw-Hill. pp. Chapter 42: Neurosurgery. ISBN 978-0-07-180092-1. OCLC 892490454. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookID=980.
- ↑ LeBlond, Richard F.; Brown, Donald D.; Suneja, Manish et al., eds (2015). "Chapter 13: The Spine, Pelvis, and Extremities". DeGowin's Diagnostic Examination (Tenth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-07-181447-8. OCLC 876336892. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=1192.
- ↑ "The effects of hip abduction on sciatic nerve biomechanics during terminal hip flexion". J Hip Preserv Surg 4 (2): 178–186. July 2017. doi:10.1093/jhps/hnx008. PMID 28630740.
- ↑ "Sciatic nerve excursion during neural mobilization with ankle movement using dynamic ultrasound imaging: a cross-sectional study". J Ultrasound 25 (2): 241–249. June 2022. doi:10.1007/s40477-021-00595-7. PMID 34036554.
- ↑ "Experimental Methods to Simulate and Evaluate Postsurgical Peripheral Nerve Scarring". J Clin Med 10 (8): 1613. April 2021. doi:10.3390/jcm10081613. PMID 33920209.
- ↑ "Pyriformis syndrome in relation to sciatic pain". Am J Surg 73 (3): 355–358. March 1947. doi:10.1016/0002-9610(47)90345-0. PMID 20289074.
- ↑ "The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome". Arthroscopy 27 (2): 172–81. February 2011. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.07.008. PMID 21071168.
- ↑ "Clinical results of endoscopic sciatic nerve decompression for deep gluteal syndrome: mean 2-year follow-up". BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17: 218. May 2016. doi:10.1186/s12891-016-1062-3. PMID 27206482.
- ↑ "Low back pain". BMJ 328 (7448): 1119–21. May 2004. doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7448.1119. PMID 15130982.
- ↑ "Acute lumbar disk pain: navigating evaluation and treatment choices". Am Fam Physician 78 (7): 835–42. October 2008. PMID 18841731.
- ↑ "Recommendations for the management of herpes zoster". Clin. Infect. Dis. 44 (Suppl 1): S1–26. 2007. doi:10.1086/510206. PMID 17143845.
- ↑ "Clinical practice. Lyme disease". The New England Journal of Medicine 370 (18): 1724–1731. May 2014. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1314325. PMID 24785207. PMC 4487875. http://portal.mah.harvard.edu/templatesnew/departments/MTA/Lyme/uploaded_documents/NEJMcp1314325.pdf.
- ↑ "Lyme Disease Data and surveillance". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019-02-05. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/.
- ↑ "Lyme Disease risk areas map". Government of Canada. 2015-01-27. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/lyme-disease/risk-lyme-disease.html#map.
- ↑ "Course and outcome of early European Lyme neuroborreliosis (Bannwarth syndrome): clinical and laboratory findings". Clinical Infectious Diseases 63 (3): 346–53. Aug 2016. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw299. PMID 27161773.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 45.4 45.5 "Comparative clinical effectiveness of management strategies for sciatica: systematic review and network meta-analyses". Spine J 15 (6): 1461–77. June 2015. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.049. PMID 24412033. http://eprints.hud.ac.uk/id/eprint/19023/3/Manuscript_-_sciatica_MTC_paper_%252820130628%2529.pdf.
- ↑ "Natural history of radiculopathy". Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 22 (1): 1–5. February 2011. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2010.10.001. PMID 21292142.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Ostelo RW (2020). "Physiotherapy management of sciatica". Journal of Physiotherapy 66 (2): 83–88. doi:10.1016/j.jphys.2020.03.005. PMID 32291226.
- ↑ "Advice to Stay Active or Structured Exercise in the Management of Sciatica: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Spine 40 (10): 1457–1466. 2015. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001036. PMID 26165218.
- ↑ Basson, Annalie; Olivier, Benita; Ellis, Richard; Coppieters, Michel; Stewart, Aimee; Mudzi, Witness (2017-08-31). "The Effectiveness of Neural Mobilization for Neuromusculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis" (in en). Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy 47 (9): 593–615. doi:10.2519/jospt.2017.7117. PMID 28704626. https://research.vu.nl/en/publications/c965ed2a-c397-403f-8790-275a4cb9fbde. "The majority of studies had a high risk of bias".
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 "Drugs for relief of pain in patients with sciatica: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ 344. February 2012. doi:10.1136/bmj.e497. PMID 22331277.
- ↑ "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for spinal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 76 (7): 1269–1278. July 2017. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210597. PMID 28153830.
- ↑ "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for sciatica". Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10 (2). October 2016. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012382. PMID 27743405.
- ↑ "Botulinum toxin injections for low-back pain and sciatica". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1). January 2011. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008257.pub2. PMID 21249702.
- ↑ "Steroids for LBP – from rationale to inconvenient truth". Swiss Med Wkly 142: w13566. 2012. doi:10.4414/smw.2012.13566. PMID 22495738.
- ↑ "Epidural Corticosteroid Injections for Radiculopathy and Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Ann. Intern. Med. 163 (5): 373–81. September 2015. doi:10.7326/M15-0934. PMID 26302454.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 "Surgery or physical activity in the management of sciatica: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Eur Spine J 25 (11): 3495–3512. November 2016. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4148-y. PMID 26210309.
- ↑ "Endoscopic Sciatic Neurolysis for Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Systematic Review". Cureus 14 (3). March 2022. doi:10.7759/cureus.23153. PMID 35444897.
- ↑ "Surgical Management of Deep Gluteal Syndrome Causing Sciatic Nerve Entrapment: A Systematic Review". Arthroscopy 33 (12): 2263–2278.e1. December 2017. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2017.06.041. PMID 28866346.
- ↑ "Laparoscopic approach to refractory extraspinal sciatica and pudendal pain caused by intrapelvic nerve entrapment". Sci Rep 11 (1): 10820. May 2021. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90319-y. PMID 34031480. Bibcode: 2021NatSR..1110820L.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 "Spinal manipulation or mobilization for radiculopathy: a systematic review". Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America 22 (1): 105–25. February 2011. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2010.11.002. PMID 21292148.
- ↑ "Cauda equina syndrome and spine manipulation: case report and review of the literature". Eur Spine J 20 (Suppl 1): S128–31. May 2011. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1745-2. PMID 21404036.
- ↑ WHO guidelines on basic training and safety in chiropractic. "2.1 Absolute contraindications to spinal manipulative therapy", p. 21. WHO
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Wilkinson, C.; Chakraverty, R.; Rickard, I.; Hendry, M.; Nafees, S.; Burton, K.; Sutton, A.; Jones, M. et al. (November 2011). Background. NIHR Journals Library. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK99305/.
External links
- "Sciatica". U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/sciatica.html.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |
